student powerpoint 3
... -Leads to Dehydration and electrolyte loss if not attended to. -3 to 4 litres of sweat loss per hour can occur, 6-10% of body weight for endurance athletes, this can only be sustained for a number of hours. - Can lead to a decrease in blood volume. ...
... -Leads to Dehydration and electrolyte loss if not attended to. -3 to 4 litres of sweat loss per hour can occur, 6-10% of body weight for endurance athletes, this can only be sustained for a number of hours. - Can lead to a decrease in blood volume. ...
Heat and the Umpire
... lacks the availability of shade, lacks the time that teams get to rest while they are up to bat, wears dark clothing, and minimal skin is exposed from which to allow heat to dissipate from your body. Add to this other issues such as hydration, cardiac issues, medical issues, medications and other fa ...
... lacks the availability of shade, lacks the time that teams get to rest while they are up to bat, wears dark clothing, and minimal skin is exposed from which to allow heat to dissipate from your body. Add to this other issues such as hydration, cardiac issues, medical issues, medications and other fa ...
Summer Heat Protection
... Shift value of 10hrs is what should be achieved. With an external temperature of 35 °C and a possible temperature under the roof covering of 80 °C, it is important to ensure that the influence this temperature has on the internal climate is delayed through Amplitude Dampening and Phase Shifting. In ...
... Shift value of 10hrs is what should be achieved. With an external temperature of 35 °C and a possible temperature under the roof covering of 80 °C, it is important to ensure that the influence this temperature has on the internal climate is delayed through Amplitude Dampening and Phase Shifting. In ...
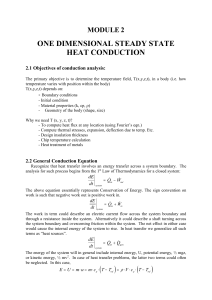
3-1C (a) If the lateral surfaces of the rod are insulated, the heat
... 3-1C (a) If the lateral surfaces of the rod are insulated, the heat transfer surface area of the cylindrical rod is the bottom or the top surface area of the rod, As = πD 2 / 4 . (b) If the top and the bottom surfaces of the rod are insulated, the heat transfer area of the rod is the lateral surface ...
... 3-1C (a) If the lateral surfaces of the rod are insulated, the heat transfer surface area of the cylindrical rod is the bottom or the top surface area of the rod, As = πD 2 / 4 . (b) If the top and the bottom surfaces of the rod are insulated, the heat transfer area of the rod is the lateral surface ...
cfd investigation of helical coil heat exchanger abstract
... exchanger has been a major issue and a topic of study for a long time. The analysis of these various correlations with certain defined data is presented in this project. In this study, an attempt has been made to analyze the effect of counter-flow on the total heat transfer from a helical tube. The ...
... exchanger has been a major issue and a topic of study for a long time. The analysis of these various correlations with certain defined data is presented in this project. In this study, an attempt has been made to analyze the effect of counter-flow on the total heat transfer from a helical tube. The ...
25 7. PASSIVE CLIMATE CONTROL FOR CULTURAL
... climates. The principle of storing heat during the day, and giving a back up at night is identical; but the role of the external fabric changes to keep out heat during the day, and get rid of it at night by ventilation. 7.1.2.4. Ventilation and air exchange: Air quantity or air velocity? When discus ...
... climates. The principle of storing heat during the day, and giving a back up at night is identical; but the role of the external fabric changes to keep out heat during the day, and get rid of it at night by ventilation. 7.1.2.4. Ventilation and air exchange: Air quantity or air velocity? When discus ...
Worksheet 6a
... Two forms of carbon are graphite, the soft, black, slippery material used in "lead" pencils and as a lubricant for locks, and diamond, the brilliant, hard gemstone. Using the enthalpies of combustion for graphite (–394 kJ/mole C) and diamond (–396 kJ/mole C), calculate the ∆H for the conversion of g ...
... Two forms of carbon are graphite, the soft, black, slippery material used in "lead" pencils and as a lubricant for locks, and diamond, the brilliant, hard gemstone. Using the enthalpies of combustion for graphite (–394 kJ/mole C) and diamond (–396 kJ/mole C), calculate the ∆H for the conversion of g ...
Dynamic insulation

Dynamic insulation is a form of insulation where cool outside air flowing through the thermal insulation in the envelope of a building will pick up heat from the insulation fibres. Buildings can be designed to exploit this to reduce the transmission heat loss (U-value) and to provide pre-warmed, draft free air to interior spaces. This is known as dynamic insulation since the U-value is no longer constant for a given wall or roof construction but varies with the speed of the air flowing through the insulation (climate adaptive building shell). Dynamic insulation is different from breathing walls. The positive aspects of dynamic insulation need to be weighed against the more conventional approach to building design which is to create an airtight envelope and provide appropriate ventilation using either natural ventilation or mechanical ventilation with heat recovery. The air-tight approach to building envelope design, unlike dynamic insulation, results in a building envelope that provides a consistent performance in terms of heat loss and risk of interstitial condensation that is independent of wind speed and direction. Under certain wind conditions a dynamically insulated building can have a higher heat transmission loss than an air-tight building with the same thickness of insulation.















![L 17 - Thermodynamics [2] Thermal Expansion Coefficients of linear](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014728078_1-e88e92f3857e030978e2ede6a9072797-300x300.png)