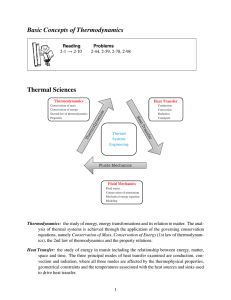
Thermal Barrier Coatings
... The cooling air needs exit passages, which may be provided by fine cooling holes drilled through the wall. The diameters of these holes are of the order of a few hundred microns, the length being proportional to the thickness of the blade wall. The holes are drilled either before the ceramic coating ...
... The cooling air needs exit passages, which may be provided by fine cooling holes drilled through the wall. The diameters of these holes are of the order of a few hundred microns, the length being proportional to the thickness of the blade wall. The holes are drilled either before the ceramic coating ...
Measuring the Heat Absorption and Retention Properties of a Solar
... saved. In response to this challenge, the organizations Salud del Sol, Mujeres Solares de Totogalpa, and engineering students from the Universidad Nacional de Ingeneria have teamed up to design a functioning solar autoclave. The current autoclave design features a solar powered oven manufactured by ...
... saved. In response to this challenge, the organizations Salud del Sol, Mujeres Solares de Totogalpa, and engineering students from the Universidad Nacional de Ingeneria have teamed up to design a functioning solar autoclave. The current autoclave design features a solar powered oven manufactured by ...
CHAPTER 3 - RIT
... wall does not change during steady heat conduction. However, the temperature along the wall and thus the energy content of the wall will change during transient conduction. 3-3C The temperature distribution in a plane wall will be a straight line during steady and one dimensional heat transfer with ...
... wall does not change during steady heat conduction. However, the temperature along the wall and thus the energy content of the wall will change during transient conduction. 3-3C The temperature distribution in a plane wall will be a straight line during steady and one dimensional heat transfer with ...
Unit 03 - WordPress.com
... difference needed to facilitate refrigerant flow through the system • Condenser: rejects system heat ...
... difference needed to facilitate refrigerant flow through the system • Condenser: rejects system heat ...
ert254-chapter 4
... Most existing heat pumps use the cold outside air as the heat source in winter (air-source HP). In cold climates their efficiency drops considerably when temperatures are below the freezing point. In such cases, geothermal (ground-source) HP that use the ground as the heat source can be used. Such h ...
... Most existing heat pumps use the cold outside air as the heat source in winter (air-source HP). In cold climates their efficiency drops considerably when temperatures are below the freezing point. In such cases, geothermal (ground-source) HP that use the ground as the heat source can be used. Such h ...
ip Chapter 22 Practice test
... a. atoms give off heat in the form of electromagnetic waves. b. large numbers of atoms move from place to place. c. electromagnetic waves travel from one place to another through a vacuum. d. electrons bump into atoms and other electrons. e. none of the above ...
... a. atoms give off heat in the form of electromagnetic waves. b. large numbers of atoms move from place to place. c. electromagnetic waves travel from one place to another through a vacuum. d. electrons bump into atoms and other electrons. e. none of the above ...
Interaction of clothing and thermoregulation
... Human temperature regulation is based upon a physiological system ‘designed’ for a naked person. Hence, the statement ‘man is a tropical animal’. Human thermoregulation can be described as a feedback system with sensors in the body core and the skin, and effectors in the form of skin blood flow (vas ...
... Human temperature regulation is based upon a physiological system ‘designed’ for a naked person. Hence, the statement ‘man is a tropical animal’. Human thermoregulation can be described as a feedback system with sensors in the body core and the skin, and effectors in the form of skin blood flow (vas ...
Comparative Study of Rectangular, Trapezoidal and Parabolic
... important aspect of electronic equipment design. The dissipation of heat is necessary for its proper function. The heat is generated by the resistance encountered by electric current. Unless proper cooling arrangement is designed, the operating temperature exceeds permissible limit. As a consequence ...
... important aspect of electronic equipment design. The dissipation of heat is necessary for its proper function. The heat is generated by the resistance encountered by electric current. Unless proper cooling arrangement is designed, the operating temperature exceeds permissible limit. As a consequence ...
Thermochemistry Problems
... water at 15.0 oC in a coffee cup calorimeter. Assume no loss of heat to the surroundings and to the calorimeter. ...
... water at 15.0 oC in a coffee cup calorimeter. Assume no loss of heat to the surroundings and to the calorimeter. ...
Dynamic insulation

Dynamic insulation is a form of insulation where cool outside air flowing through the thermal insulation in the envelope of a building will pick up heat from the insulation fibres. Buildings can be designed to exploit this to reduce the transmission heat loss (U-value) and to provide pre-warmed, draft free air to interior spaces. This is known as dynamic insulation since the U-value is no longer constant for a given wall or roof construction but varies with the speed of the air flowing through the insulation (climate adaptive building shell). Dynamic insulation is different from breathing walls. The positive aspects of dynamic insulation need to be weighed against the more conventional approach to building design which is to create an airtight envelope and provide appropriate ventilation using either natural ventilation or mechanical ventilation with heat recovery. The air-tight approach to building envelope design, unlike dynamic insulation, results in a building envelope that provides a consistent performance in terms of heat loss and risk of interstitial condensation that is independent of wind speed and direction. Under certain wind conditions a dynamically insulated building can have a higher heat transmission loss than an air-tight building with the same thickness of insulation.