Egyptian Part 1 IG - Prairie Public Broadcasting
... Mediterranean Sea, the Nile River travels a breathtaking 4,125 miles. Egyptian civilization, like the Nile River, is a timeline flowing from the dynasties of mighty kings and queens to the architectural wonders of pyramids and tombs. Once unified, then divided, Egypt’s strength eventually became its ...
... Mediterranean Sea, the Nile River travels a breathtaking 4,125 miles. Egyptian civilization, like the Nile River, is a timeline flowing from the dynasties of mighty kings and queens to the architectural wonders of pyramids and tombs. Once unified, then divided, Egypt’s strength eventually became its ...
Secular Architecture
... plastered internally and painted in earth colors. During Neolithic period multi-roomed thin walled houses of mud brick were being constructed. There also was an emergence of non-residential buildings for work, storage and ritual purposes, culminating in monumental temple architecture. The towns had ...
... plastered internally and painted in earth colors. During Neolithic period multi-roomed thin walled houses of mud brick were being constructed. There also was an emergence of non-residential buildings for work, storage and ritual purposes, culminating in monumental temple architecture. The towns had ...
Egypt`s Empire
... The Great Pyramid is built in honor of the pharaoh Khufu The ruling pharaohs in Memphis of the Old Kingdom began to lose power around 2200 BC. After the Old Kingdom fell apart, Egypt entered a time of chaos for over 200 years. The Middle Kingdom lasted from c.2055 BC to c. 1650 BC. A new dynasty of ...
... The Great Pyramid is built in honor of the pharaoh Khufu The ruling pharaohs in Memphis of the Old Kingdom began to lose power around 2200 BC. After the Old Kingdom fell apart, Egypt entered a time of chaos for over 200 years. The Middle Kingdom lasted from c.2055 BC to c. 1650 BC. A new dynasty of ...
Ancient Egypt stations e15
... Around 3100 BC, there were two separate kingdoms in Egypt, Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Soon afterwards, King Narmer (from Upper Egypt) united the two kingdoms. When the unification happened, it became the world’s first ever nation-state. King Narmer was the first king of Egypt’s first dynasty, and ...
... Around 3100 BC, there were two separate kingdoms in Egypt, Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Soon afterwards, King Narmer (from Upper Egypt) united the two kingdoms. When the unification happened, it became the world’s first ever nation-state. King Narmer was the first king of Egypt’s first dynasty, and ...
The Middle and New Kingdoms
... pharaohs declined. Building and maintaining pyramids cost a lot of money. Pharaohs could not collect enough taxes to keep up with the expenses. At the same time, ambitious nobles used their government positions to take power from the pharaohs. In time, nobles gained enough power to challenge the pha ...
... pharaohs declined. Building and maintaining pyramids cost a lot of money. Pharaohs could not collect enough taxes to keep up with the expenses. At the same time, ambitious nobles used their government positions to take power from the pharaohs. In time, nobles gained enough power to challenge the pha ...
Egyptian History 101
... there were two kingdoms -- Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Upper Egypt was in the south. It controlled the areas along the upper regions of the Nile. Lower Egypt was in the north. It occupied the Nile delta, a fertile stretch of land near the mouth of the river. ...
... there were two kingdoms -- Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Upper Egypt was in the south. It controlled the areas along the upper regions of the Nile. Lower Egypt was in the north. It occupied the Nile delta, a fertile stretch of land near the mouth of the river. ...
unit overview: early civilizations
... The first great civilizations in world history arose in Mesopotamia, Egypt, India, and China in the period from 3500-500 B.C. Often referred to as Ancient History, this era witnessed the emergence of unique cultures that produced architectural wonders, the world’s first empires, and a wide range of ...
... The first great civilizations in world history arose in Mesopotamia, Egypt, India, and China in the period from 3500-500 B.C. Often referred to as Ancient History, this era witnessed the emergence of unique cultures that produced architectural wonders, the world’s first empires, and a wide range of ...
Intro to AE Class Notes
... j. The top register depicts Hathor twice (pronounced hattor) – the goddess of the heavens and protector of the pharaoh’s family and has Narmer’s serekh (name in hieroglyphics) in the center k. The bottom register shows two more enemies fleeing from allpowerful Narmer. l. The hawk is the god Horus, a ...
... j. The top register depicts Hathor twice (pronounced hattor) – the goddess of the heavens and protector of the pharaoh’s family and has Narmer’s serekh (name in hieroglyphics) in the center k. The bottom register shows two more enemies fleeing from allpowerful Narmer. l. The hawk is the god Horus, a ...
C3.1 - The Kingdom of Egypt - World History and Honors History 9
... A. The Pyramids Designed by professional craftsmen; peasants worked one month a year, not built by slaves ...
... A. The Pyramids Designed by professional craftsmen; peasants worked one month a year, not built by slaves ...
sample
... on the land. The native Egyptians, meanwhile, maintained their own cultural imperatives and survived the changes in their world. Their temples, courts, monuments, and deities continued to serve the land as foreigners arrived and disappeared. The Chronology will provide an overview of these historica ...
... on the land. The native Egyptians, meanwhile, maintained their own cultural imperatives and survived the changes in their world. Their temples, courts, monuments, and deities continued to serve the land as foreigners arrived and disappeared. The Chronology will provide an overview of these historica ...
Old Kingdom – Status of Women. Unlike the position of women in
... A wife was entitled to inherit one-third of that community property on the death of her husband, while the other two-thirds was divided among the children, followed up by the brothers and sisters of the deceased. To circumvent this possibility and to enable life to receive either a larger part of th ...
... A wife was entitled to inherit one-third of that community property on the death of her husband, while the other two-thirds was divided among the children, followed up by the brothers and sisters of the deceased. To circumvent this possibility and to enable life to receive either a larger part of th ...
Zoser`s Step Pyramid at Saqqara is thought to be
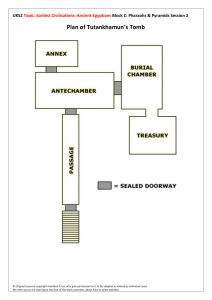
... UKS2 Topic: Earliest Civilisations: Ancient Egyptians Block C: Pharaohs & Pyramids Session 2 Ramesses II 1279 – 1213 BCE (BC) Ramesses II or ‘Ramesses the Great’ as he is also known, followed in the footsteps of his father Seti/Sethos I around 1279 BCE. He was the third Pharaoh of the 19th Dynasty ...
... UKS2 Topic: Earliest Civilisations: Ancient Egyptians Block C: Pharaohs & Pyramids Session 2 Ramesses II 1279 – 1213 BCE (BC) Ramesses II or ‘Ramesses the Great’ as he is also known, followed in the footsteps of his father Seti/Sethos I around 1279 BCE. He was the third Pharaoh of the 19th Dynasty ...
Homework 5 Score 8 - Leon M. Goldstein High School for the Sciences
... myths. Societies like these viewed time as cyclical. This idea is demonstrated in their calendars where every month or so, they believed the Tigris-Euphrates or Nile River would overflow. Both societies were also opened to attack and were invaded by areas like Kush and the Babylonians. Though Mesopo ...
... myths. Societies like these viewed time as cyclical. This idea is demonstrated in their calendars where every month or so, they believed the Tigris-Euphrates or Nile River would overflow. Both societies were also opened to attack and were invaded by areas like Kush and the Babylonians. Though Mesopo ...
Ancient Egypt Unit
... “What role did the pharaoh play in Egypt’s government and religion?” (The pharaoh gave instructions and supervised government affairs and projects. He was also considered divine and was thought to give life to Egypt and its people.) “What was the relationship between the pharaoh and the Egyptian god ...
... “What role did the pharaoh play in Egypt’s government and religion?” (The pharaoh gave instructions and supervised government affairs and projects. He was also considered divine and was thought to give life to Egypt and its people.) “What was the relationship between the pharaoh and the Egyptian god ...
SECTION_3_TEXT__egypt
... Egyptian history, fought the Hittites, a group from Asia Minor. The two powers fought fiercely for years, but neither could defeat the other. Ramses and the Hittite leader eventually signed a peace treaty. Afterwards, the Egyptians and the Hittites became allies. Egypt faced threats in other parts o ...
... Egyptian history, fought the Hittites, a group from Asia Minor. The two powers fought fiercely for years, but neither could defeat the other. Ramses and the Hittite leader eventually signed a peace treaty. Afterwards, the Egyptians and the Hittites became allies. Egypt faced threats in other parts o ...
The Third Intermediate Period, which spans the TwentyFirst to
... power became split more and more between the pharaoh and the High Priests of Amun at Thebes. Egypt was temporarily reunified during the TwentySecond Dynasty and experienced a period of stability, but shattered into two states after the reign of Osorkon II. Civil war raged in Thebes and was eventual ...
... power became split more and more between the pharaoh and the High Priests of Amun at Thebes. Egypt was temporarily reunified during the TwentySecond Dynasty and experienced a period of stability, but shattered into two states after the reign of Osorkon II. Civil war raged in Thebes and was eventual ...
Amun
... Tawaret was a goddess who protected women during pregnancy and childbirth. Many of the gods and goddesses in ancient Egypt had temples built to honour them. Other gods and goddesses like Tawaret and Bes were worshipped by people in their own homes. This is an amulet of the goddess Tawaret. People of ...
... Tawaret was a goddess who protected women during pregnancy and childbirth. Many of the gods and goddesses in ancient Egypt had temples built to honour them. Other gods and goddesses like Tawaret and Bes were worshipped by people in their own homes. This is an amulet of the goddess Tawaret. People of ...
The Old Kingdom - White Plains Public Schools
... projects. • Irrigation is the process of bringing water from the rivers to the neighboring farms. • In order to finish these irrigation projects, the people of Upper Egypt needed to work together with the people of Lower Egypt. E. Napp ...
... projects. • Irrigation is the process of bringing water from the rivers to the neighboring farms. • In order to finish these irrigation projects, the people of Upper Egypt needed to work together with the people of Lower Egypt. E. Napp ...
Timeline of Ancient Egypt - Lorenz Educational Press
... reached the heights it did in Egypt. Because of the difficulty of crossing the deserts with a large army, the country was rarely invaded. The Black Land provided plentiful crops and a place for a large, stable population to grow and develop. Egypt has also been called “the Gift of the Nile.” Each ye ...
... reached the heights it did in Egypt. Because of the difficulty of crossing the deserts with a large army, the country was rarely invaded. The Black Land provided plentiful crops and a place for a large, stable population to grow and develop. Egypt has also been called “the Gift of the Nile.” Each ye ...
Study Guide-Ancient Egypt-Pages 100-127
... o They traded with them for weapons, ivory, incense, lumber/trees and gold. They invented the alphabet so they could communicate with the Egyptians o 41. What made Amenhotep IV (Akhenaton) and Tutankhamen (King Tut) unusual pharaohs? o Amenhotep tried to change Egypt’s religion to be monotheistic. H ...
... o They traded with them for weapons, ivory, incense, lumber/trees and gold. They invented the alphabet so they could communicate with the Egyptians o 41. What made Amenhotep IV (Akhenaton) and Tutankhamen (King Tut) unusual pharaohs? o Amenhotep tried to change Egypt’s religion to be monotheistic. H ...
3.4 The New Kingdom The New Kingdom: Ahmose`s rise to power
... Other than priests and government officials, no one in Egypt was more honored than scribes. ...
... Other than priests and government officials, no one in Egypt was more honored than scribes. ...
The Third Intermediate Period The Kushites The Assyrians The 26th
... The Assyrians In 671 b.c.e., the Assyrians invaded Egypt from the east. You may remember the Assyrians from your study of ancient Mesopotamia. They were known for their iron weapons and their skill in siege warfare and fighting on horseback. Over the next 15 years, these ruthless warriors drove out ...
... The Assyrians In 671 b.c.e., the Assyrians invaded Egypt from the east. You may remember the Assyrians from your study of ancient Mesopotamia. They were known for their iron weapons and their skill in siege warfare and fighting on horseback. Over the next 15 years, these ruthless warriors drove out ...
Ancient Egypt The Gift of the Nile
... same pleasures of their mortal life in the afterlife. The body had to be recognized so it was mummified. Worldly goods such as jewelry, pottery and gold were buried with the body to be enjoyed in the afterlife. ...
... same pleasures of their mortal life in the afterlife. The body had to be recognized so it was mummified. Worldly goods such as jewelry, pottery and gold were buried with the body to be enjoyed in the afterlife. ...
Art of ancient Egypt

Ancient Egyptian art is the painting, sculpture, architecture and other arts produced by the civilization of Ancient Egypt in the lower Nile Valley from about 3000 BC to 100 AD. Ancient Egyptian art reached a high level in painting and sculpture, and was both highly stylized and symbolic. Much of the surviving art comes from tombs and monuments and thus there is an emphasis on life after death and the preservation of knowledge of the past.Ancient Egyptian art was created using media ranging from drawings on papyrus through wood, stone, and paintings. Ancient Egyptian art displays an extraordinarily vivid representation of the Ancient Egyptian's socioeconomic status and belief systems. Egyptian styles changed remarkably little over more than three thousand years.