MAX2037 Ultrasound Variable-Gain Amplifier General Description Features
... is designed for high linearity, high dynamic range, and low-noise performance targeting ultrasound imaging and Doppler applications. Each amplifier features differential inputs and outputs and a total gain range of typically 42dB. In addition, the VGAs offer very low output-referred noise performanc ...
... is designed for high linearity, high dynamic range, and low-noise performance targeting ultrasound imaging and Doppler applications. Each amplifier features differential inputs and outputs and a total gain range of typically 42dB. In addition, the VGAs offer very low output-referred noise performanc ...
MAX4210/MAX4211 High-Side Power and Current Monitors General Description
... The MAX4211 is a full-featured current and power monitor. The device combines a high-side current-sense amplifier, 1.21V bandgap reference, and two comparators with open-drain outputs to make detector circuits for overpower, overcurrent, and/or overvoltage conditions. The open-drain outputs can be c ...
... The MAX4211 is a full-featured current and power monitor. The device combines a high-side current-sense amplifier, 1.21V bandgap reference, and two comparators with open-drain outputs to make detector circuits for overpower, overcurrent, and/or overvoltage conditions. The open-drain outputs can be c ...
11.3 Gbps, Active Back-Termination, Differential Laser Diode Driver ADN2531
... The DATAP and DATAN pins are terminated internally with a 100 Ω differential termination resistor. This minimizes signal reflections at the input that could otherwise lead to degradation in the output eye diagram. It is not recommended to drive the ADN2531 with single-ended data signal sources. The ...
... The DATAP and DATAN pins are terminated internally with a 100 Ω differential termination resistor. This minimizes signal reflections at the input that could otherwise lead to degradation in the output eye diagram. It is not recommended to drive the ADN2531 with single-ended data signal sources. The ...
MAX9918/MAX9919/MAX9920 -20V to +75V Input Range, Precision Uni-/Bidirectional, Current-Sense Amplifiers
... input common-mode range that extends from -20V to +75V. These amplifiers are well suited for current monitoring of inductive loads such as motors and solenoids, where common-mode voltages can become negative due to inductive kickback, reverse-battery conditions, or transient events. The MAX9918/MAX9 ...
... input common-mode range that extends from -20V to +75V. These amplifiers are well suited for current monitoring of inductive loads such as motors and solenoids, where common-mode voltages can become negative due to inductive kickback, reverse-battery conditions, or transient events. The MAX9918/MAX9 ...
SN65C3221, SN75C3221 (Rev. E)
... † Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not implied. Exposure to ...
... † Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not implied. Exposure to ...
ES_LPC2377 Errata sheet LPC2377 Rev. 6.1 — 1 July 2012 Errata sheet
... products planned, as well as for the planned application and use of customer’s third party customer(s). Customers should provide appropriate design and operating safeguards to minimize the risks associated with their applications and products. NXP Semiconductors does not accept any liability related ...
... products planned, as well as for the planned application and use of customer’s third party customer(s). Customers should provide appropriate design and operating safeguards to minimize the risks associated with their applications and products. NXP Semiconductors does not accept any liability related ...
MB3771 Power Supply Monitor
... falls below 1.23 V the RESET output signal goes to “low” level. Comp. B may be used to detect any given voltage(8.Application Circuit 8.3 : Arbitrary Voltage Supply Monitor), and can also be used as a forced reset pin (with reset hold time) with TTL input (8.Application Circuit 8.6 : 5V Power Supply ...
... falls below 1.23 V the RESET output signal goes to “low” level. Comp. B may be used to detect any given voltage(8.Application Circuit 8.3 : Arbitrary Voltage Supply Monitor), and can also be used as a forced reset pin (with reset hold time) with TTL input (8.Application Circuit 8.6 : 5V Power Supply ...
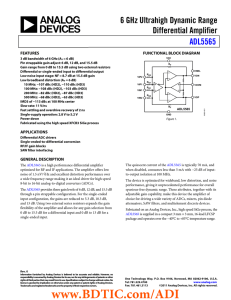
6 GHz Ultrahigh Dynamic Range Differential Amplifier ADL5565
... The ADL5565 is a high performance differential amplifier optimized for RF and IF applications. The amplifier offers low noise of 1.5 nV/√Hz and excellent distortion performance over a wide frequency range making it an ideal driver for high speed 8-bit to 16-bit analog-to-digital converters (ADCs). T ...
... The ADL5565 is a high performance differential amplifier optimized for RF and IF applications. The amplifier offers low noise of 1.5 nV/√Hz and excellent distortion performance over a wide frequency range making it an ideal driver for high speed 8-bit to 16-bit analog-to-digital converters (ADCs). T ...
1-Electronic signal Processing
... THERMAL NOISE Definition from C.D. Motchenbacher book (“Low Noise Electronic System Design, Wiley Interscience”) : ...
... THERMAL NOISE Definition from C.D. Motchenbacher book (“Low Noise Electronic System Design, Wiley Interscience”) : ...
Low Power Fir Filter Design Using Truncated Multiplier A.Deepika , A.Bhuvaneswari
... widely used in digital signal applications such as speech coding, image processing, sampling of multiple systems, etc. Although the stability and linear phase is guaranteed, the complexity and power consumption of the linear phase FIR filter are usually much higher than that of the infinite impulse ...
... widely used in digital signal applications such as speech coding, image processing, sampling of multiple systems, etc. Although the stability and linear phase is guaranteed, the complexity and power consumption of the linear phase FIR filter are usually much higher than that of the infinite impulse ...
instruction manual - Davidson Sales Shop
... must be equal to, or greater than that specified in Table 1-1. If the resistance is less than the specified minimum, a resistor must be added in series with the field. This resistor value plus the field resistance, must be equal to or greater than the minimum field resistance. Input Power (1) The in ...
... must be equal to, or greater than that specified in Table 1-1. If the resistance is less than the specified minimum, a resistor must be added in series with the field. This resistor value plus the field resistance, must be equal to or greater than the minimum field resistance. Input Power (1) The in ...
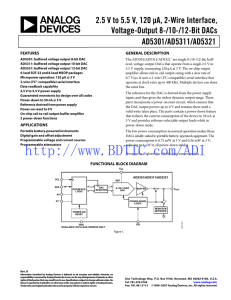
AD5301 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... For the DAC, relative accuracy or integral nonlinearity (INL) is a measure of the maximum deviation, in LSBs, from a straight line passing through the actual endpoints of the DAC transfer function. Typical INL vs. code plots can be seen in Figure 5 to Figure 7. Differential Nonlinearity (DNL) DNL is ...
... For the DAC, relative accuracy or integral nonlinearity (INL) is a measure of the maximum deviation, in LSBs, from a straight line passing through the actual endpoints of the DAC transfer function. Typical INL vs. code plots can be seen in Figure 5 to Figure 7. Differential Nonlinearity (DNL) DNL is ...
MAX5065/MAX5067 Dual-Phase, +0.6V to +3.3V Output Parallelable, Average-Current-Mode Controllers General Description
... package with a minimum number of external components. The MAX5065/MAX5067 utilize a dual-phase, average-current-mode control that enables optimal use of low RDS(ON) MOSFETs, eliminating the need for external heatsinks even when delivering high output currents. Differential sensing enables accurate c ...
... package with a minimum number of external components. The MAX5065/MAX5067 utilize a dual-phase, average-current-mode control that enables optimal use of low RDS(ON) MOSFETs, eliminating the need for external heatsinks even when delivering high output currents. Differential sensing enables accurate c ...
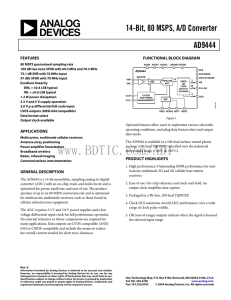
14-Bit, 80 MSPS, A/D Converter AD9444 FEATURES
... clock pulse should be left in the Logic 1 state to achieve rated performance. Pulse width low is the minimum time the clock pulse should be left in the low state. At a given clock rate, these specifications define an acceptable clock duty cycle. Differential Nonlinearity (DNL, No Missing Codes) An i ...
... clock pulse should be left in the Logic 1 state to achieve rated performance. Pulse width low is the minimum time the clock pulse should be left in the low state. At a given clock rate, these specifications define an acceptable clock duty cycle. Differential Nonlinearity (DNL, No Missing Codes) An i ...
LTM8025 - 36V, 3A Step-Down uModule Converter
... 1. Look at Table 1 and find the row that has the desired input range and output voltage. 2. Apply the recommended CIN, COUT, RADJ and RT values. 3. Connect BIAS as indicated. While these component combinations have been tested for proper operation, it is incumbent upon the user to verify proper opera ...
... 1. Look at Table 1 and find the row that has the desired input range and output voltage. 2. Apply the recommended CIN, COUT, RADJ and RT values. 3. Connect BIAS as indicated. While these component combinations have been tested for proper operation, it is incumbent upon the user to verify proper opera ...
GNS RF2411
... Balanced mixer RF Input port. This pin is NOT internally DC-blocked. An external blocking capacitor must be provided if the pin is connected to a device with a DC path. A value of 100pF is recommended for 900MHz and 22pF for 1800MHz. Matching is required; see the applications schematics. To minimize ...
... Balanced mixer RF Input port. This pin is NOT internally DC-blocked. An external blocking capacitor must be provided if the pin is connected to a device with a DC path. A value of 100pF is recommended for 900MHz and 22pF for 1800MHz. Matching is required; see the applications schematics. To minimize ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).