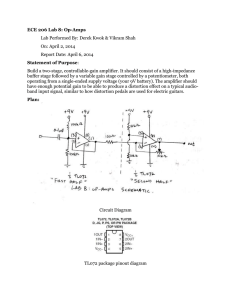
The MAD-Chip Board
... PCF 8575 is used for disabling or enabling the MAD chip inputs individually. PCF 8591 is used for monitoring the regulated voltages + applied threshold (4x 8 Bit ADC) and for setting the threshold per board (1x 8 BitADC). The threshold voltage from the ADC will be divided by e.g. 20 using a passive ...
... PCF 8575 is used for disabling or enabling the MAD chip inputs individually. PCF 8591 is used for monitoring the regulated voltages + applied threshold (4x 8 Bit ADC) and for setting the threshold per board (1x 8 BitADC). The threshold voltage from the ADC will be divided by e.g. 20 using a passive ...
Agile Mixed Signal Addresses Analog Design Challenges
... Many diverse electronic systems contain significant analog functionality. The system might need to interface directly to the real world through sensors to monitor and control the environment, for example, in an industrial automation application. Other applications might need to monitor the operating ...
... Many diverse electronic systems contain significant analog functionality. The system might need to interface directly to the real world through sensors to monitor and control the environment, for example, in an industrial automation application. Other applications might need to monitor the operating ...
File
... clipped waveforms. The clipped waves were notably less rich, but also louder, while the unclipped waveforms were softer and more full-sounding and resonant. Results Screen captures: shown above. Ratio of amplitudes for input buffer stage: 163/141 = 1.16. This is approximately 1, which makes sense be ...
... clipped waveforms. The clipped waves were notably less rich, but also louder, while the unclipped waveforms were softer and more full-sounding and resonant. Results Screen captures: shown above. Ratio of amplitudes for input buffer stage: 163/141 = 1.16. This is approximately 1, which makes sense be ...
MAX1190 Dual 10-Bit, 120Msps, 3.3V, Low-Power ADC General Description
... The MAX1190 is a 3.3V, dual 10-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC) featuring fully differential wideband trackand-hold (T/H) inputs, driving two ADCs. The MAX1190 is optimized for low power, small size, and high-dynamic performance for applications in imaging, instrumentation, and digital communic ...
... The MAX1190 is a 3.3V, dual 10-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC) featuring fully differential wideband trackand-hold (T/H) inputs, driving two ADCs. The MAX1190 is optimized for low power, small size, and high-dynamic performance for applications in imaging, instrumentation, and digital communic ...
MAX1196 Dual 8-Bit, 40Msps, 3V, Low-Power ADC with General Description
... INTERNAL REFERENCE (REFIN = REFOUT through 10kΩ resistor; REFP, REFN, and COM levels are generated internally.) ...
... INTERNAL REFERENCE (REFIN = REFOUT through 10kΩ resistor; REFP, REFN, and COM levels are generated internally.) ...
LF412 Low Offset, Low Drift Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier
... consequently there is negligible effect on stability margin. However, if the feedback pole is less than approximately 6 times the expected 3 dB frequency a lead capacitor should be placed from the output to the input of the op amp. The value of the added capacitor should be such that the RC time con ...
... consequently there is negligible effect on stability margin. However, if the feedback pole is less than approximately 6 times the expected 3 dB frequency a lead capacitor should be placed from the output to the input of the op amp. The value of the added capacitor should be such that the RC time con ...
DM74LS09 Quad 2-Input AND Gates with Open
... N1 (IOH) = total maximum output high current for all outputs tied to pull-up resistor N2 (IIH) = total maximum input high current for all inputs tied to pull-up resistor N3 (IIL) = total maximum input low current for all inputs tied to pull-up resistor ...
... N1 (IOH) = total maximum output high current for all outputs tied to pull-up resistor N2 (IIH) = total maximum input high current for all inputs tied to pull-up resistor N3 (IIL) = total maximum input low current for all inputs tied to pull-up resistor ...
AD7401A 数据手册DataSheet下载
... The AD7401A1 is a second-order, sigma-delta (Σ-Δ) modulator that converts an analog input signal into a high speed, 1-bit data stream with on-chip digital isolation based on Analog Devices, Inc., iCoupler® technology. The AD7401A operates from a 5 V power supply and accepts a differential input sign ...
... The AD7401A1 is a second-order, sigma-delta (Σ-Δ) modulator that converts an analog input signal into a high speed, 1-bit data stream with on-chip digital isolation based on Analog Devices, Inc., iCoupler® technology. The AD7401A operates from a 5 V power supply and accepts a differential input sign ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 9. What is a flip-flop? What is the maximum count that can be obtained in a counter having n flip-flops? 10. Give the difference between asynchronous and synchronous counters. What is the advantage of ...
... 9. What is a flip-flop? What is the maximum count that can be obtained in a counter having n flip-flops? 10. Give the difference between asynchronous and synchronous counters. What is the advantage of ...
university of massachusetts dartmouth
... amplitude of 0.707 volts, and is “phase shifted” to the right of the source voltage. First we will determine the amount of phase shift between the two sinusoidal waveforms. Let’s take a look at just the waveform of the input voltage. One cycle of that voltage is contained within 10 horizontal divisi ...
... amplitude of 0.707 volts, and is “phase shifted” to the right of the source voltage. First we will determine the amount of phase shift between the two sinusoidal waveforms. Let’s take a look at just the waveform of the input voltage. One cycle of that voltage is contained within 10 horizontal divisi ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).