
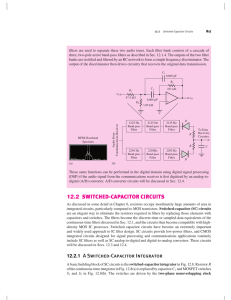
12.2 switched-capacitor circuits
... linearity errors for input codes of 001, 011, 100, and 110. The overall linearity error for the DAC is specified as the magnitude of the largest error that occurs. Hence this converter will be specified as having a linearity error of either 0.5 LSB or 6.25 percent of full-scale voltage. A good conve ...
... linearity errors for input codes of 001, 011, 100, and 110. The overall linearity error for the DAC is specified as the magnitude of the largest error that occurs. Hence this converter will be specified as having a linearity error of either 0.5 LSB or 6.25 percent of full-scale voltage. A good conve ...
Lab 1: Common-source Amplifiers Introduction
... reading of the signal generator to be correct. Most of the signal generators have a 50-Ω output impedance and the voltage reading is correct only if its load is 50 Ω. You will need this 50-Ω termination many times in future labs when you use a signal generator although it won’t be explicitly shown i ...
... reading of the signal generator to be correct. Most of the signal generators have a 50-Ω output impedance and the voltage reading is correct only if its load is 50 Ω. You will need this 50-Ω termination many times in future labs when you use a signal generator although it won’t be explicitly shown i ...
AKSHAYA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
... 12. What is meant by depletion region? In PN junction, the diffusion of holes and electrons start initially. Near the junction, holes recombine in N-region to form immobile positive ions. Similarly electrons recombine in P-region to form immobile negative ions. With sufficient accumulation of such ...
... 12. What is meant by depletion region? In PN junction, the diffusion of holes and electrons start initially. Near the junction, holes recombine in N-region to form immobile positive ions. Similarly electrons recombine in P-region to form immobile negative ions. With sufficient accumulation of such ...
EUP2983 White LED Driver For Buck-Boost Application
... The EUP2983 is a constant current boost converter specially designed for driving white LEDs with wide input range. The unique converter topology provide a load voltage which can be greater or less than the input voltage. With the tightly regulated load current, the EUP2983 allows series connection w ...
... The EUP2983 is a constant current boost converter specially designed for driving white LEDs with wide input range. The unique converter topology provide a load voltage which can be greater or less than the input voltage. With the tightly regulated load current, the EUP2983 allows series connection w ...
AN-7733 FL7732 设计工具流程(升降压式) Enter Input/Output Spec. Transformer Design
... VOUT condition. The switching frequency should be <65kHz. Enter Np over Np.min. If Np is too big to fit in transformer window, reduce Max. Duty. Pulse-by-pulse current limit is 0.67V. If VCS.MAX is too close to 0.67V, increase Max. Duty. t DIS means secondary diode conduction time at peak input volt ...
... VOUT condition. The switching frequency should be <65kHz. Enter Np over Np.min. If Np is too big to fit in transformer window, reduce Max. Duty. Pulse-by-pulse current limit is 0.67V. If VCS.MAX is too close to 0.67V, increase Max. Duty. t DIS means secondary diode conduction time at peak input volt ...
king of tone guitar pedal modeling with nodal analysis
... Several approaches have been researched to address the nonlinear elements, especially diodes, in the circuit. These approaches include incremental model for diode, Newton’s iteration method [7], or wave ...
... Several approaches have been researched to address the nonlinear elements, especially diodes, in the circuit. These approaches include incremental model for diode, Newton’s iteration method [7], or wave ...
a AN-584 APPLICATION NOTE
... the transfer function is controllable by adding passive feedback networks. However, only one feedback network is required to “close the loop” and fully constrain the operation. But depending on the function desired, two feedback networks can be used. This is possible as a result of having two output ...
... the transfer function is controllable by adding passive feedback networks. However, only one feedback network is required to “close the loop” and fully constrain the operation. But depending on the function desired, two feedback networks can be used. This is possible as a result of having two output ...
a Low Cost Analog Multiplier AD633
... filtering, ES. The break frequency is modulated by EC, the control input. The break frequency, f2, equals ...
... filtering, ES. The break frequency is modulated by EC, the control input. The break frequency, f2, equals ...
AD633 Data Sheet
... filtering, ES. The break frequency is modulated by EC, the control input. The break frequency, f2, equals ...
... filtering, ES. The break frequency is modulated by EC, the control input. The break frequency, f2, equals ...
Modulation Schemes for Single-Laser 100 Gb/s Links
... based on required optical power for achieving a target bit-error ratio (BER) as a function of the modulator bandwidth. For optical powers near the ideal receiver sensitivity, the dominant noise source is thermal noise [14], [15]. In order to accommodate power penalties from impairments and receiver ...
... based on required optical power for achieving a target bit-error ratio (BER) as a function of the modulator bandwidth. For optical powers near the ideal receiver sensitivity, the dominant noise source is thermal noise [14], [15]. In order to accommodate power penalties from impairments and receiver ...
NTE74LS196 Integrated Circuit TTL − Presettable
... The NTE74LS196 is a high−speed monolithic decade counter in a 14−Lead plastic DIP type package consisting of four DC coupled, master−slave flip−flops which are internally interconnected to provide a divide−by−two and a divide−by−five counter. This device is fully programmable; that is, the outputs m ...
... The NTE74LS196 is a high−speed monolithic decade counter in a 14−Lead plastic DIP type package consisting of four DC coupled, master−slave flip−flops which are internally interconnected to provide a divide−by−two and a divide−by−five counter. This device is fully programmable; that is, the outputs m ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).







![[PDF]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008779535_1-33893a4d9836cc906f0b89cab7218c12-300x300.png)














