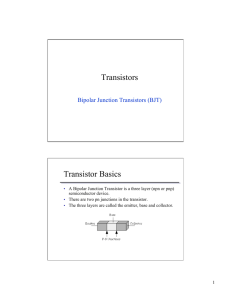
Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT)
... • The ac current gain for a transistor is different than the ...
... • The ac current gain for a transistor is different than the ...
ECE1250_Cards_Guide
... Generic negative feedback amplifier circuit. Positive gain for first system input voltage. Negative gain for second system input voltage. Sums the positive and negative gain signals. Gain G can be any positive value. Positive and negative gains are linked. High input resistance for + input, intermed ...
... Generic negative feedback amplifier circuit. Positive gain for first system input voltage. Negative gain for second system input voltage. Sums the positive and negative gain signals. Gain G can be any positive value. Positive and negative gains are linked. High input resistance for + input, intermed ...
FEATURES DESCRIPTION
... All typical values are at TA = 25°C and with VCC = 3.3 V. |VITH| = 200 mV for operation at –55°C The algebraic convention, in which the less-positive (more-negative) limit is designated minimum, is used in this data sheet for the negative-going differential input voltage threshold only. ...
... All typical values are at TA = 25°C and with VCC = 3.3 V. |VITH| = 200 mV for operation at –55°C The algebraic convention, in which the less-positive (more-negative) limit is designated minimum, is used in this data sheet for the negative-going differential input voltage threshold only. ...
Functional Block Descriptions - VLF Designs specializing in Analog
... label) and 2 alternate frequencies that are selectable by jumper and given in the attached calibration sheet. If a new frequency is selected, the VCO coil, L1 must be set to center the range of the phase comparator error signal at approximately 2VDC at TP1. Set the squelch adjustment on the receiver ...
... label) and 2 alternate frequencies that are selectable by jumper and given in the attached calibration sheet. If a new frequency is selected, the VCO coil, L1 must be set to center the range of the phase comparator error signal at approximately 2VDC at TP1. Set the squelch adjustment on the receiver ...
575A - Ortec
... If it becomes necessary to return this instrument for repair, it is essential that Customer Services be contacted in advance of its return so that a Return Authorization Number can be assigned to the unit. Also, ORTEC must be informed, either in writing, by telephone [(865) 482-4411] or by facsimile ...
... If it becomes necessary to return this instrument for repair, it is essential that Customer Services be contacted in advance of its return so that a Return Authorization Number can be assigned to the unit. Also, ORTEC must be informed, either in writing, by telephone [(865) 482-4411] or by facsimile ...
Feb-1977 - HP Labs
... results with 6V2 digits (except on ac voltages and on the 0.1-dcV and 100ÃÃ ranges). Basic accuracy for dc volts and ohms is 0.005% . ...
... results with 6V2 digits (except on ac voltages and on the 0.1-dcV and 100ÃÃ ranges). Basic accuracy for dc volts and ohms is 0.005% . ...
HA028480 Iss 10
... external digital or relay outputs. (Note that this depends on the type and number of the hardware outputs fitted). ...
... external digital or relay outputs. (Note that this depends on the type and number of the hardware outputs fitted). ...
TPA2000D2 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... power MOSFET transistors. These transistors reproduce the analog signal through high-frequency switching of the output stage. The TPA2000D2 is configured as a bridge-tied load (BTL) amplifier capable of delivering greater than 2 W of continuous average power into a 3-Ω load at less than 1% THD+N fro ...
... power MOSFET transistors. These transistors reproduce the analog signal through high-frequency switching of the output stage. The TPA2000D2 is configured as a bridge-tied load (BTL) amplifier capable of delivering greater than 2 W of continuous average power into a 3-Ω load at less than 1% THD+N fro ...
TDA8358J Full bridge vertical deflection output circuit in LVDMOS
... between pins OUTB and GND. Specified for Tj = 125 °C. The temperature coefficient for Vloss(1) is a positive value. 4. This value specifies the sum of the voltage losses of the internal current paths between pins VP and OUTB, and between pins OUTA and GND. Specified for Tj = 125 °C. The temperature ...
... between pins OUTB and GND. Specified for Tj = 125 °C. The temperature coefficient for Vloss(1) is a positive value. 4. This value specifies the sum of the voltage losses of the internal current paths between pins VP and OUTB, and between pins OUTA and GND. Specified for Tj = 125 °C. The temperature ...
chapter 13 Transceiver Design Example
... Example of I/Q Mismatches after Long Interconnects Differential I and Q signals experience deterministic mismatches as they travel on long interconnects. Explain why and devise a method of suppressing this effect. Consider the arrangement shown in (a). Owing to the finite resistance and coupling ca ...
... Example of I/Q Mismatches after Long Interconnects Differential I and Q signals experience deterministic mismatches as they travel on long interconnects. Explain why and devise a method of suppressing this effect. Consider the arrangement shown in (a). Owing to the finite resistance and coupling ca ...
Mini8 ® Controller
... external digital or relay outputs. (Note that this depends on the type and number of the hardware outputs fitted). ...
... external digital or relay outputs. (Note that this depends on the type and number of the hardware outputs fitted). ...
Airtalk I/O Extender
... Digital outputs Up to 8 digital outputs are available. These outputs are all open collector power transistors switching to ground (zero volt) level. The output is either off “high impedance” or on “low impedance current path to ground”. If the output is “off” the input that is associated with this o ...
... Digital outputs Up to 8 digital outputs are available. These outputs are all open collector power transistors switching to ground (zero volt) level. The output is either off “high impedance” or on “low impedance current path to ground”. If the output is “off” the input that is associated with this o ...
MAX503 5V, Low-Power, Parallel-Input, Voltage-Output, 10-Bit DAC _______________General Description
... _______________General Description The MAX503 is a low-power, 10-bit, voltage-output digitalto-analog converter (DAC) that uses single 5V or dual ±5V supplies. This device has an internal voltage reference plus an output buffer amplifier. Operating current is only 250µA from a single 5V supply, maki ...
... _______________General Description The MAX503 is a low-power, 10-bit, voltage-output digitalto-analog converter (DAC) that uses single 5V or dual ±5V supplies. This device has an internal voltage reference plus an output buffer amplifier. Operating current is only 250µA from a single 5V supply, maki ...
Transmission Line Terminations: It`s the End That Counts
... capacitor. The scope is a HyperLynx simulation of a 50 Ohm transmission line, 5 ns long, terminated with a 50 Ohm resistor in series with a .002 uF capacitor. The green line is the driver voltage. The red line, trailing 5 ns later, is the voltage at the receiver (and at the resistor). The blue line ...
... capacitor. The scope is a HyperLynx simulation of a 50 Ohm transmission line, 5 ns long, terminated with a 50 Ohm resistor in series with a .002 uF capacitor. The green line is the driver voltage. The red line, trailing 5 ns later, is the voltage at the receiver (and at the resistor). The blue line ...
Si5110 Data Sheet -- SiPHY OC-48/STM
... The Si5110 is a complete low-power transceiver for high-speed serial communication systems operating between OC-48 and 2.7 Gbps. The receive path consists of a fully-integrated limiting amplifier, clock and data recovery unit (CDR), and 1:4 deserializer. The transmit path combines a low-jitter clock ...
... The Si5110 is a complete low-power transceiver for high-speed serial communication systems operating between OC-48 and 2.7 Gbps. The receive path consists of a fully-integrated limiting amplifier, clock and data recovery unit (CDR), and 1:4 deserializer. The transmit path combines a low-jitter clock ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).