Op-Amp - Book Spar
... substituting A = ∞ in eq’s (ii) & (iii) above, the output Vo of the opamp should range from +∞ to -∞. However, in practice, Vo is limited by the magnitudes of the power supply voltages. If the supply voltage are ± 15V, (Terminals 4 & 5) V0 would be about ±10 V. ...
... substituting A = ∞ in eq’s (ii) & (iii) above, the output Vo of the opamp should range from +∞ to -∞. However, in practice, Vo is limited by the magnitudes of the power supply voltages. If the supply voltage are ± 15V, (Terminals 4 & 5) V0 would be about ±10 V. ...
OPA827
... (150µV, max), very low drift over temperature (1.5µV/°C, typ), low bias current (15pA, typ), and very low 0.1Hz to 10Hz noise (250nVPP, typ). The device operates over a wide supply voltage range, ±4V to ±18V on a low supply current (4.8mA/Ch, typ). ...
... (150µV, max), very low drift over temperature (1.5µV/°C, typ), low bias current (15pA, typ), and very low 0.1Hz to 10Hz noise (250nVPP, typ). The device operates over a wide supply voltage range, ±4V to ±18V on a low supply current (4.8mA/Ch, typ). ...
MIC23031 - Microchip
... from a battery increases the devices operating time and is critical in hand held devices. There are two types of losses in switching converters; DC losses and switching losses. DC losses are simply the power dissipation of I2R. Power is dissipated in the high side switch during the on cycle. Power l ...
... from a battery increases the devices operating time and is critical in hand held devices. There are two types of losses in switching converters; DC losses and switching losses. DC losses are simply the power dissipation of I2R. Power is dissipated in the high side switch during the on cycle. Power l ...
MAX197 Multi-Range (±10V, ±5V, +10V, +5V), _______________General Description
... 100ksps throughput rate can be achieved. It is possible to digitize high-speed transient events and measure periodic signals with bandwidths exceeding the ADC’s sampling rate by using undersampling techniques. To avoid high-frequency signals being aliased into the frequency band of interest, anti-al ...
... 100ksps throughput rate can be achieved. It is possible to digitize high-speed transient events and measure periodic signals with bandwidths exceeding the ADC’s sampling rate by using undersampling techniques. To avoid high-frequency signals being aliased into the frequency band of interest, anti-al ...
485 LaserPak User's Manual
... interface. This quick start guide uses the computer interface. More information on the analog interface can be found later in the manual. To control the LaserPak from the PC, use the Arroyo Control software located on the CD that came with the instrument (it can also be downloaded from our web site) ...
... interface. This quick start guide uses the computer interface. More information on the analog interface can be found later in the manual. To control the LaserPak from the PC, use the Arroyo Control software located on the CD that came with the instrument (it can also be downloaded from our web site) ...
Electronics Devices and Circuits
... drop IL Z0 is produced on it. The final D.C. output voltage reduces by this amount which should be ideally zero (i.e., Z0 = 0) Z0 can be reduced by 1) Using transistor as emitter follower. 2) Using ve feedback in the circuit dv c i.e. it is defined as the rate of change of sweep voltage dt w.r.t. t ...
... drop IL Z0 is produced on it. The final D.C. output voltage reduces by this amount which should be ideally zero (i.e., Z0 = 0) Z0 can be reduced by 1) Using transistor as emitter follower. 2) Using ve feedback in the circuit dv c i.e. it is defined as the rate of change of sweep voltage dt w.r.t. t ...
FEATURES APPLICATIONS D
... voltage-feedback architecture. Intended for xDSL driver applications, the OPA2613 also supports this low input noise with exceptionally low harmonic distortion, particularly in differential configurations. Adequate output current is provided to drive the potentially heavy load of a twisted-pair line ...
... voltage-feedback architecture. Intended for xDSL driver applications, the OPA2613 also supports this low input noise with exceptionally low harmonic distortion, particularly in differential configurations. Adequate output current is provided to drive the potentially heavy load of a twisted-pair line ...
dc/ac converters using silicon controlled rectifiers for fluorescent
... the voltage between a and b does not exceed a specific value, the rectifier in the quiescent state passes no current (apart from a leakage current of no more than a few milliamperes); this holds for both polarities of the voltage between a and b. To make the rectifier conductive - which, without cau ...
... the voltage between a and b does not exceed a specific value, the rectifier in the quiescent state passes no current (apart from a leakage current of no more than a few milliamperes); this holds for both polarities of the voltage between a and b. To make the rectifier conductive - which, without cau ...
AMS2954 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... A 1.0 µF or greater capacitor is required between output and ground for stability at output voltages of 5V or more. At lower output voltages, more capacitance is required (2.2µ or more is recommended for 2.5V, 3.0V and 3.3V versions). Without this capacitor the part will oscillate. Most types of tan ...
... A 1.0 µF or greater capacitor is required between output and ground for stability at output voltages of 5V or more. At lower output voltages, more capacitance is required (2.2µ or more is recommended for 2.5V, 3.0V and 3.3V versions). Without this capacitor the part will oscillate. Most types of tan ...
MAX15041 Low-Cost, 3A, 4.5V to 28V Input, 350kHz, PWM General Description
... The MAX15041 is a high-efficiency, peak-currentmode, step-down DC-DC converter with integrated high-side (170mΩ, typ) and low-side (105mΩ, typ) power switches. The output voltage is set from 0.606V to 0.9 x VIN by using an adjustable, external resistive divider and can deliver up to 3A load current. ...
... The MAX15041 is a high-efficiency, peak-currentmode, step-down DC-DC converter with integrated high-side (170mΩ, typ) and low-side (105mΩ, typ) power switches. The output voltage is set from 0.606V to 0.9 x VIN by using an adjustable, external resistive divider and can deliver up to 3A load current. ...
Input Offset Voltage
... Note: These ratings are for specific circuit conditions, and they often include minimum, maximum and typical values. ...
... Note: These ratings are for specific circuit conditions, and they often include minimum, maximum and typical values. ...
a Dual Fractional-N/Integer-N Frequency Synthesizer ADF4252
... wireless receivers and transmitters. Both the RF and IF synthesizers consist of a low noise digital PFD (phase frequency detector), a precision charge pump, and a programmable reference divider. The RF synthesizer has a ⌺-⌬-based fractional interpolator that allows programmable fractional-N division ...
... wireless receivers and transmitters. Both the RF and IF synthesizers consist of a low noise digital PFD (phase frequency detector), a precision charge pump, and a programmable reference divider. The RF synthesizer has a ⌺-⌬-based fractional interpolator that allows programmable fractional-N division ...
AD8603_DataSheet
... Chttp://www.mianfeiwendang.com/doc/ea0f083302a80ec7e2c19ac3F = 50 pF yields a phase margin of about 45° for the values shown in Figure 45. ...
... Chttp://www.mianfeiwendang.com/doc/ea0f083302a80ec7e2c19ac3F = 50 pF yields a phase margin of about 45° for the values shown in Figure 45. ...
Feedback (Negative and Positive) File
... drops below that lower reference level. The result is a clean square-wave output again, despite significant amounts of distortion in the AC input signal. In order for a "glitch" to cause the comparator to switch from one state to another, it would have to be at least as big (tall) as the difference ...
... drops below that lower reference level. The result is a clean square-wave output again, despite significant amounts of distortion in the AC input signal. In order for a "glitch" to cause the comparator to switch from one state to another, it would have to be at least as big (tall) as the difference ...
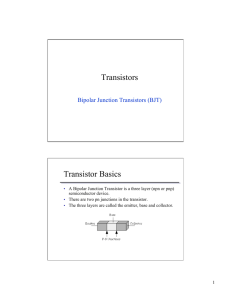
Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT)
... • The ac current gain for a transistor is different than the ...
... • The ac current gain for a transistor is different than the ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).