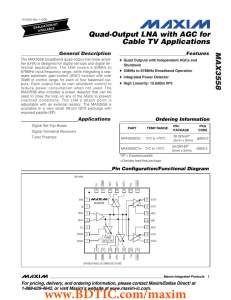
CC RTM CARD LAYOUT GENERAL PLACEMENT The figure above
... In general the ICs in the clocking circuitry should be placed close together. U4,U5,U8 and U11 are the first group and U14,U15,U16 are the second and U3,U10, and U6 are the third group. U12 should be placed close to the RJ45 connector block. The rules concerning the PLL ICs, U16 and U3 are as follow ...
... In general the ICs in the clocking circuitry should be placed close together. U4,U5,U8 and U11 are the first group and U14,U15,U16 are the second and U3,U10, and U6 are the third group. U12 should be placed close to the RJ45 connector block. The rules concerning the PLL ICs, U16 and U3 are as follow ...
Active-Clamped, Spread-Spectrum, Current-Mode PWM Controllers MAX5974A/MAX5974B/MAX5974C/MAX5974D EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE
... The MAX5974A/MAX5974B feature unique circuitry to achieve output regulation without using an optocoupler, while the MAX5974C/MAX5974D utilize the traditional optocoupler feedback method. An internal error amplifier with a 1% reference is very useful in nonisolated design, eliminating the need for an ...
... The MAX5974A/MAX5974B feature unique circuitry to achieve output regulation without using an optocoupler, while the MAX5974C/MAX5974D utilize the traditional optocoupler feedback method. An internal error amplifier with a 1% reference is very useful in nonisolated design, eliminating the need for an ...
SN55LVDS33-SP 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... to improve noise rejection on slowly changing input signals. The input thresholds are still no more than +50 mV over the full input common-mode voltage range. The receivers can withstand ±15-kV Human-Body Model (HBM) and ±600-V Machine Model (MM) electrostatic discharges to the receiver input pins w ...
... to improve noise rejection on slowly changing input signals. The input thresholds are still no more than +50 mV over the full input common-mode voltage range. The receivers can withstand ±15-kV Human-Body Model (HBM) and ±600-V Machine Model (MM) electrostatic discharges to the receiver input pins w ...
AD9260 数据手册DataSheet下载
... performance and flexibility. A series of three half-band FIR filter stages provide 8× decimation filtering with 85 dB of stopband attenuation and 0.004 dB of pass-band ripple. An onboard digital multiplexer allows the user to access data from the various stages of the decimation filter. The on-chip ...
... performance and flexibility. A series of three half-band FIR filter stages provide 8× decimation filtering with 85 dB of stopband attenuation and 0.004 dB of pass-band ripple. An onboard digital multiplexer allows the user to access data from the various stages of the decimation filter. The on-chip ...
MAX3558
... to AGC_ voltage of 0.5V and maximum gain corresponds to AGC_ voltage of 3V. AGC inputs can be driven from a demodulator’s AGC output, which normally controls a tuner’s RF AGC, or from the MAX3558’s onchip power detector. Should an overload condition occur, the closed-loop AGC circuitry continues to ...
... to AGC_ voltage of 0.5V and maximum gain corresponds to AGC_ voltage of 3V. AGC inputs can be driven from a demodulator’s AGC output, which normally controls a tuner’s RF AGC, or from the MAX3558’s onchip power detector. Should an overload condition occur, the closed-loop AGC circuitry continues to ...
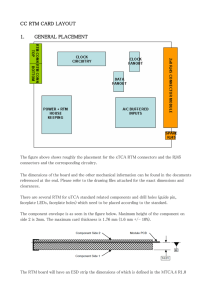
In the example shown in Figure 5-1, the p-p output... The conventional way to power ...
... for the selected gain range or even in excess of the supply voltage. These overloads fall into two general classes: steady state and transient (ESD, etc.), both of which occur for only a fraction of a second. With 3-op amp in-amp designs, when operating at low gains (10 or less), the gain resistor a ...
... for the selected gain range or even in excess of the supply voltage. These overloads fall into two general classes: steady state and transient (ESD, etc.), both of which occur for only a fraction of a second. With 3-op amp in-amp designs, when operating at low gains (10 or less), the gain resistor a ...
Charge Pump, Loop Filter and VCO for Phase Lock
... inappropriate values may either lead the loop to oscillate for long without reaching the locked state or it may so happen that once locked, small variations in the input data may cause the loop to unlock. A second order low pass filter is used as loop filter. The main function of the loop filter is ...
... inappropriate values may either lead the loop to oscillate for long without reaching the locked state or it may so happen that once locked, small variations in the input data may cause the loop to unlock. A second order low pass filter is used as loop filter. The main function of the loop filter is ...
AD7689
... one LSB is 76.3 μV. 4 See the Terminology section. These specifications include full temperature range variation but not the error contribution from the external reference. 5 With VDD = 5 V, unless otherwise noted. 6 All specifications expressed in decibels are referred to a full-scale input FSR and ...
... one LSB is 76.3 μV. 4 See the Terminology section. These specifications include full temperature range variation but not the error contribution from the external reference. 5 With VDD = 5 V, unless otherwise noted. 6 All specifications expressed in decibels are referred to a full-scale input FSR and ...
Programmable Automatic Shift System
... If engine revolutions are to be monitored one of the malfunction inlets (AUX 1) is used. Two different R.P.M. limits are compared.The maximum permitted R.P.M. of the engine is always monitored by SHIFTRONIC. When the programmed limit is exceeded the transmission will automatically shift into neutral ...
... If engine revolutions are to be monitored one of the malfunction inlets (AUX 1) is used. Two different R.P.M. limits are compared.The maximum permitted R.P.M. of the engine is always monitored by SHIFTRONIC. When the programmed limit is exceeded the transmission will automatically shift into neutral ...
DAC108S085 10-Bit Micro Power OCTAL Digital-to-Analog
... Note 2: All voltages are measured with respect to GND = 0V, unless otherwise specified. Note 3: When the input voltage at any pin exceeds 5.5V or is less than GND, the current at that pin should be limited to 10 mA. The 30 mA maximum package input current rating limits the number of pins that can s ...
... Note 2: All voltages are measured with respect to GND = 0V, unless otherwise specified. Note 3: When the input voltage at any pin exceeds 5.5V or is less than GND, the current at that pin should be limited to 10 mA. The 30 mA maximum package input current rating limits the number of pins that can s ...
MAX5500/MAX5501 Low-Power, Quad, 12-Bit Voltage-Output DACs with Serial Interface General Description
... when the MAX5500/MAX5501 are in shutdown. The reference input capacitance is also code dependent and typically ranges from 20pF with an input code of all 0s to 100pF with an input code of all 1s. ...
... when the MAX5500/MAX5501 are in shutdown. The reference input capacitance is also code dependent and typically ranges from 20pF with an input code of all 0s to 100pF with an input code of all 1s. ...
Model 6176 Channel Strip
... father, M.T. “Bill” Putnam, in 1960. The 610 was a rotary-control console and it was also the first console of a modular design. Although technologically simple compared to modern consoles, the 610 possessed a warmth and character that kept it in demand for decades. A prominent component of my fathe ...
... father, M.T. “Bill” Putnam, in 1960. The 610 was a rotary-control console and it was also the first console of a modular design. Although technologically simple compared to modern consoles, the 610 possessed a warmth and character that kept it in demand for decades. A prominent component of my fathe ...
AD8278 英文数据手册DataSheet 下载
... power. The AD8278 and AD8279 provide exceptional commonmode rejection ratio (80 dB) and high bandwidth while amplifying input signals that are well beyond the supply rails. The on-chip resistors are laser trimmed for excellent gain accuracy and high CMRR. They also have extremely low gain drift vs. ...
... power. The AD8278 and AD8279 provide exceptional commonmode rejection ratio (80 dB) and high bandwidth while amplifying input signals that are well beyond the supply rails. The on-chip resistors are laser trimmed for excellent gain accuracy and high CMRR. They also have extremely low gain drift vs. ...
WT 1600 Total Solution Numerical, Waveform, and Trend Displays
... Current and power DC accuracy (5 A input element) -----Add 20 µA to current and 20 µA × (voltage reading) to power Current and power DC accuracy (50 A input element) -----Add 1 mA to current and 1 mA × (voltage reading) to power External input -----Add (0.05/scaling value) A to current and (0.05/sca ...
... Current and power DC accuracy (5 A input element) -----Add 20 µA to current and 20 µA × (voltage reading) to power Current and power DC accuracy (50 A input element) -----Add 1 mA to current and 1 mA × (voltage reading) to power External input -----Add (0.05/scaling value) A to current and (0.05/sca ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).