Series and Parallel Resonance - ECE, Rutgers
... Build the circuit of fig. 7 using R = 620 Ω, L = 100 mH, and C = 0.1 µF. Apply a sinusoidal input to the circuit and display both input and output on the scope. Set the rms value of Vs = 1.00 volts. ...
... Build the circuit of fig. 7 using R = 620 Ω, L = 100 mH, and C = 0.1 µF. Apply a sinusoidal input to the circuit and display both input and output on the scope. Set the rms value of Vs = 1.00 volts. ...
Preliminary Work
... 1. Remove the high pass capacitor (the one in series with the source). 2. Adjust the period (PER) and the pulse width (PW=0.5*PER) until you can see what the low pass filtering does to the square wave. Start with a square wave with a frequency of 100 kHz (PW=5u and PER=10u). Be sure to explain in yo ...
... 1. Remove the high pass capacitor (the one in series with the source). 2. Adjust the period (PER) and the pulse width (PW=0.5*PER) until you can see what the low pass filtering does to the square wave. Start with a square wave with a frequency of 100 kHz (PW=5u and PER=10u). Be sure to explain in yo ...
The text of the original article (Word 2000 format)
... The instrument case is then fabricated. The drilled PCB can be used as a template to accurately mark and drill the box front panel for all terminals, mounting pillars and switches. After this is done, carefully use a wood chisel to remove the internal reinforcing ribs at either end of the Jaycar box ...
... The instrument case is then fabricated. The drilled PCB can be used as a template to accurately mark and drill the box front panel for all terminals, mounting pillars and switches. After this is done, carefully use a wood chisel to remove the internal reinforcing ribs at either end of the Jaycar box ...
Operational Amplifiers in Chemical Instrumentation
... instrument or piece of electronic equipment, it would be likely to find one or more op amps. This fact, along with the ease of complex functions that may be accomplished, makes clear the importance of understanding their principles of operation. In this chapter, we will briefly discuss some operatio ...
... instrument or piece of electronic equipment, it would be likely to find one or more op amps. This fact, along with the ease of complex functions that may be accomplished, makes clear the importance of understanding their principles of operation. In this chapter, we will briefly discuss some operatio ...
Word Document - UCSD VLSI CAD Laboratory
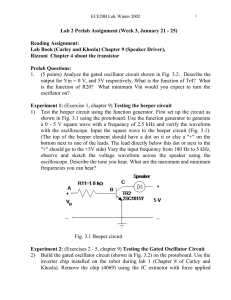
... part of the power supply. The transistor TR4 (2SA1015Y) is wired like ECB. If it is 2SA1015H it is EBC (see Chapter 1 Fig. 1.7). Observe Vout on the oscilloscope when Vin is 0 V and 5V. Sketch the waveform in your labbook when Vin = 5V, record the frequency and amplitude. Compare with Prelab results ...
... part of the power supply. The transistor TR4 (2SA1015Y) is wired like ECB. If it is 2SA1015H it is EBC (see Chapter 1 Fig. 1.7). Observe Vout on the oscilloscope when Vin is 0 V and 5V. Sketch the waveform in your labbook when Vin = 5V, record the frequency and amplitude. Compare with Prelab results ...
Trig-Tek™ Product Information
... The unit will operate with high-temperature accelerometers where pyroelectric effects may be encountered and will function with 100 kΩ or greater shunt input resistance. The unit has an alarm circuit to alert if preset levels are exceeded as well as a relay contact closure. Up to six 203M modules ca ...
... The unit will operate with high-temperature accelerometers where pyroelectric effects may be encountered and will function with 100 kΩ or greater shunt input resistance. The unit has an alarm circuit to alert if preset levels are exceeded as well as a relay contact closure. Up to six 203M modules ca ...
AFM training quiz (this is a take home quiz, refer to your common
... c) Legs are set too short. d) Legs are set too long. ...
... c) Legs are set too short. d) Legs are set too long. ...
SNA-386 DC-3 GHz, Cascadable GaAs MMIC Amplifier Product Description
... this information, and all such information shall be entirely at the users own risk. Prices and specifications are subject to change without notice. No patent rights or licenses to any of the circuits described herein are implied or granted to any third party. Sirenza Microdevices does not authorize ...
... this information, and all such information shall be entirely at the users own risk. Prices and specifications are subject to change without notice. No patent rights or licenses to any of the circuits described herein are implied or granted to any third party. Sirenza Microdevices does not authorize ...
z 33-231 Physical Analysis
... a) Show that the damping force has the expected direction when x is large, but that for small x it has the same direction as v and is thus an "anti-damping" force. What consequences do you think this will have for the motion? b) Study the motion of this system, using x vs t plots and phase plots wit ...
... a) Show that the damping force has the expected direction when x is large, but that for small x it has the same direction as v and is thus an "anti-damping" force. What consequences do you think this will have for the motion? b) Study the motion of this system, using x vs t plots and phase plots wit ...
Lab 3: RLC Circuits - Weber State University
... Fig. 2: (a) Impulse and (b) step responses of an under-damped series RLC circuit (4) Build a circuit according to Figure 1 with R1 being a fixed resistor plus a potentiometer. Apply a square-wave signal as the input (for best results use 0 to 5V square wave at 2.5 kHz; you may need to adjust the fre ...
... Fig. 2: (a) Impulse and (b) step responses of an under-damped series RLC circuit (4) Build a circuit according to Figure 1 with R1 being a fixed resistor plus a potentiometer. Apply a square-wave signal as the input (for best results use 0 to 5V square wave at 2.5 kHz; you may need to adjust the fre ...
Experiment 5 Objective – Filter design and testing with a Current
... In contrast, a current conveyor (CC) is a current mode analog circuit. In other words, all the inputs and output are current. A CC circuit offers some advantages such as higher bandwidth, higher dynamic range, and lower power supply voltages. AD 844 chip is similar to LM 741 but it can also work as ...
... In contrast, a current conveyor (CC) is a current mode analog circuit. In other words, all the inputs and output are current. A CC circuit offers some advantages such as higher bandwidth, higher dynamic range, and lower power supply voltages. AD 844 chip is similar to LM 741 but it can also work as ...
SNA-286 DC-6.0 GHz, Cascadable GaAs MMIC Amplifier Product Description
... this information, and all such information shall be entirely at the users own risk. Prices and specifications are subject to change without notice. No patent rights or licenses to any of the circuits described herein are implied or granted to any third party. Sirenza Microdevices does not authorize ...
... this information, and all such information shall be entirely at the users own risk. Prices and specifications are subject to change without notice. No patent rights or licenses to any of the circuits described herein are implied or granted to any third party. Sirenza Microdevices does not authorize ...
Discussion7
... Some After-Class Questions for you When capacitors or inductors used in AC circuits, is the current and voltage peak at the same time? Why or why not? In a linear system, does the frequency of a sinusoid convey information? Can phasor analysis be performed on multiple frequencies circuits? ...
... Some After-Class Questions for you When capacitors or inductors used in AC circuits, is the current and voltage peak at the same time? Why or why not? In a linear system, does the frequency of a sinusoid convey information? Can phasor analysis be performed on multiple frequencies circuits? ...
Effects of Frequency Domain Phenomena on Time Domain Digital
... delays due to the current components “hugging” the corner increasing the mean length • 2 rights do not necessarily equal a left and a right, especially for wide traces • 45o bends, round and chamfered bends exhibit reduced effects Interconnect II ...
... delays due to the current components “hugging” the corner increasing the mean length • 2 rights do not necessarily equal a left and a right, especially for wide traces • 45o bends, round and chamfered bends exhibit reduced effects Interconnect II ...
Optical PLL for homodyne detection
... detected BPSK signal (Real(In1)) – measured from the upper branch of the balanced detector (I(t)) Represents the imaginary part of the detected BPSK signal (Imag(In1)) – measured from the lower branch of the balanced detector (Q(t)). Under ideal conditions, this signal should be zero (the phase modu ...
... detected BPSK signal (Real(In1)) – measured from the upper branch of the balanced detector (I(t)) Represents the imaginary part of the detected BPSK signal (Imag(In1)) – measured from the lower branch of the balanced detector (Q(t)). Under ideal conditions, this signal should be zero (the phase modu ...
General Licensing Class
... A. An amplifier and a divider B. A frequency multiplier and a mixer C. A circulator and a filter operating in a feedback loop D. A filter and an amplifier operating in a feedback loop ...
... A. An amplifier and a divider B. A frequency multiplier and a mixer C. A circulator and a filter operating in a feedback loop D. A filter and an amplifier operating in a feedback loop ...
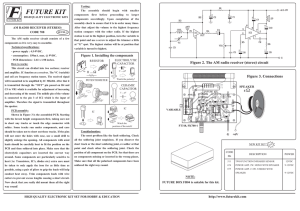
AM Receiver - Profe Saul
... receiver becomes "deaf". If the circuit oscillates,then R1's value may be decreased; try 68k. If there is a lack of sensitivity, then try increasing R1 to around 150k. R1 could also be replaced by a fixed resisor say 33k and a preset resistor of 100k. This will give adjustment of sensitivity and sel ...
... receiver becomes "deaf". If the circuit oscillates,then R1's value may be decreased; try 68k. If there is a lack of sensitivity, then try increasing R1 to around 150k. R1 could also be replaced by a fixed resisor say 33k and a preset resistor of 100k. This will give adjustment of sensitivity and sel ...
Chapter 1 (Part 3) - Introduction to Basic Filters
... When the output power gain drops to 50%, the voltage gain drops 3 dB (0.707 of the maximun value. The filter network voltage gain in dB is calculated from the actual voltage gain (A) using the equation A(dB) = 20 log A Where A=Vout/Vin ...
... When the output power gain drops to 50%, the voltage gain drops 3 dB (0.707 of the maximun value. The filter network voltage gain in dB is calculated from the actual voltage gain (A) using the equation A(dB) = 20 log A Where A=Vout/Vin ...
Superheterodyne receiver

In electronics, a superheterodyne receiver (often shortened to superhet) uses frequency mixing to convert a received signal to a fixed intermediate frequency (IF) which can be more conveniently processed than the original radio carrier frequency. It was invented by US engineer Edwin Armstrong in 1918 during World War I. Virtually all modern radio receivers use the superheterodyne principle. At the cost of an extra frequency converter stage, the superheterodyne receiver provides superior selectivity and sensitivity compared with simpler designs.