Health Canada - Northern Region
... and mental health/mental illness, as they contribute significantly to the burden of diabetes comorbidities, costs and complications. As such, projects that seek to address screening, early detection and/or self-management of cardiovascular disease or mental illness/health among Canadians living with ...
... and mental health/mental illness, as they contribute significantly to the burden of diabetes comorbidities, costs and complications. As such, projects that seek to address screening, early detection and/or self-management of cardiovascular disease or mental illness/health among Canadians living with ...
Chapter 36 Insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents
... Cause and risk factors of type2 DM • Age greater than 40 years • ethnic groups, including African Americans, Hispanic Americans, Asian Americans, and Native Americans, have a higher risk for diabetes. • Family history of diabetes • Diabetes during a previous pregnancy • Excess body weight (especial ...
... Cause and risk factors of type2 DM • Age greater than 40 years • ethnic groups, including African Americans, Hispanic Americans, Asian Americans, and Native Americans, have a higher risk for diabetes. • Family history of diabetes • Diabetes during a previous pregnancy • Excess body weight (especial ...
SD-15 Outline - American Academy of Optometry
... 1921- Banting & Best isolate “pancreatic extract” (insulin), successfully use it to treat a depancreatized dog ...
... 1921- Banting & Best isolate “pancreatic extract” (insulin), successfully use it to treat a depancreatized dog ...
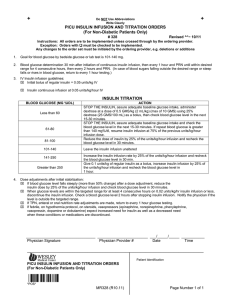
PICU INSULIN INFUSION AND TITRATION ORDERS (For Non
... insulin dose by 25% of the units/kg/hour infusion and check blood glucose level in 30 minutes. When glucose levels are within the targeted range for at least 4 consecutive hours on 0.02 units/kg/hr insulin infusion or less, discontinue the insulin infusion. Check a blood glucose level 2 hours afte ...
... insulin dose by 25% of the units/kg/hour infusion and check blood glucose level in 30 minutes. When glucose levels are within the targeted range for at least 4 consecutive hours on 0.02 units/kg/hr insulin infusion or less, discontinue the insulin infusion. Check a blood glucose level 2 hours afte ...
HOW TO LIVE WITH DIABETES .
... Diabetes Mellitus). This is the most common form of diabetes mellitus, and is strongly associated with obesity. In this, a combination of factors play their role. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus is a group of disorders usually characterized by variable degrees of insulin resistance, impaired insulin secret ...
... Diabetes Mellitus). This is the most common form of diabetes mellitus, and is strongly associated with obesity. In this, a combination of factors play their role. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus is a group of disorders usually characterized by variable degrees of insulin resistance, impaired insulin secret ...
Information Technology Solutions
... her lifestyle or even take medications to maintain her glucose at healthy levels. Many of the gestational diabetic patients are not used to the blood or pain of finger pricking. Some may be concerned with the risk of breaking their skin barrier when conducting the tests. 'Kiss & Tell' offers these p ...
... her lifestyle or even take medications to maintain her glucose at healthy levels. Many of the gestational diabetic patients are not used to the blood or pain of finger pricking. Some may be concerned with the risk of breaking their skin barrier when conducting the tests. 'Kiss & Tell' offers these p ...
HOW TO LIVE WITH DIABETES
... HYPOGLYCAEMIA is the most important phenomenon, which all those diabetics who are either on insulin or on antidiabetic tablets must know. Hypo means low & glycaemia means sugar i.e. low blood glucose. Some times the level of glucose in blood falls below normal. If the patient is alert and has been t ...
... HYPOGLYCAEMIA is the most important phenomenon, which all those diabetics who are either on insulin or on antidiabetic tablets must know. Hypo means low & glycaemia means sugar i.e. low blood glucose. Some times the level of glucose in blood falls below normal. If the patient is alert and has been t ...
Urine Metabolic Screening an useful screening tool?
... • To balance insulin dosage with activity level and food intake to ensure stable blood glucose • 20% or more reduction of insulin dosage • Extra reduction for extreme physical activity, prolonged hikes or water sports • Pre- and post-camp insulin dose advice – Small reduction of 10% for immediate ...
... • To balance insulin dosage with activity level and food intake to ensure stable blood glucose • 20% or more reduction of insulin dosage • Extra reduction for extreme physical activity, prolonged hikes or water sports • Pre- and post-camp insulin dose advice – Small reduction of 10% for immediate ...
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (Immune Mediated)
... A standard water deficit (85 mL/kg) is assumed yields about 4 L/M2 for children of all sizes DKA has essentially resolved (total CO2 >15 mEq/L; pH >7.30; sodium stable between 135 and 145 mEq/L; no emesis). A flow sheet is mandatory for accurate monitoring of changes in acidosis, electrolytes, fluid ...
... A standard water deficit (85 mL/kg) is assumed yields about 4 L/M2 for children of all sizes DKA has essentially resolved (total CO2 >15 mEq/L; pH >7.30; sodium stable between 135 and 145 mEq/L; no emesis). A flow sheet is mandatory for accurate monitoring of changes in acidosis, electrolytes, fluid ...
Cr and Insulin Resistance
... Using Ginsberg’s estimated lifetime cost savings of $27,000 ($36,000 in 2004 dollars) per patient with good diabetes control, lifetime cost savings of those diagnosed with T2DM in 2004 calculates to approximately $42 billion ...
... Using Ginsberg’s estimated lifetime cost savings of $27,000 ($36,000 in 2004 dollars) per patient with good diabetes control, lifetime cost savings of those diagnosed with T2DM in 2004 calculates to approximately $42 billion ...
First Presentation of Diabetes as Diabetic
... ndividuals with Friedreich’s ataxia (FA) have an increased risk of developing diabetes. However, the type, onset, and course of diabetes in people with FA are not well characterized. In FA-associated diabetes, both insulin deficiency and insulin resistance have been reported. The presentation and cl ...
... ndividuals with Friedreich’s ataxia (FA) have an increased risk of developing diabetes. However, the type, onset, and course of diabetes in people with FA are not well characterized. In FA-associated diabetes, both insulin deficiency and insulin resistance have been reported. The presentation and cl ...
Blood glucose case studies - Lambeth Diabetes Intermediate Care
... Consider whether she is at risk of sudden decline in renal function (for example another emergency admission with heart failure) Sick day rules for metformin Metformin does not cause renal damage but patients with low eGFR are at increased risk of fatal lactic acidosis associated with acute illness ...
... Consider whether she is at risk of sudden decline in renal function (for example another emergency admission with heart failure) Sick day rules for metformin Metformin does not cause renal damage but patients with low eGFR are at increased risk of fatal lactic acidosis associated with acute illness ...
Elizabeth`s DM Questions
... 41) How can we treat it? By adjusting the time insulin is taken @ night or increasing the dose 42) What is the Somogyi effect? rebound elevation of glucose brought on by hypoglycemia. This may lead to ketosis or coma 43) Thiazolidnedones (Avandia) and Biguanides (Metformin) help to decrease overa ...
... 41) How can we treat it? By adjusting the time insulin is taken @ night or increasing the dose 42) What is the Somogyi effect? rebound elevation of glucose brought on by hypoglycemia. This may lead to ketosis or coma 43) Thiazolidnedones (Avandia) and Biguanides (Metformin) help to decrease overa ...
Endocrine Review - Dr. NurseAna's Nursing Reviews
... Body senses when you eat, the blood sugar goes up too high What the body does it says “look this is too high” I need to produce more insulin Pancreas starts to secret insulin Initially early in the course of the disease type 2 DM patients have elevated insulin levels Pancreas is pumping up more and ...
... Body senses when you eat, the blood sugar goes up too high What the body does it says “look this is too high” I need to produce more insulin Pancreas starts to secret insulin Initially early in the course of the disease type 2 DM patients have elevated insulin levels Pancreas is pumping up more and ...
Diabetic ketoacidosis
... hyperglycemia with relative or absolute insulin deficiency and an increase in counterregulatory hormones. Sufficient amounts of insulin are not present to suppress lipolysis and oxidation of free fatty acids, which results in ketone body production and subsequent metabolic acidosis. DKA occurs more ...
... hyperglycemia with relative or absolute insulin deficiency and an increase in counterregulatory hormones. Sufficient amounts of insulin are not present to suppress lipolysis and oxidation of free fatty acids, which results in ketone body production and subsequent metabolic acidosis. DKA occurs more ...
The final exam includes information presented in the following
... The branch of medicine dealing with the endocrine glands and their hormones Identify organs or glands that are deficient or non-functioning and use some type of pharmaceutical agent or hormone to replace, suppress or support the dysfunction glands Specific for certain genetic disorders and disease p ...
... The branch of medicine dealing with the endocrine glands and their hormones Identify organs or glands that are deficient or non-functioning and use some type of pharmaceutical agent or hormone to replace, suppress or support the dysfunction glands Specific for certain genetic disorders and disease p ...
Sickle Cell Disease
... birth than any other body system • Hormonal control of many body functions is lacking until 12-18 months of age • Infants might manifest imbalances in concentration of fluids, electrolytes, amino acids, glucose, and trace substances ...
... birth than any other body system • Hormonal control of many body functions is lacking until 12-18 months of age • Infants might manifest imbalances in concentration of fluids, electrolytes, amino acids, glucose, and trace substances ...
Diabetes and Pregnancy
... Screening. Due to the potential complications associated with GDM, the authors of the 2008 guidelines recommend that screening be performed for all women between 24 and 28 weeks’ gestation. The screening test should be performed earlier (during the first trimester) in women with multiple risk facto ...
... Screening. Due to the potential complications associated with GDM, the authors of the 2008 guidelines recommend that screening be performed for all women between 24 and 28 weeks’ gestation. The screening test should be performed earlier (during the first trimester) in women with multiple risk facto ...
Insulin Secretory and Insulin Resistance Defects in Type 2 Diabetes
... 2025.2 Fueling the diabetes epidemic is the rising incidence of obesity, food intake hypercaloric with regard to metabolic need, and sedentary lifestyle. These environmental factors play a contributory role in the development of type 2 DM, influencing expression of disease in genetically predisposed ...
... 2025.2 Fueling the diabetes epidemic is the rising incidence of obesity, food intake hypercaloric with regard to metabolic need, and sedentary lifestyle. These environmental factors play a contributory role in the development of type 2 DM, influencing expression of disease in genetically predisposed ...
Diabetes Mellitus - Advocate Health Care
... Insulin secretagogue or insulin Insulin resistance Insulin sensitizer Hepatic glucose overproduction Restrain liver production of glucose ...
... Insulin secretagogue or insulin Insulin resistance Insulin sensitizer Hepatic glucose overproduction Restrain liver production of glucose ...
Document
... Glucose tolerance is classified into three categories based on the fasting plasma glucose (FPG) FPG <5.6 mmol/l (100 mg/dl) is considered normal FPG ≥5.6 mmol/l (100 mg/dl) but <7,0 mmol/l (126 mg/dl) is defined as impaired fasting glucose (IFG) FPG ≥7,0 mmol/l (126 mg/dl) warrants the diagnosis of ...
... Glucose tolerance is classified into three categories based on the fasting plasma glucose (FPG) FPG <5.6 mmol/l (100 mg/dl) is considered normal FPG ≥5.6 mmol/l (100 mg/dl) but <7,0 mmol/l (126 mg/dl) is defined as impaired fasting glucose (IFG) FPG ≥7,0 mmol/l (126 mg/dl) warrants the diagnosis of ...
New Onset Diabetes After Transplant (NODAT)
... Diabetes is a metabolic disease that causes high blood glucose levels. The diagnosis of NODAT follows two or more blood tests showing above-normal blood glucose levels after a patient has had a kidney transplant. This most often occurs in the first 12 weeks after transplant, but diabetes can develop ...
... Diabetes is a metabolic disease that causes high blood glucose levels. The diagnosis of NODAT follows two or more blood tests showing above-normal blood glucose levels after a patient has had a kidney transplant. This most often occurs in the first 12 weeks after transplant, but diabetes can develop ...
Care of the Client with Diabetes Mellitus: Type 1 and Type 2
... 3. active autoimmunity 4. progressive beta cell destruction 5. overt diabetes mellitus 2. Genetic Predisposition:recessive gene + autoimmune response can destroy islet cells on the pancreas 3. Type 1 DM does not develop in all people who have a genetic predisposition 4. Autoimmune disorder ...
... 3. active autoimmunity 4. progressive beta cell destruction 5. overt diabetes mellitus 2. Genetic Predisposition:recessive gene + autoimmune response can destroy islet cells on the pancreas 3. Type 1 DM does not develop in all people who have a genetic predisposition 4. Autoimmune disorder ...
Diabetes in Pregnancy
... delivery1 • During the 4-6 hours prior to delivery, there is increased risk of transient neonatal hypoglycemia1 • Labor and delivery in women with insulin-dependent type 1 diabetes should be managed by an endocrinologist or a diabetes specialist1 • Blood glucose levels should be monitored closely du ...
... delivery1 • During the 4-6 hours prior to delivery, there is increased risk of transient neonatal hypoglycemia1 • Labor and delivery in women with insulin-dependent type 1 diabetes should be managed by an endocrinologist or a diabetes specialist1 • Blood glucose levels should be monitored closely du ...
Modern Insulin Therapy - University of Colorado Denver
... • High genetic risk individuals • New-onset T1D • Further define epidemiology, natural history, and risk factors of T1D • Parents must decide if they will support prevention research ...
... • High genetic risk individuals • New-onset T1D • Further define epidemiology, natural history, and risk factors of T1D • Parents must decide if they will support prevention research ...
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes (or gestational diabetes mellitus, GDM) is a condition in which women without previously diagnosed diabetes exhibit high blood glucose (blood sugar) levels during pregnancy (especially during their third trimester). Gestational diabetes is caused when insulin receptors do not function properly. This is likely due to pregnancy-related factors such as the presence of human placental lactogen that interferes with susceptible insulin receptors. This in turn causes inappropriately elevated blood sugar levels.Gestational diabetes generally has few symptoms and it is most commonly diagnosed by screening during pregnancy. Diagnostic tests detect inappropriately high levels of glucose in blood samples. Gestational diabetes affects 3-10% of pregnancies, depending on the population studied.As with diabetes mellitus in pregnancy in general, babies born to mothers with untreated gestational diabetes are typically at increased risk of problems such as being large for gestational age (which may lead to delivery complications), low blood sugar, and jaundice. If untreated, it can also cause seizures or stillbirth. Gestational diabetes is a treatable condition and women who have adequate control of glucose levels can effectively decrease these risks. The food plan is often the first recommended target for strategic management of GDM.Women with unmanaged gestational diabetes are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus (or, very rarely, latent autoimmune diabetes or Type 1) after pregnancy, as well as having a higher incidence of pre-eclampsia and Caesarean section; their offspring are prone to developing childhood obesity, with type 2 diabetes later in life. Most women are able to manage their blood glucose levels with a modified diet and the introduction of moderate exercise, but some require antidiabetic drugs, including insulin.