CHEM 322 ... Spring 2015 ...
... (a) write an expression that gives the output voltage in terms of the three input voltages and the various resistances. (b) indicate the mathematical operation performed by the circuit when R1 = Rf1 = 200 k; R4 = Rf2 = 400 k; R2 = 50 k; R3 = 10 k. 4. Derive a relationship between vin and vout fo ...
... (a) write an expression that gives the output voltage in terms of the three input voltages and the various resistances. (b) indicate the mathematical operation performed by the circuit when R1 = Rf1 = 200 k; R4 = Rf2 = 400 k; R2 = 50 k; R3 = 10 k. 4. Derive a relationship between vin and vout fo ...
Lecture 2: Wireless Transmission
... • Effective bandwidth - narrow band of frequencies that most of the signal’s energy is contained in ...
... • Effective bandwidth - narrow band of frequencies that most of the signal’s energy is contained in ...
Application of physics-based device models for circuit - Mos-AK
... • Considered models are good to apply for small-signal analyses. • For successful implementation, parameter extraction tool is needed, because optimization procedure is an essential part of the entire flow. • Assessment of performance impact and accuracy gain as compared to the compact models is rea ...
... • Considered models are good to apply for small-signal analyses. • For successful implementation, parameter extraction tool is needed, because optimization procedure is an essential part of the entire flow. • Assessment of performance impact and accuracy gain as compared to the compact models is rea ...
Document
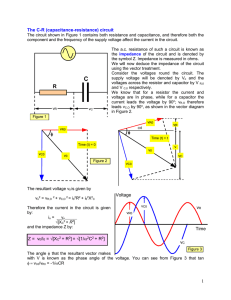
... its frequency response using either LabView or VEE software for data acquisition. In class we also discussed the notch filter in which undesired frequencies are attenuated in the “stop band” centered about the resonant frequency fr. For example, it may be necessary to attenuate a 50 Hz or 400 Hz noi ...
... its frequency response using either LabView or VEE software for data acquisition. In class we also discussed the notch filter in which undesired frequencies are attenuated in the “stop band” centered about the resonant frequency fr. For example, it may be necessary to attenuate a 50 Hz or 400 Hz noi ...
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE)
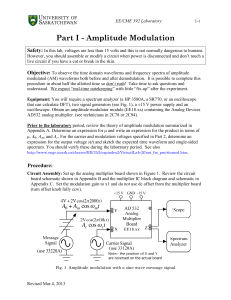
... prepares the information for transfer on the transmission link, and raises the output power to a satisfactory level for successful transfer. For a transmitter, a specific frequency (carrier frequency) is generated, which modulate the input base-band signal that contains the information, and increase ...
... prepares the information for transfer on the transmission link, and raises the output power to a satisfactory level for successful transfer. For a transmitter, a specific frequency (carrier frequency) is generated, which modulate the input base-band signal that contains the information, and increase ...
RECOMMENDATION ITU-R F.760-1 - Protection of terrestrial line
... perfectly correlated. The power flux-density noted above may need further reduction to allow for differential fading caused by rain and/or multipath. Propagation measurements of differential fading suggest that an allowance of 6 dB (see Note) for differential fading would be required to protect the ...
... perfectly correlated. The power flux-density noted above may need further reduction to allow for differential fading caused by rain and/or multipath. Propagation measurements of differential fading suggest that an allowance of 6 dB (see Note) for differential fading would be required to protect the ...
What is electricity?
... 16.1 Open and closed circuits Current only flows when there is a complete and unbroken path, or a closed circuit. Flipping a switch to the “off” position creates an open circuit by making a break in the wire. ...
... 16.1 Open and closed circuits Current only flows when there is a complete and unbroken path, or a closed circuit. Flipping a switch to the “off” position creates an open circuit by making a break in the wire. ...
Lecture 17 - Louisiana State University Physics & Astronomy
... Ideal LC circuit without resistance: oscillations go on for ever; = (LC)-1/2 Real circuit has resistance, dissipates energy: oscillations die out, or are “damped” Math is complicated! Important points: ...
... Ideal LC circuit without resistance: oscillations go on for ever; = (LC)-1/2 Real circuit has resistance, dissipates energy: oscillations die out, or are “damped” Math is complicated! Important points: ...