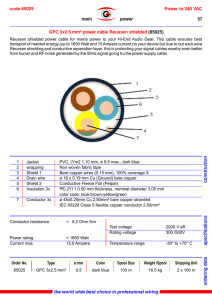
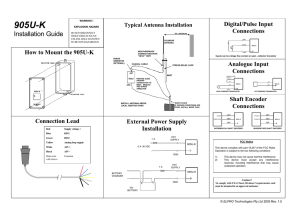
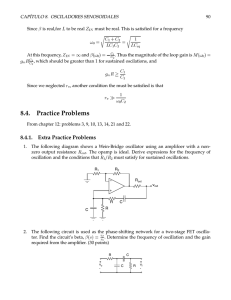
Advanced State Electrician Certification
... state use of and limits of common electrical meters, analog and digital, and define meter categories I through IV; describe atomic theory concerning conductors, insulators and semi-conductors, positive and negative charges and electron flow; contrast and explain the various forms of electricity: sta ...
... state use of and limits of common electrical meters, analog and digital, and define meter categories I through IV; describe atomic theory concerning conductors, insulators and semi-conductors, positive and negative charges and electron flow; contrast and explain the various forms of electricity: sta ...
Circuit Timing
... due to the propagation delay of the logic gates. tp of a signal depends on the signal path inside the logic circuit For a logic gate tpLH may not equal tpHL, (e.g. in TTL) tp is specified in the manufacturer data sheets of the IC’s Example: The delay for 74x00 in nanoseconds for TTL & CMOS ...
... due to the propagation delay of the logic gates. tp of a signal depends on the signal path inside the logic circuit For a logic gate tpLH may not equal tpHL, (e.g. in TTL) tp is specified in the manufacturer data sheets of the IC’s Example: The delay for 74x00 in nanoseconds for TTL & CMOS ...
Series Circuits
... that the total resistance of this circuit is 11.3 kΩ, which happens to be equal to the sum of all of the resistances in the series loop. ...
... that the total resistance of this circuit is 11.3 kΩ, which happens to be equal to the sum of all of the resistances in the series loop. ...
Types Of Electrical Circuits
... from only having one path for the charges to move along. Charges must move in "series" first going to one resistor then the next. If one of the items in the circuit is broken then no charge will move through the circuit because there is only one path. There is no alternative route Parallel Circuit: ...
... from only having one path for the charges to move along. Charges must move in "series" first going to one resistor then the next. If one of the items in the circuit is broken then no charge will move through the circuit because there is only one path. There is no alternative route Parallel Circuit: ...
... f0, f < f0, and f > f0? Explain your interpretation of the spreadsheet calculation. F. Parallel RLC Circuit In this section you will consider the impedance of a parallel RLC circuit as a function of frequency. The signal generator with a resistor in series is used as a current source. Figure ...
... f0, f < f0, and f > f0? Explain your interpretation of the spreadsheet calculation. F. Parallel RLC Circuit In this section you will consider the impedance of a parallel RLC circuit as a function of frequency. The signal generator with a resistor in series is used as a current source. Figure ...
EI010 405 Electronic Instrumentation
... Module 1 (12 Hours) Measurement of electrical parameters: Types of ammeters and voltmeters – Principle of operation , construction and sources of errors and compensation of d’Arsonval galvanometers- PMMC Instruments – Moving Iron Instruments – Dynamometer type Instruments – Rectifier type ammeters a ...
... Module 1 (12 Hours) Measurement of electrical parameters: Types of ammeters and voltmeters – Principle of operation , construction and sources of errors and compensation of d’Arsonval galvanometers- PMMC Instruments – Moving Iron Instruments – Dynamometer type Instruments – Rectifier type ammeters a ...
Radiation and dual nature Electromagnetic waves Current electricity
... 3. series LCR circuit impendence resistance phase difference and phase diagram 4. resonance in LCR circuit and average power associated with LCR circuit 5. arrange power associated with inductive circuit 6. mean value of AC over complete cycle ...
... 3. series LCR circuit impendence resistance phase difference and phase diagram 4. resonance in LCR circuit and average power associated with LCR circuit 5. arrange power associated with inductive circuit 6. mean value of AC over complete cycle ...
PAWS - Western Carolina University
... One good way to lay them out is place them all in a parallel pattern, but solder them all in series on the reverse side. Solder one end to the FET gate and the other end to the FET drain. Solder connecting wires as necessary to do this. 11) Decide on a place to put DC power (3 volts) and ground. You ...
... One good way to lay them out is place them all in a parallel pattern, but solder them all in series on the reverse side. Solder one end to the FET gate and the other end to the FET drain. Solder connecting wires as necessary to do this. 11) Decide on a place to put DC power (3 volts) and ground. You ...
A SIGE LOW PHASE NOISE PUSH
... power of the signal at the fundamental frequency f 0 is below −28 dBm in the whole tuning range. This indicates a high symmetry of the fabricated push-push oscillator and a proper odd mode operation. The power consumption of the whole device is about 57 mW. The circuit has not yet been optimized for ...
... power of the signal at the fundamental frequency f 0 is below −28 dBm in the whole tuning range. This indicates a high symmetry of the fabricated push-push oscillator and a proper odd mode operation. The power consumption of the whole device is about 57 mW. The circuit has not yet been optimized for ...
View File
... Example We can calculate the theoretical highest bit rate of a regular telephone line. A telephone line normally has a bandwidth of 3000. The signal-to-noise ratio is usually 3162. For this channel the capacity is calculated as ...
... Example We can calculate the theoretical highest bit rate of a regular telephone line. A telephone line normally has a bandwidth of 3000. The signal-to-noise ratio is usually 3162. For this channel the capacity is calculated as ...