07-NileshJoshi
... System is said to be causal if the present value of the output signal depends only on the present and or the past value of the input signal. Such a system is often referred to as being nonanticipatory, as the output doesn’t anticipate future value of the input. The if the resistor and capacitor are ...
... System is said to be causal if the present value of the output signal depends only on the present and or the past value of the input signal. Such a system is often referred to as being nonanticipatory, as the output doesn’t anticipate future value of the input. The if the resistor and capacitor are ...
angle modulation
... The frequency varies. The rate of change of carrier frequency changes is the same as the frequency of the information signal. The amount of carrier frequency changes is proportional to the amplitude of the information signal. The amplitude is constant. ...
... The frequency varies. The rate of change of carrier frequency changes is the same as the frequency of the information signal. The amount of carrier frequency changes is proportional to the amplitude of the information signal. The amplitude is constant. ...
Chapter 3-Webster Amplifiers and Signal Processing
... differential voltage is multiplied by A, the gain of the op amp, to generate the output-voltage source. Any current flowing to the output terminal vo must pass through the output resistance Ro. ...
... differential voltage is multiplied by A, the gain of the op amp, to generate the output-voltage source. Any current flowing to the output terminal vo must pass through the output resistance Ro. ...
ICS843201-375 - Integrated Device Technology
... feedback divider. Frequency margining mode operation occurs when the MODE input is HIGH. The phase detector and the M divider force the VCO output frequency to be M times the reference frequency by adjusting the VCO control voltage. The output of the VCO is scaled by an output divider prior to being ...
... feedback divider. Frequency margining mode operation occurs when the MODE input is HIGH. The phase detector and the M divider force the VCO output frequency to be M times the reference frequency by adjusting the VCO control voltage. The output of the VCO is scaled by an output divider prior to being ...
EXPERIMENT #4
... waveform. What + and - output voltages does the signal get clipped at? During your work with OpAmps you should always be wary of such distortions and you may find that you need to adjust the dc offset or the amplitude of the generator if the output of the amplifier is saturating. In addition to this ...
... waveform. What + and - output voltages does the signal get clipped at? During your work with OpAmps you should always be wary of such distortions and you may find that you need to adjust the dc offset or the amplitude of the generator if the output of the amplifier is saturating. In addition to this ...
High-speed Digital Architectures
... timing and frequency signals are derived from a master clock oscillator (an exception would be the clock that drives the DSP which operates asynchronously from the rest of the system) ...
... timing and frequency signals are derived from a master clock oscillator (an exception would be the clock that drives the DSP which operates asynchronously from the rest of the system) ...
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 4.1 Introduction This
... The waveform above, figure 4.3 shows the result before run in the power amplifier circuit. Actually the form related is the output of the oscillator circuit but it was through the RC circuit, capacitor C7, 47pF and the Resistor R2, 33Kohm. The Voltage drop at the base of transistor Q6, is low compar ...
... The waveform above, figure 4.3 shows the result before run in the power amplifier circuit. Actually the form related is the output of the oscillator circuit but it was through the RC circuit, capacitor C7, 47pF and the Resistor R2, 33Kohm. The Voltage drop at the base of transistor Q6, is low compar ...
Considerations and designs for a system of tdc`s with
... square. The total number of 4-cell modules is then 11,340. There will be about 1 event every five collisions in each line of modules assuming 40 charge particles collision Data generated for each cell per event is about 5 bytes . ...
... square. The total number of 4-cell modules is then 11,340. There will be about 1 event every five collisions in each line of modules assuming 40 charge particles collision Data generated for each cell per event is about 5 bytes . ...
Microwave Engineering - Universiti Sains Malaysia
... 1. Maximize the Qu of the resonator. 2. Maximize reactive energy by means of a high RF voltage across the resonator. Use a low LC ratio. 3. Avoid device saturation and try to use anti parallel (back to back) tuning diodes. 4. Choose your active device with the lowest NF (noise figure). 5. Choose a d ...
... 1. Maximize the Qu of the resonator. 2. Maximize reactive energy by means of a high RF voltage across the resonator. Use a low LC ratio. 3. Avoid device saturation and try to use anti parallel (back to back) tuning diodes. 4. Choose your active device with the lowest NF (noise figure). 5. Choose a d ...
OpenSynth PLL - Reactance Labs
... the Reference Oscillator and VCO. Initially, these two may be running at slightly different frequencies and certainly with different phase. The Phase Detector compares the two and generates a correction signal which is amplified and then filtered by the Loop Filter, ultimately commanding the VCO to ...
... the Reference Oscillator and VCO. Initially, these two may be running at slightly different frequencies and certainly with different phase. The Phase Detector compares the two and generates a correction signal which is amplified and then filtered by the Loop Filter, ultimately commanding the VCO to ...
IDT23S08T - Integrated Device Technology
... The IDT23S08T is a high-speed phase-lock loop (PLL) clock multiplier. It is designed to address high-speed clock distribution and multiplication applications. The zero delay is achieved by aligning the phase between the incoming clock and the output clock, operable within the range of 10 to 133MHz. ...
... The IDT23S08T is a high-speed phase-lock loop (PLL) clock multiplier. It is designed to address high-speed clock distribution and multiplication applications. The zero delay is achieved by aligning the phase between the incoming clock and the output clock, operable within the range of 10 to 133MHz. ...
Chapter9-Lect1 - faraday - Eastern Mediterranean University
... (120 V at 60 Hz) versus (220 V at 50 Hz) AC In North and South America the most common available ac supply is 120 V at 60 Hz, while in Europe and the Eastern countries it is 220 V at 50 Hz. Technically there is no noticeable difference between 50 and 60 cycles per second (Hz). The effect of f ...
... (120 V at 60 Hz) versus (220 V at 50 Hz) AC In North and South America the most common available ac supply is 120 V at 60 Hz, while in Europe and the Eastern countries it is 220 V at 50 Hz. Technically there is no noticeable difference between 50 and 60 cycles per second (Hz). The effect of f ...
Sample and Hold Model 9752 Assembly and Using Manual
... Use two-circuit, Tip-Sleeve (TS or mono), cords for patching in or out of the Sample and Hold when connecting with external devices. Within a 9700-series system, either single conductor (Tip-only), or TS cords may be used. If this seems confusing, remember that a regular mono cable will always work ...
... Use two-circuit, Tip-Sleeve (TS or mono), cords for patching in or out of the Sample and Hold when connecting with external devices. Within a 9700-series system, either single conductor (Tip-only), or TS cords may be used. If this seems confusing, remember that a regular mono cable will always work ...
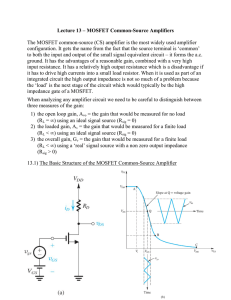
MOSFET Common Source Amplifiers
... Lecture 13 – MOSFET Common-Source Amplifiers The MOSFET common-source (CS) amplifier is the most widely used amplifier configuration. It gets the name from the fact that the source terminal is ‘common’ to both the input and output of the small signal equivalent circuit – it forms the a.c. ground. It ...
... Lecture 13 – MOSFET Common-Source Amplifiers The MOSFET common-source (CS) amplifier is the most widely used amplifier configuration. It gets the name from the fact that the source terminal is ‘common’ to both the input and output of the small signal equivalent circuit – it forms the a.c. ground. It ...
Zen I/V - First Watt
... free then you can modify or delete them. C3 and C4 capacitively couple the output so that we don't have DC arguments. R5 is simply a resistive load, which you can modify or delete if you like. C5 is the high frequency filter, which you can also modify or delete. There is no feedback. The Jfets were ...
... free then you can modify or delete them. C3 and C4 capacitively couple the output so that we don't have DC arguments. R5 is simply a resistive load, which you can modify or delete if you like. C5 is the high frequency filter, which you can also modify or delete. There is no feedback. The Jfets were ...
Lucky_Sevens_CDR_6Mar14
... Rationale A block diagram showing the high level system design can be found under Figure 1 in the appendix. LabVIEW programming along with the MyDAQ was chosen to read inputs, generate, and output an audio signal because of its usability and flexibility in design. The photodector circuits were desig ...
... Rationale A block diagram showing the high level system design can be found under Figure 1 in the appendix. LabVIEW programming along with the MyDAQ was chosen to read inputs, generate, and output an audio signal because of its usability and flexibility in design. The photodector circuits were desig ...
Discussion7
... Some After-Class Questions for you When capacitors or inductors used in AC circuits, is the current and voltage peak at the same time? Why or why not? In a linear system, does the frequency of a sinusoid convey information? Can phasor analysis be performed on multiple frequencies circuits? ...
... Some After-Class Questions for you When capacitors or inductors used in AC circuits, is the current and voltage peak at the same time? Why or why not? In a linear system, does the frequency of a sinusoid convey information? Can phasor analysis be performed on multiple frequencies circuits? ...
5 modulasi+encoding.
... – Mid bit transition is clocking only – Transition at start of a bit period represents zero – No transition at start of a bit period represents one – Used by IEEE 802.5 ...
... – Mid bit transition is clocking only – Transition at start of a bit period represents zero – No transition at start of a bit period represents one – Used by IEEE 802.5 ...
Solution for HW6 - EECS: www
... The circuit has a capacitor in series with the input, so it will be high-pass .Applying the voltage division principle, we find, H(f)=R2/(R2+R1+1/(j2 pi f C))= j 2 pi f R2 C /((R2+R1)j 2 pi f+1) =.1 j f/fB /(jf/(fB)+1) fB=1/(2 pi (R2+R1)C)=15.92Hz ...
... The circuit has a capacitor in series with the input, so it will be high-pass .Applying the voltage division principle, we find, H(f)=R2/(R2+R1+1/(j2 pi f C))= j 2 pi f R2 C /((R2+R1)j 2 pi f+1) =.1 j f/fB /(jf/(fB)+1) fB=1/(2 pi (R2+R1)C)=15.92Hz ...