Nov 2000 Infinite Sample-and-Hold Outperforms Many Legacy
... above) Nyquist (fS/2). The resulting output frequency is then the difference between the sample frequency or one of its harmonics and the input frequency. This type of sampling usually requires the bandwidth of the signal being sampled to be less than Nyquist (1/2 fS) or multiple signal components w ...
... above) Nyquist (fS/2). The resulting output frequency is then the difference between the sample frequency or one of its harmonics and the input frequency. This type of sampling usually requires the bandwidth of the signal being sampled to be less than Nyquist (1/2 fS) or multiple signal components w ...
The George Washington University School of Engineering and
... • The input passes through a simple BPF with a gain of 1. • The output of the BPF is rectified and passed through an RC filter with a time constant of 0.5ms. • Put the output across a 1Meg Ohm resistor. ...
... • The input passes through a simple BPF with a gain of 1. • The output of the BPF is rectified and passed through an RC filter with a time constant of 0.5ms. • Put the output across a 1Meg Ohm resistor. ...
Design optimizations of phase noise, power consumption and
... range, and the start-up condition is difficult to meet for small transconductance. So, further study for flicker noise reduction is needed. Flicker noise of the transistor can be reduced by switching on and off periodically, as shown in Fig. 2, which will lessen “long-term memory” physicallyŒ2; 3 . ...
... range, and the start-up condition is difficult to meet for small transconductance. So, further study for flicker noise reduction is needed. Flicker noise of the transistor can be reduced by switching on and off periodically, as shown in Fig. 2, which will lessen “long-term memory” physicallyŒ2; 3 . ...
Delta Modulation For Voice Transmission
... better than a 32kHz clock. Figure 11 shows the 10mV voice output waveform at 1/2 the clock rate, when there is no audio input. After filtering, this ...
... better than a 32kHz clock. Figure 11 shows the 10mV voice output waveform at 1/2 the clock rate, when there is no audio input. After filtering, this ...
EE 233 Circuit Theory Lab 3: Simple Filters
... The objectives of this lab are to understand the Bode plots of electronic circuits, such as integrators and differentiators, learn SPICE simulation to design electronic circuits, and analyze and measure characteristics of simple analog amplifiers built with op-amps. The circuits that are built in th ...
... The objectives of this lab are to understand the Bode plots of electronic circuits, such as integrators and differentiators, learn SPICE simulation to design electronic circuits, and analyze and measure characteristics of simple analog amplifiers built with op-amps. The circuits that are built in th ...
Performance of Electronic Dispersion Compensation for Multi-Level
... scheme is according to [1] and adapted to RZ-8DPSK and star RZ-16-DQAM modulation. Results and discussion Fig. 4 depicts CD versus OSNR penalty at a BER of 10-4 for the investigated modulation formats without EDC. The approximated residual dispersion tolerance for 2 dB OSNR penalty is displayed in ...
... scheme is according to [1] and adapted to RZ-8DPSK and star RZ-16-DQAM modulation. Results and discussion Fig. 4 depicts CD versus OSNR penalty at a BER of 10-4 for the investigated modulation formats without EDC. The approximated residual dispersion tolerance for 2 dB OSNR penalty is displayed in ...
UT7R995 Clock Generator - Aeroflex Microelectronic Solutions
... XTAL1 and XTAL2 are the input and output, respectively, of an inverting amplifier within the UT7R995C. This inverting amplifier provides the initial 180o phase shift of the reference clock whose frequency, and subsequent 180o phase shift, is set by the quartz crystal and its surrounding RLC network. ...
... XTAL1 and XTAL2 are the input and output, respectively, of an inverting amplifier within the UT7R995C. This inverting amplifier provides the initial 180o phase shift of the reference clock whose frequency, and subsequent 180o phase shift, is set by the quartz crystal and its surrounding RLC network. ...
HWS400 - Hexawave
... The HWS400 is a GaAs MMIC SPDT terminated (non-reflective) switch in a low cost QFN12L (3x3 mm) plastic package and can be used in both 50 ohm and 75 ohm systems. The HWS400 features low insertion loss and high isolation with very low DC ...
... The HWS400 is a GaAs MMIC SPDT terminated (non-reflective) switch in a low cost QFN12L (3x3 mm) plastic package and can be used in both 50 ohm and 75 ohm systems. The HWS400 features low insertion loss and high isolation with very low DC ...
Chapter 4 - UniMAP Portal
... • RLC determine the resonant frequency • The crystal has a low impedance Parallel resonant condition • RLC and CM determine the resonant frequency • The crystal has a high impedance The series and parallel resonant frequencies are very close, within 1% of each other. ...
... • RLC determine the resonant frequency • The crystal has a low impedance Parallel resonant condition • RLC and CM determine the resonant frequency • The crystal has a high impedance The series and parallel resonant frequencies are very close, within 1% of each other. ...
A 4.3 GHz BiCMOS VCO with multiple 360° method
... scl ≈ 10 cm/s, I C is the collector current of each of the transistors Q1–Q4 in Fig. 3, V T is the thermal voltage at room temperature and W is measured in m. Inductors L1–L2 and L3–L4 were implemented on-chip using two differential spiral inductors provided by the Austriamicrosystems (AMS) foundry ...
... scl ≈ 10 cm/s, I C is the collector current of each of the transistors Q1–Q4 in Fig. 3, V T is the thermal voltage at room temperature and W is measured in m. Inductors L1–L2 and L3–L4 were implemented on-chip using two differential spiral inductors provided by the Austriamicrosystems (AMS) foundry ...
TRANSPAK T761 ™ AC Input Isolating Field Configurable
... The T761 has 12 widely adjustable input ranges and 2 output ranges, all of which are field selectable via top-accessed DIP switches. The T761 provides 600 VDC of isolation with outputs of either 4-20mA or 10-50mA. The current outputs are in proportion to selected AC voltage or current input. The T76 ...
... The T761 has 12 widely adjustable input ranges and 2 output ranges, all of which are field selectable via top-accessed DIP switches. The T761 provides 600 VDC of isolation with outputs of either 4-20mA or 10-50mA. The current outputs are in proportion to selected AC voltage or current input. The T76 ...
2 Impedance and Transfer Functions
... Filters are mostly used for eliminating noise, so to see them in action we need to create a noisy signal. This can be achieved by adding a high frequency signal from the function generator to a 60 Hz signal derived from the wall power lines. To start, locate the 6.3 V transformer and plug it in. Obs ...
... Filters are mostly used for eliminating noise, so to see them in action we need to create a noisy signal. This can be achieved by adding a high frequency signal from the function generator to a 60 Hz signal derived from the wall power lines. To start, locate the 6.3 V transformer and plug it in. Obs ...
ICS252 - Integrated Device Technology
... applications where the clock is driving a component with a maximum frequency rating, down spread should be applied. In this case, the maximum frequency, including modulation, is the target frequency. The effective average frequency is less than the target frequency. The ICS252 operates in both cente ...
... applications where the clock is driving a component with a maximum frequency rating, down spread should be applied. In this case, the maximum frequency, including modulation, is the target frequency. The effective average frequency is less than the target frequency. The ICS252 operates in both cente ...
Section_6_-_Summary_
... wide range of output frequencies, give a comprehensive insight in the complex behaviour of interharmonic component frequencies; also some characteristic aspects, such as the degeneration in harmonics or the overlapping of an interharmonic couple of different origins, are described. Although it is we ...
... wide range of output frequencies, give a comprehensive insight in the complex behaviour of interharmonic component frequencies; also some characteristic aspects, such as the degeneration in harmonics or the overlapping of an interharmonic couple of different origins, are described. Although it is we ...
Phase-locked-loop with lock detector
... Phase-locked-loop with lock detector waveforms for the PC1 loop locked at fo are shown in Fig.7. The frequency capture range (2fc) is defined as the frequency range of input signals on which the PLL will lock if it was initially out-of-lock. The frequency lock range (2fL) is defined as the frequency ...
... Phase-locked-loop with lock detector waveforms for the PC1 loop locked at fo are shown in Fig.7. The frequency capture range (2fc) is defined as the frequency range of input signals on which the PLL will lock if it was initially out-of-lock. The frequency lock range (2fL) is defined as the frequency ...
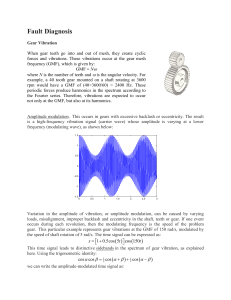
Fault Diagnosis
... frequency (GMF), which is given by: GMF N where N is the number of teeth and is the angular velocity. For example, a 40 tooth gear mounted on a shaft rotating at 3600 rpm would have a GMF of (40×3600/60) = 2400 Hz. These periodic forces produce harmonics in the spectrum according to the Fourier ...
... frequency (GMF), which is given by: GMF N where N is the number of teeth and is the angular velocity. For example, a 40 tooth gear mounted on a shaft rotating at 3600 rpm would have a GMF of (40×3600/60) = 2400 Hz. These periodic forces produce harmonics in the spectrum according to the Fourier ...