INA260 Precision Current and Power Monitor with Low
... The INA260 is a digital-output, current, power, and voltage monitor with an I2C and SMBus™-compatible interface with an integrated precision shunt resistor. It enables high-accuracy current and power measurements and over-current detection at common-mode voltages that can vary from 0 V to 36 V, inde ...
... The INA260 is a digital-output, current, power, and voltage monitor with an I2C and SMBus™-compatible interface with an integrated precision shunt resistor. It enables high-accuracy current and power measurements and over-current detection at common-mode voltages that can vary from 0 V to 36 V, inde ...
Scheme of work
... component be calculated using the current and potential difference? Why does increasing the potential difference in a circuit also increase the current? What is meant by resistance? Find the resistance of some electrical components using current and potential difference readings. ...
... component be calculated using the current and potential difference? Why does increasing the potential difference in a circuit also increase the current? What is meant by resistance? Find the resistance of some electrical components using current and potential difference readings. ...
MAX1182 Dual 10-Bit, 65Msps, 3V, Low-Power ADC General Description
... The MAX1182 is a 3V, dual 10-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC) featuring fully-differential wideband trackand-hold (T/H) inputs, driving two pipelined, 9-stage ADCs. The MAX1182 is optimized for low-power, highdynamic performance applications in imaging, instrumentation and digital communication ...
... The MAX1182 is a 3V, dual 10-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC) featuring fully-differential wideband trackand-hold (T/H) inputs, driving two pipelined, 9-stage ADCs. The MAX1182 is optimized for low-power, highdynamic performance applications in imaging, instrumentation and digital communication ...
Steady-State Response of RC Circuit to Periodic Square Wave Input
... If the resistor in the circuit is disconnected, R → ∞; then the system becomes lossless and every push results in a potential increment of C1 tON volts for the capacitor. The system for R → ∞ is a perfect integrator. The response is unbounded (see Figure 2). When the resistance is placed back into t ...
... If the resistor in the circuit is disconnected, R → ∞; then the system becomes lossless and every push results in a potential increment of C1 tON volts for the capacitor. The system for R → ∞ is a perfect integrator. The response is unbounded (see Figure 2). When the resistance is placed back into t ...
Converting the galvanometer into an ammeter: Rs
... Compare the readings of the home made and commercial ammeters and find their percentage difference. List your calculations in the previous table. ...
... Compare the readings of the home made and commercial ammeters and find their percentage difference. List your calculations in the previous table. ...
A Resistively Degenerated Wide-Band Passive Mixer with Low
... be perfectly separated, due to mismatches in the Mixer cores. All mismatch factors can be modeled and referred to a gate voltage difference, so that the turn-on resistance will be different. This could cause strong second-order distortion in passive Mixers. By adding Rdeg, the current split can be m ...
... be perfectly separated, due to mismatches in the Mixer cores. All mismatch factors can be modeled and referred to a gate voltage difference, so that the turn-on resistance will be different. This could cause strong second-order distortion in passive Mixers. By adding Rdeg, the current split can be m ...
MAX1444 10-Bit, 40Msps, 3.0V, Low-Power ADC with Internal Reference General Description
... differential signal path. This ADC is optimized for lowpower, high dynamic performance applications in imaging and digital communications. The MAX1444 operates from a single 2.7V to 3.6V supply, consuming only 57mW while delivering a 59.5dB signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) at a 20MHz input frequency. The ...
... differential signal path. This ADC is optimized for lowpower, high dynamic performance applications in imaging and digital communications. The MAX1444 operates from a single 2.7V to 3.6V supply, consuming only 57mW while delivering a 59.5dB signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) at a 20MHz input frequency. The ...
Cookbook for SAR ADC measurements
... not dependent just on ADC clock. User can select from various options dependent on ADLSMP bit in ADCx_CFG1 register and ADLSTS bits in ADCx_CFG2 register. In such case, the total conversion time is not significantly affected by increased acquisition time. This feature is particularly useful in case ...
... not dependent just on ADC clock. User can select from various options dependent on ADLSMP bit in ADCx_CFG1 register and ADLSTS bits in ADCx_CFG2 register. In such case, the total conversion time is not significantly affected by increased acquisition time. This feature is particularly useful in case ...
General Description Features
... Electrical Characteristics (continued) (ISHUNT = 1mA, CL = 0.1µF, TA = -40°C to +85°C, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA = +25°C.) ...
... Electrical Characteristics (continued) (ISHUNT = 1mA, CL = 0.1µF, TA = -40°C to +85°C, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA = +25°C.) ...
Short Circuits Volume 1 by Jaycar Electronics
... Once power is applied, a complete circuit is made and current flows from the battery positive terminal, through the resistor, through the LED and its internal circuitry and then back out to the battery negative terminal. ...
... Once power is applied, a complete circuit is made and current flows from the battery positive terminal, through the resistor, through the LED and its internal circuitry and then back out to the battery negative terminal. ...
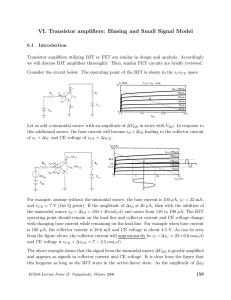
MOSFET Small Signal Model and Analysis •Just as we did
... go is internal to the transistor and can not be avoided. Any additional resistor due to external circuitry will lower the gain. For this reason current sources are often used as the “load” instead of bias resistors in amplifier circuits. ...
... go is internal to the transistor and can not be avoided. Any additional resistor due to external circuitry will lower the gain. For this reason current sources are often used as the “load” instead of bias resistors in amplifier circuits. ...
MAX15014–MAX15017 1A, 4.5V to 40V Input Buck Converters with General Description
... LDO_OUT Output Current.................................Internally Limited Switch DC Current (DRAIN and LX pins combined) TJ = +125°C.......................................................................1.9A TJ = +150°C.....................................................................1.25A ...
... LDO_OUT Output Current.................................Internally Limited Switch DC Current (DRAIN and LX pins combined) TJ = +125°C.......................................................................1.9A TJ = +150°C.....................................................................1.25A ...
MAX3051 +3.3V, 1Mbps, Low-Supply-Current CAN Transceiver General Description
... 500kbps. Controlling the rise and fall slopes reduces EMI and allows the use of an unshielded twisted pair or a parallel pair of wires as bus lines. The equation for selecting the resistor value is given by: ...
... 500kbps. Controlling the rise and fall slopes reduces EMI and allows the use of an unshielded twisted pair or a parallel pair of wires as bus lines. The equation for selecting the resistor value is given by: ...
MAX1181 Dual 10-Bit, 80Msps, 3V, Low-Power ADC General Description
... An internal 2.048V precision bandgap reference sets the full-scale range of the ADC. A flexible reference structure allows the use of the internal or external reference, if desired for applications requiring increased accuracy or a different input voltage range. The MAX1181 features parallel, CMOS-c ...
... An internal 2.048V precision bandgap reference sets the full-scale range of the ADC. A flexible reference structure allows the use of the internal or external reference, if desired for applications requiring increased accuracy or a different input voltage range. The MAX1181 features parallel, CMOS-c ...
Chapter 2: Resistive Circuits
... the framework of simple networks. Our approach here is to begin with the simplest passive element, the resistor, and the mathematical relationship that exists between the voltage across it and the current through it, as specified by Ohm’s law. As we build our confidence and proficiency by successful ...
... the framework of simple networks. Our approach here is to begin with the simplest passive element, the resistor, and the mathematical relationship that exists between the voltage across it and the current through it, as specified by Ohm’s law. As we build our confidence and proficiency by successful ...
Variable Frequency Drive / Inverter
... P gain for PID control 0 to 999.9[%] I gain for PID control 0.1 to 32.0[sec] D gain for PID control 0.1 to 30.0[sec] F gain for PID control 0 to 999.9[%] Limit frequency for PID control 0 to Max. frequency[Hz] ...
... P gain for PID control 0 to 999.9[%] I gain for PID control 0.1 to 32.0[sec] D gain for PID control 0.1 to 30.0[sec] F gain for PID control 0 to 999.9[%] Limit frequency for PID control 0 to Max. frequency[Hz] ...
General Description Features
... Note 2: Junction temperature TJ = TC + (θJC x VCC x ICC). This formula can only be used if the component is soldered down to a printed circuit board pad containing multiple ground vias to remove the heat. The junction temperature must not exceed 150°C. Note 3: Package thermal resistances were obtain ...
... Note 2: Junction temperature TJ = TC + (θJC x VCC x ICC). This formula can only be used if the component is soldered down to a printed circuit board pad containing multiple ground vias to remove the heat. The junction temperature must not exceed 150°C. Note 3: Package thermal resistances were obtain ...
Lab E4: B-field of a Solenoid
... indicate an average. The voltage V alternates (+) and (-) so the average voltage V is zero, but the voltage-squared V2 is always positive so the average of V2 is non-zero and positive. If V(t) is a sinusoid, then it turns out that the rms amplitude Vrms and the amplitude Vo are related by Vo = 2 Vrm ...
... indicate an average. The voltage V alternates (+) and (-) so the average voltage V is zero, but the voltage-squared V2 is always positive so the average of V2 is non-zero and positive. If V(t) is a sinusoid, then it turns out that the rms amplitude Vrms and the amplitude Vo are related by Vo = 2 Vrm ...
Vacuum switching - Schneider Electric
... level, and for vacuum below this level. However, the difference in cost remains low, which explains how the two offers, vacuum and SF6, can coexist, for all medium voltage levels from 7.2 to 36 kV. ...
... level, and for vacuum below this level. However, the difference in cost remains low, which explains how the two offers, vacuum and SF6, can coexist, for all medium voltage levels from 7.2 to 36 kV. ...
General Description Benefits and Features
... These op amps are designed to be part of the PA control circuitry, biasing RF PAs in wireless headsets. The MAX4231/ MAX4233 offer a SHDN feature that drives the output low. This ensures that the RF PA is fully disabled when needed, preventing unconverted signals to the RF antenna. The MAX4230 famil ...
... These op amps are designed to be part of the PA control circuitry, biasing RF PAs in wireless headsets. The MAX4231/ MAX4233 offer a SHDN feature that drives the output low. This ensures that the RF PA is fully disabled when needed, preventing unconverted signals to the RF antenna. The MAX4230 famil ...
Lab E4: B-field of a Solenoid
... 120V. What is the peak value or amplitude of this voltage? 6. The earth’s magnetic field is about 0.5 gauss. The SI unit of magnetic field is the tesla (T) [1 Tesla = 10,000 gauss] . A probe coil with N = 10,000 turns and area A 10 cm 2 is oriented with the coil perpendicular to the earth’s field. ...
... 120V. What is the peak value or amplitude of this voltage? 6. The earth’s magnetic field is about 0.5 gauss. The SI unit of magnetic field is the tesla (T) [1 Tesla = 10,000 gauss] . A probe coil with N = 10,000 turns and area A 10 cm 2 is oriented with the coil perpendicular to the earth’s field. ...