Sub-uHz MOSFET 1/f noise measurements
... However, the transistors are located close to each other on the same die and share the same temperature. Therefore the DIT term is correlated across the two transistors, while the DIn term is not. MOSFET currents depend polynomially on temperature via two parameters: threshold voltage and carrier mo ...
... However, the transistors are located close to each other on the same die and share the same temperature. Therefore the DIT term is correlated across the two transistors, while the DIn term is not. MOSFET currents depend polynomially on temperature via two parameters: threshold voltage and carrier mo ...
Physics 270, Assignment 4
... We now want the equivalent resistance between the points a and b in the …gure. We can model the system as three resistors in parallel. The top wire con…guration has three resistors in series and therefore an equivalent resistance of Rt = 3 (100 ) = 300 . The middle wire has only two resistors in ser ...
... We now want the equivalent resistance between the points a and b in the …gure. We can model the system as three resistors in parallel. The top wire con…guration has three resistors in series and therefore an equivalent resistance of Rt = 3 (100 ) = 300 . The middle wire has only two resistors in ser ...
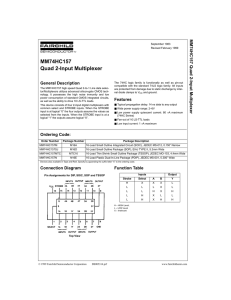
74HC157 pdf
... 2. A critical component in any component of a life support 1. Life support devices or systems are devices or systems device or system whose failure to perform can be reawhich, (a) are intended for surgical implant into the sonably expected to cause the failure of the life support body, or (b) suppor ...
... 2. A critical component in any component of a life support 1. Life support devices or systems are devices or systems device or system whose failure to perform can be reawhich, (a) are intended for surgical implant into the sonably expected to cause the failure of the life support body, or (b) suppor ...
Chapter28
... Topics Covered in Chapter 28 28-1: Transistor Construction 28-2: Proper Transistor Biasing ...
... Topics Covered in Chapter 28 28-1: Transistor Construction 28-2: Proper Transistor Biasing ...
Electrical Indicating Devices
... Clamp-on meters make for quick and safe current measurements. ...
... Clamp-on meters make for quick and safe current measurements. ...
Low Power Pulse Width Modulator
... providing pulse-by-pulse overcurrent control for excessive loads. This comparator also causes CF to be charged for the remainder of the clock cycle. The charging current is ...
... providing pulse-by-pulse overcurrent control for excessive loads. This comparator also causes CF to be charged for the remainder of the clock cycle. The charging current is ...
DATASHEET SEARCH SITE | WWW.ALLDATASHEET.COM
... No technical content pages of this document may be reproduced in any form or transmitted by any means without prior permission of ROHM CO.,LTD. The contents described herein are subject to change without notice. The specifications for the product described in this document are for reference only. Up ...
... No technical content pages of this document may be reproduced in any form or transmitted by any means without prior permission of ROHM CO.,LTD. The contents described herein are subject to change without notice. The specifications for the product described in this document are for reference only. Up ...
1 - turboecelegends
... current mirror. For its analysis, we assume identical transistors and neglect the Early effect, i.e. we assume VA → ∞. This makes the saturation current IS and current gain β independent of the collector base voltage VCE . The input current to the mirror is labeled IREF . This current might come fro ...
... current mirror. For its analysis, we assume identical transistors and neglect the Early effect, i.e. we assume VA → ∞. This makes the saturation current IS and current gain β independent of the collector base voltage VCE . The input current to the mirror is labeled IREF . This current might come fro ...
Transient Analysis of Electrical Circuits Using Runge
... harmonic oscillator for current and will resonate in a similar way as an LC circuit will. The main difference that the presence of the resistor makes is that any oscillation induced in the circuit will die away over time if it is not kept going by a source. This effect of the resistor is called damp ...
... harmonic oscillator for current and will resonate in a similar way as an LC circuit will. The main difference that the presence of the resistor makes is that any oscillation induced in the circuit will die away over time if it is not kept going by a source. This effect of the resistor is called damp ...
AD8215 - Analog Devices
... voltage directly interfaces with any typical converter. Excellent common-mode rejection from −2 V to +65 V is independent of the 5 V supply. The AD8215 performs unidirectional current measurements across a shunt resistor in a variety of industrial and automotive applications, such as motor controls, ...
... voltage directly interfaces with any typical converter. Excellent common-mode rejection from −2 V to +65 V is independent of the 5 V supply. The AD8215 performs unidirectional current measurements across a shunt resistor in a variety of industrial and automotive applications, such as motor controls, ...
MAX8569A/MAX8569B 200mA Step-Up Converters in 6-Pin SOT23 and TDFN General Description
... The MAX8569A and MAX8569B compact high-efficiency step-up converters feature low-quiescent supply current to ensure the highest possible efficiency over a wide load range. With a minimum 1.5V input voltage, these devices are well suited for applications with two alkaline cells, two nickel-metal-hydr ...
... The MAX8569A and MAX8569B compact high-efficiency step-up converters feature low-quiescent supply current to ensure the highest possible efficiency over a wide load range. With a minimum 1.5V input voltage, these devices are well suited for applications with two alkaline cells, two nickel-metal-hydr ...
Reading 5 SERIES CIRCUITS When components in a
... The sum of the voltage drops in a series circuit is equal to the applied voltage. Going back to figure 1, we have three resistances R1, R2 and R3 in series, connected to a 10 volt supply. We can calculate the voltage across R1 because we know the resistance and we know the current through R1. Let's ...
... The sum of the voltage drops in a series circuit is equal to the applied voltage. Going back to figure 1, we have three resistances R1, R2 and R3 in series, connected to a 10 volt supply. We can calculate the voltage across R1 because we know the resistance and we know the current through R1. Let's ...
COURSE SYLLABUS GUIDE
... Attendance and Punctuality – Effect on Grade Student must maintain 60% or higher on quiz grades, to pass, no matter what the overall average is. Instructor also may adjust the grade up or down based on attendance and punctuality. Any student who misses more than the equivalent of 5 class sessions wi ...
... Attendance and Punctuality – Effect on Grade Student must maintain 60% or higher on quiz grades, to pass, no matter what the overall average is. Instructor also may adjust the grade up or down based on attendance and punctuality. Any student who misses more than the equivalent of 5 class sessions wi ...
Series Circuits
... The sum of the voltage drops in a series circuit is equal to the applied voltage. Going back to figure 1, we have three resistances R1, R2 and R3 in series, connected to a 10 volt supply. We can calculate the voltage across R1 because we know the resistance and we know the current through R1. Let's ...
... The sum of the voltage drops in a series circuit is equal to the applied voltage. Going back to figure 1, we have three resistances R1, R2 and R3 in series, connected to a 10 volt supply. We can calculate the voltage across R1 because we know the resistance and we know the current through R1. Let's ...
Document
... The frequency of the mains voltage is 50 Hz. The current i1 splits at the node to form the currents i2 and i3. All the current waveforms are sinusoidal; however i1 and i2 have a phase angle between them of 90 degrees. The amplitudes of the currents i1 and i2 are √3 Amps and 1 Amp respectively. ...
... The frequency of the mains voltage is 50 Hz. The current i1 splits at the node to form the currents i2 and i3. All the current waveforms are sinusoidal; however i1 and i2 have a phase angle between them of 90 degrees. The amplitudes of the currents i1 and i2 are √3 Amps and 1 Amp respectively. ...
EE1000 Spring 2015, Lecture 3 (January 20, 2015)
... A parallel circuit is a circuit in which the resistors are arranged with their heads connected together, and their tails connected together. The current in a parallel circuit breaks up, with some flowing along each parallel branch and re-combining when the branches meet again. The voltage across eac ...
... A parallel circuit is a circuit in which the resistors are arranged with their heads connected together, and their tails connected together. The current in a parallel circuit breaks up, with some flowing along each parallel branch and re-combining when the branches meet again. The voltage across eac ...
+ + + + + + + + Space charge region
... recombine near the junction and disappear. The uncompensated Acceptor and Donor ions set up an Electric field which halts majority carrier Diffusion and causes minority carrier Drift. The two kinds of majority carriers diffusing across the junction meet each other near the junction and undergo recom ...
... recombine near the junction and disappear. The uncompensated Acceptor and Donor ions set up an Electric field which halts majority carrier Diffusion and causes minority carrier Drift. The two kinds of majority carriers diffusing across the junction meet each other near the junction and undergo recom ...