6-1-Periodic Law
... It was found that if Mendeleev's table was ordered by atomic number instead of atomic mass the inconsistencies in the table were eliminated. This is the blueprint for the modern periodic table. ...
... It was found that if Mendeleev's table was ordered by atomic number instead of atomic mass the inconsistencies in the table were eliminated. This is the blueprint for the modern periodic table. ...
Review Packet
... scientist has made a mistake? Hint: How does the number of electrons change as you move from left to right across a period? ...
... scientist has made a mistake? Hint: How does the number of electrons change as you move from left to right across a period? ...
Name Date Class ORGANIZING THE ELEMENTS Section Review
... Use this completion exercise to check your understanding of the concepts and terms that are introduced in this section. Each blank can be completed with a term, short phrase, or number. Chemists used the _______ of elements to sort them into ...
... Use this completion exercise to check your understanding of the concepts and terms that are introduced in this section. Each blank can be completed with a term, short phrase, or number. Chemists used the _______ of elements to sort them into ...
Document
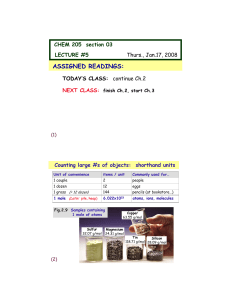
... How many atoms of carbon are in your pencil’s “lead”, which is GRAPHITE, C(s) ? • Estimate: 7.0 g of graphite, C(s) • Atomic mass: C = 12.01 g/mol ...
... How many atoms of carbon are in your pencil’s “lead”, which is GRAPHITE, C(s) ? • Estimate: 7.0 g of graphite, C(s) • Atomic mass: C = 12.01 g/mol ...
Periodic Table - MunterChemistry
... – As the nuclear charge increases, the electrons are held more tightly ...
... – As the nuclear charge increases, the electrons are held more tightly ...
File - Ricci Math and Science
... Matching ___ 9. Group of metals that have two (2) valence electrons. ___ 10. Very reactive nonmetals that include iodine. ...
... Matching ___ 9. Group of metals that have two (2) valence electrons. ___ 10. Very reactive nonmetals that include iodine. ...
4.1 Vocabulary
... An atom of iron contains 26 protons, so the atomic number of iron is 26. Atomic number is used in identifying atoms. element a pure substance made of only one type of atom Copper, helium, calcium, and neon are all types of elements. Each element is made up of one kind of atom. A copper atom is diffe ...
... An atom of iron contains 26 protons, so the atomic number of iron is 26. Atomic number is used in identifying atoms. element a pure substance made of only one type of atom Copper, helium, calcium, and neon are all types of elements. Each element is made up of one kind of atom. A copper atom is diffe ...
Chapter 12: Chemical Periodicity
... predict the existence of other elements. Experimentation continued and improved. By 1940 all 90 naturally occurring elements had been discovered. Since then work in nuclear science has led to the discovery of radioactive elements. Only about one quarter of the elements occur in the free (or elementa ...
... predict the existence of other elements. Experimentation continued and improved. By 1940 all 90 naturally occurring elements had been discovered. Since then work in nuclear science has led to the discovery of radioactive elements. Only about one quarter of the elements occur in the free (or elementa ...
The Periodic Table
... • there are 7 periods • the periods correspond with the number of electron shells or energy levels • As you go from left to right across a period, the number of protons (atomic number) increases by 1. ...
... • there are 7 periods • the periods correspond with the number of electron shells or energy levels • As you go from left to right across a period, the number of protons (atomic number) increases by 1. ...
Unit 2 - Periodic Behavior and Ionic Bonding
... 2. Metals have characteristically low electronegativity a. Lowest in the lower left corner of the table 3. Electronegativity tends to increase across a period 4. Electronegativity tends to decrease down a group of main-group elements ...
... 2. Metals have characteristically low electronegativity a. Lowest in the lower left corner of the table 3. Electronegativity tends to increase across a period 4. Electronegativity tends to decrease down a group of main-group elements ...
2.2 Periodic Chart
... distinctive colours (Ne is reddish) when electricity is passed through them. Their ion charges of zero indicate that they do not form charged ions. ...
... distinctive colours (Ne is reddish) when electricity is passed through them. Their ion charges of zero indicate that they do not form charged ions. ...
Chapter 5 Review Sheet Be sure to study the following vocabulary
... Halogens- the elements in Group 17 of the periodic table; they are very reactive nonmetals; their atoms have 7 valence electrons Noble Gases- The elements in Group 18 of the periodic table; they are unreactive nonmetals; their outer energy level is full Atomic mass- number of protons and number of n ...
... Halogens- the elements in Group 17 of the periodic table; they are very reactive nonmetals; their atoms have 7 valence electrons Noble Gases- The elements in Group 18 of the periodic table; they are unreactive nonmetals; their outer energy level is full Atomic mass- number of protons and number of n ...
KEY - Unit 4 - Find Someone Who
... 4. Define ionization energy. Amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom ...
... 4. Define ionization energy. Amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom ...
Ch 2 Test Review part 2
... 17. Which statement describes how melting point changes across a period on the periodic table? a. Melting point gradually decreases. b. Melting point gradually increases. c. Melting point decreases and then increases. d. Melting point increases and then decreases. 18. Which of the foll ...
... 17. Which statement describes how melting point changes across a period on the periodic table? a. Melting point gradually decreases. b. Melting point gradually increases. c. Melting point decreases and then increases. d. Melting point increases and then decreases. 18. Which of the foll ...
Periodic Table Timeline
... He also discusses some of the earliest ideas of atoms, molecules, and chemical reactions marking the beginning of the history of modern chemistry. ...
... He also discusses some of the earliest ideas of atoms, molecules, and chemical reactions marking the beginning of the history of modern chemistry. ...
Chapter 4 Notes - Riverton High School
... They are never found uncombined in nature. They have two valence electrons. Alkaline earth metals include magnesium and calcium, among others. ...
... They are never found uncombined in nature. They have two valence electrons. Alkaline earth metals include magnesium and calcium, among others. ...
Recording Measurements
... Chemical Properties Ionization ElectroElectrons energy negativity Low High Low High Lose Gain ...
... Chemical Properties Ionization ElectroElectrons energy negativity Low High Low High Lose Gain ...
Honors Chemistry- Chapter 5 Homework Packet The Periodic Law
... 2) What is the relationship between the electron configuration of an element and the period in which that element appears on the periodic table? ...
... 2) What is the relationship between the electron configuration of an element and the period in which that element appears on the periodic table? ...
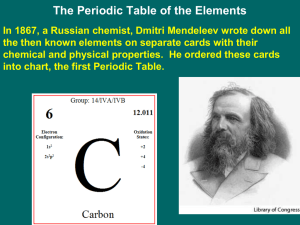
The Periodic Law (Unit #5) Study Guide 1. Who is credited with
... 1. Who is credited with developing the first successful periodic table? __Mendeleev_________ 2. This person used atomic _mass_____ and _properties___ of elements to arrange the elements in periodic order. 3. Henry Moseley found that elements in the periodic table fit into patterns better when arrang ...
... 1. Who is credited with developing the first successful periodic table? __Mendeleev_________ 2. This person used atomic _mass_____ and _properties___ of elements to arrange the elements in periodic order. 3. Henry Moseley found that elements in the periodic table fit into patterns better when arrang ...
The periodic table
... elements according to atomic mass only produced problems. Elements that should have been grouped ...
... elements according to atomic mass only produced problems. Elements that should have been grouped ...
Questions on The Periodic Table
... accurate atomic weights determined? Give examples. 7.What are the three particles making up the atom, their mass, charge and location? 8. What is the mass number of an atom? 9. What is the atomic number of an atom and why is it important? 10. What are isotopes? Give an example. 11. What is the basis ...
... accurate atomic weights determined? Give examples. 7.What are the three particles making up the atom, their mass, charge and location? 8. What is the mass number of an atom? 9. What is the atomic number of an atom and why is it important? 10. What are isotopes? Give an example. 11. What is the basis ...
Chapter 5 student
... of elements in those groups. • Predict the reactivity of some elements based on their locations within a group. • Identify some properties of common A group elements. ...
... of elements in those groups. • Predict the reactivity of some elements based on their locations within a group. • Identify some properties of common A group elements. ...
View PDF
... a. atomic number. b. atomic mass. c. mass number. d. atomic mass unit. 5. How is the atomic mass of an element determined? a. Average the atomic masses of all its isotopes. b. Use the atomic mass of the most abundant isotope. c. Take a weighted average of the masses of the isotopes present in nature ...
... a. atomic number. b. atomic mass. c. mass number. d. atomic mass unit. 5. How is the atomic mass of an element determined? a. Average the atomic masses of all its isotopes. b. Use the atomic mass of the most abundant isotope. c. Take a weighted average of the masses of the isotopes present in nature ...