What Shapes the Local Universe Galaxy Luminosity Function?
... spirals should be blue and the majority of ellip3cals and len3culars should be red. Previous studies of local luminosity func3ons with morphology-‐selected samples have largely produced conflic3ng ...
... spirals should be blue and the majority of ellip3cals and len3culars should be red. Previous studies of local luminosity func3ons with morphology-‐selected samples have largely produced conflic3ng ...
PH607 – Galaxies
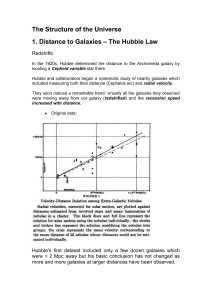
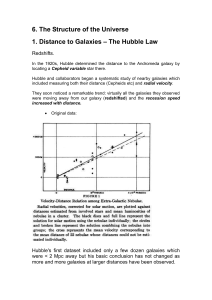
... and Ho is essentially an inverse Hubble time. Can define a Hubble length: c / H0 ~ 4000 Mpc at which this expression for the recession velocity extrapolates to the speed of light - more detailed relativistic treatment is needed for distances of this order. Can also define a Hubble time: 1 / H0 ~ 101 ...
... and Ho is essentially an inverse Hubble time. Can define a Hubble length: c / H0 ~ 4000 Mpc at which this expression for the recession velocity extrapolates to the speed of light - more detailed relativistic treatment is needed for distances of this order. Can also define a Hubble time: 1 / H0 ~ 101 ...
Molecular Gas in Nearby Dwarf Galaxies:
... Correlations with B-K could arise from enhanced photodissociation/less dust in bluer systems… …but systems with no CO tend to be underluminous (for their mass) in K-band, not overluminous in B-band ...
... Correlations with B-K could arise from enhanced photodissociation/less dust in bluer systems… …but systems with no CO tend to be underluminous (for their mass) in K-band, not overluminous in B-band ...
The Milky Way Galaxy - Academic Computer Center
... Jupiter’s orbit but with a This is called a supermassive mass several million times black hole. Most other galaxies the mass of the Sun. are also thought to have these huge • Since so little light is visible black holes in their centers. from this object it is thought to be a very large black hole. ...
... Jupiter’s orbit but with a This is called a supermassive mass several million times black hole. Most other galaxies the mass of the Sun. are also thought to have these huge • Since so little light is visible black holes in their centers. from this object it is thought to be a very large black hole. ...
The Milky Way - National Tsing Hua University
... There are billions of the galaxies in the sky, and astronomers can’t study every one. Rather they must use statistical evidence, and that raises a common question about the scientific method: • If statistics isn’t certainty, how can scientists use it to ...
... There are billions of the galaxies in the sky, and astronomers can’t study every one. Rather they must use statistical evidence, and that raises a common question about the scientific method: • If statistics isn’t certainty, how can scientists use it to ...
A bright, dust-obscured, millimetre
... Accepted 2008 July 29. Received 2008 July 24; in original form 2008 March 24 ...
... Accepted 2008 July 29. Received 2008 July 24; in original form 2008 March 24 ...
Answers - Physics
... Cold, Warm, Hot Density: Lowest is Hot, then Warm, then Cold is densest. Tempt: Hot is hottest, then Warm, then Cold is coldest (have to give you some easy points) For the circle of life the gas starts at the Hot phase after the death of a massive star. That gas slowly cools with time until it is th ...
... Cold, Warm, Hot Density: Lowest is Hot, then Warm, then Cold is densest. Tempt: Hot is hottest, then Warm, then Cold is coldest (have to give you some easy points) For the circle of life the gas starts at the Hot phase after the death of a massive star. That gas slowly cools with time until it is th ...
Discussion Session A: “Evidence”
... • A) Correla8ons between nuclear SFR and instantaneous LAGN • B) Correla8on of SFR and average LAGN (or BH accre8on rate) • C) Increased AGN frac'on in SF galaxies • D) Radio AGN are associated ...
... • A) Correla8ons between nuclear SFR and instantaneous LAGN • B) Correla8on of SFR and average LAGN (or BH accre8on rate) • C) Increased AGN frac'on in SF galaxies • D) Radio AGN are associated ...
Searching for Planets During Predicted Mesolensing Events: II
... probability of an event occurring is very low. In addition, detection can be made challenging through the “dazzling by the light of the much nearer star”, the lens. Einstein’s doubts have not deterred astronomers, with their familiarity of the universe of possible lenses and background sources, from ...
... probability of an event occurring is very low. In addition, detection can be made challenging through the “dazzling by the light of the much nearer star”, the lens. Einstein’s doubts have not deterred astronomers, with their familiarity of the universe of possible lenses and background sources, from ...
CBO_Paper2_UnderstandingtheStoryOfTheUniverse
... galaxies contain millions, billions, or even trillions of stars, this mass is not large enough to account for the gravitational pull exerted on other galaxies to prevent them from falling apart. In order to account for this gravitational pull, the physicists input dark matter into their computer sim ...
... galaxies contain millions, billions, or even trillions of stars, this mass is not large enough to account for the gravitational pull exerted on other galaxies to prevent them from falling apart. In order to account for this gravitational pull, the physicists input dark matter into their computer sim ...
Weak gravitational lensing
While the presence of any mass bends the path of light passing near it, this effect rarely produces the giant arcs and multiple images associated with strong gravitational lensing. Most lines of sight in the universe are thoroughly in the weak lensing regime, in which the deflection is impossible to detect in a single background source. However, even in these cases, the presence of the foreground mass can be detected, by way of a systematic alignment of background sources around the lensing mass. Weak gravitational lensing is thus an intrinsically statistical measurement, but it provides a way to measure the masses of astronomical objects without requiring assumptions about their composition or dynamical state.