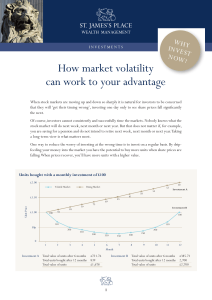
How market volatility can work to your advantage
... make regular investments. Given current market volatility, now might be a good time to start. ...
... make regular investments. Given current market volatility, now might be a good time to start. ...
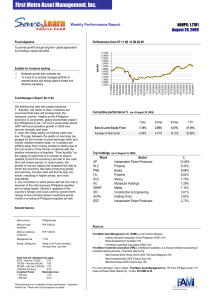
EDITOR`S CORNER Managing Investments for
... An investor should demand acceptable risk, measured against all three objectives, while the manager adds value to at least two of the three measures most of the time. Although performance can be evaluated regularly, it is also important to recognize that the whims of the capital markets can bring ab ...
... An investor should demand acceptable risk, measured against all three objectives, while the manager adds value to at least two of the three measures most of the time. Although performance can be evaluated regularly, it is also important to recognize that the whims of the capital markets can bring ab ...
Country Risk Premium
... RReq = rf + L (E RM - rf) + RPc, where RPc is the country risk premium. In some cases, adding RPc makes sense, but in many cases it does not. The trick is to know when. Local Industry-Country Betas or ADR Betas. Merrill Lynch, in “The Art and Science of DCF Valuation in Latin America,” discusses ho ...
... RReq = rf + L (E RM - rf) + RPc, where RPc is the country risk premium. In some cases, adding RPc makes sense, but in many cases it does not. The trick is to know when. Local Industry-Country Betas or ADR Betas. Merrill Lynch, in “The Art and Science of DCF Valuation in Latin America,” discusses ho ...
principles of finance
... break-even point and the degree of operating leverage to do which of the following? a. Increase decrease b. Decrease decrease c. Decrease increase d. Increase increase 5. Which of the following terms of trade credit is most favorable for the buyer? a. 2/15 net 30 b. 2/15 net 45 c. 3/10 net 30 d. 3/1 ...
... break-even point and the degree of operating leverage to do which of the following? a. Increase decrease b. Decrease decrease c. Decrease increase d. Increase increase 5. Which of the following terms of trade credit is most favorable for the buyer? a. 2/15 net 30 b. 2/15 net 45 c. 3/10 net 30 d. 3/1 ...
Lecture 12
... Studies of stock returns indicate they are approximately normally distributed. Two statistics describe a normal distribution, the mean and the standard deviation (which is the square root of the variance). The standard deviation shows how spread out is the distribution. For stock returns, a more ...
... Studies of stock returns indicate they are approximately normally distributed. Two statistics describe a normal distribution, the mean and the standard deviation (which is the square root of the variance). The standard deviation shows how spread out is the distribution. For stock returns, a more ...
security analysis - Goenka College of Commerce and Business
... factors that can affect the prices of securities. The role of a security analyst is to gather market information and advice the investors to adopt a suitable market strategy. ...
... factors that can affect the prices of securities. The role of a security analyst is to gather market information and advice the investors to adopt a suitable market strategy. ...
08.20.09-salef - First Metro Asset Management Inc
... To invest in an actively managed portfolio of selected stocks with strong balance sheets and ...
... To invest in an actively managed portfolio of selected stocks with strong balance sheets and ...
R i
... • Arbitrage –Creation of riskless profits by trading relative mispricing among securities 1. Constructing a zero-investment portfolio today and earn a profit for certain in the future 2. 2. Or if there is a security priced differently in two markets, a long position in the cheaper market financed by ...
... • Arbitrage –Creation of riskless profits by trading relative mispricing among securities 1. Constructing a zero-investment portfolio today and earn a profit for certain in the future 2. 2. Or if there is a security priced differently in two markets, a long position in the cheaper market financed by ...
required rate of return2
... – Preferred stock – shares some of the characteristics of debt (the dividend is prespecified at the time of issue and is paid out before common dividends) and some of the characteristics of equity (the preferred dividend is not tax deductible). (see Illustration 8.13 on p. 213 for an example) – Conv ...
... – Preferred stock – shares some of the characteristics of debt (the dividend is prespecified at the time of issue and is paid out before common dividends) and some of the characteristics of equity (the preferred dividend is not tax deductible). (see Illustration 8.13 on p. 213 for an example) – Conv ...
Economics 471 Lecture 2 Elementary Probability, Portfolio Theory
... so our picture looks like Figure X. As we vary p we move along the upper curve instead of the (rather boring) straight line connecting the two points. So what? Why is the curve such a big improvement? The answer lies in the tangent line drawn through (µ0 , 0) in the figure. Combining R1 and R2 give ...
... so our picture looks like Figure X. As we vary p we move along the upper curve instead of the (rather boring) straight line connecting the two points. So what? Why is the curve such a big improvement? The answer lies in the tangent line drawn through (µ0 , 0) in the figure. Combining R1 and R2 give ...
Nov. 30, 2015 - Centre Funds
... sign of financial engineering, e.g., stock buybacks, as well as the strong influence from low borrowing costs. Unlike in 2000, stock prices are not inflated relative to earnings; rather, earnings are inflated, masking the expensiveness of stocks from a rudimentary P/E ratio basis. Overall, within th ...
... sign of financial engineering, e.g., stock buybacks, as well as the strong influence from low borrowing costs. Unlike in 2000, stock prices are not inflated relative to earnings; rather, earnings are inflated, masking the expensiveness of stocks from a rudimentary P/E ratio basis. Overall, within th ...
Question and Problem Answers Chapter 5
... at par regardless. The T-Bills are risk free in the nominal sense because the 8% return will be realized in all possible states. However, this 8% return is composed of the real risk free rate (say 3%) plus an inflation premium (5%). If inflation averaged 9% over the year rather than the expected 5% ...
... at par regardless. The T-Bills are risk free in the nominal sense because the 8% return will be realized in all possible states. However, this 8% return is composed of the real risk free rate (say 3%) plus an inflation premium (5%). If inflation averaged 9% over the year rather than the expected 5% ...
An alternative school of thought
... Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results. If the currency in which the past performance is displayed differs from the currency of the country in which the investor resides, then the investor should be aware that due to the exchange rate fluctuations the performance shown may be ...
... Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results. If the currency in which the past performance is displayed differs from the currency of the country in which the investor resides, then the investor should be aware that due to the exchange rate fluctuations the performance shown may be ...
Written exam 2008 spring
... amount, meaning the capital structure has not changed? The question is wrong because you can’t change proportion of debt and have the same capital structure, sorry b) Increasing growth rate? Higher cash-flows – higher value of the company c) The company takes on more debt and gets a higher financial ...
... amount, meaning the capital structure has not changed? The question is wrong because you can’t change proportion of debt and have the same capital structure, sorry b) Increasing growth rate? Higher cash-flows – higher value of the company c) The company takes on more debt and gets a higher financial ...
Active Portfolio Management and Performance Measure
... Risk adjusted fund performance is ranked and then Stars are assigned according to the following table (5 stars is the highest rating) ...
... Risk adjusted fund performance is ranked and then Stars are assigned according to the following table (5 stars is the highest rating) ...
Risk and return (1)
... • The average annual return on U.S. stocks from 1926 – 2001 was 11.6%. The average risk premium was 7.9%. • Stocks are quite risky. The standard deviation of monthly returns for the overall market is 4.5% (15.6% annually). • Individual stocks are much riskier. The average monthly standard deviation ...
... • The average annual return on U.S. stocks from 1926 – 2001 was 11.6%. The average risk premium was 7.9%. • Stocks are quite risky. The standard deviation of monthly returns for the overall market is 4.5% (15.6% annually). • Individual stocks are much riskier. The average monthly standard deviation ...
The Efficient Market Hypothesis
... • Fundamental Analysis - using economic and accounting information to predict stock prices. – Semi strong form efficiency & fundamental analysis ...
... • Fundamental Analysis - using economic and accounting information to predict stock prices. – Semi strong form efficiency & fundamental analysis ...
Portfolio Selection and the Asset Allocation Decision
... Allocation of portfolio assets to broad asset categories ...
... Allocation of portfolio assets to broad asset categories ...
Document
... Stephen Ross, 1976, APT, link expected returns to risk Three key propositions ◦ Security returns can be described by a factor model ◦ Sufficient securities to diversify away idiosyncratic risk ◦ Well-functioning security markets do not allow for the persistence of arbitrage opportunities ...
... Stephen Ross, 1976, APT, link expected returns to risk Three key propositions ◦ Security returns can be described by a factor model ◦ Sufficient securities to diversify away idiosyncratic risk ◦ Well-functioning security markets do not allow for the persistence of arbitrage opportunities ...
Views of Risk
... • Evaluate investments in terms of risk & return relative to the market as a whole • The riskier a stock, the greater profit potential • Thus RISK IS OPPORTUNITY ...
... • Evaluate investments in terms of risk & return relative to the market as a whole • The riskier a stock, the greater profit potential • Thus RISK IS OPPORTUNITY ...
Seeking higher returns or lower risk through ETFs
... This ETF aims to offer diversified exposure to a broadly diversified portfolio of global stocks, achieving returns in line with the MSCI World Index with potentially less risk. The ETF is designed to allow Australian investors to diversify into global stocks with confidence through market cycles, wi ...
... This ETF aims to offer diversified exposure to a broadly diversified portfolio of global stocks, achieving returns in line with the MSCI World Index with potentially less risk. The ETF is designed to allow Australian investors to diversify into global stocks with confidence through market cycles, wi ...
STOCK Beta
... boxes. Each of those down the diagonal—the shaded boxes - contains the variance weighted by the square of the proportion invested, on the next slide. ...
... boxes. Each of those down the diagonal—the shaded boxes - contains the variance weighted by the square of the proportion invested, on the next slide. ...
Beta (finance)

In finance, the beta (β) of an investment is a measure of the risk arising from exposure to general market movements as opposed to idiosyncratic factors. The market portfolio of all investable assets has a beta of exactly 1. A beta below 1 can indicate either an investment with lower volatility than the market, or a volatile investment whose price movements are not highly correlated with the market. An example of the first is a treasury bill: the price does not go up or down a lot, so it has a low beta. An example of the second is gold. The price of gold does go up and down a lot, but not in the same direction or at the same time as the market.A beta greater than one generally means that the asset both is volatile and tends to move up and down with the market. An example is a stock in a big technology company. Negative betas are possible for investments that tend to go down when the market goes up, and vice versa. There are few fundamental investments with consistent and significant negative betas, but some derivatives like equity put options can have large negative betas.Beta is important because it measures the risk of an investment that cannot be reduced by diversification. It does not measure the risk of an investment held on a stand-alone basis, but the amount of risk the investment adds to an already-diversified portfolio. In the capital asset pricing model, beta risk is the only kind of risk for which investors should receive an expected return higher than the risk-free rate of interest.The definition above covers only theoretical beta. The term is used in many related ways in finance. For example, the betas commonly quoted in mutual fund analyses generally measure the risk of the fund arising from exposure to a benchmark for the fund, rather than from exposure to the entire market portfolio. Thus they measure the amount of risk the fund adds to a diversified portfolio of funds of the same type, rather than to a portfolio diversified among all fund types.Beta decay refers to the tendency for a company with a high beta coefficient (β > 1) to have its beta coefficient decline to the market beta. It is an example of regression toward the mean.