Chapter 1
... to participate in the current profits and anticipated future growth of the enterprise. Stocks present potentially higher returns than bonds, but the shareholder must be prepared to take greater risk. We categorize common stocks based on relative growth rates, sector and industry, geographic area ...
... to participate in the current profits and anticipated future growth of the enterprise. Stocks present potentially higher returns than bonds, but the shareholder must be prepared to take greater risk. We categorize common stocks based on relative growth rates, sector and industry, geographic area ...
Systematic and Unsystematic Risk
... R + U (expected + unexpected) Investors form “expectations” about future Expected information is already discounted by the market • i.e., the value of the information is already incorporated into the stock prices • Attempts to exploit Public information (make large returns) will not be successful C ...
... R + U (expected + unexpected) Investors form “expectations” about future Expected information is already discounted by the market • i.e., the value of the information is already incorporated into the stock prices • Attempts to exploit Public information (make large returns) will not be successful C ...
Weekly Commentary 04-17-17
... of principal and interest and, if held to maturity, offer a fixed rate of return and fixed principal value. However, the value of fund shares is not guaranteed and will fluctuate. * Corporate bonds are considered higher risk than government bonds but normally offer a higher yield and are subject to ...
... of principal and interest and, if held to maturity, offer a fixed rate of return and fixed principal value. However, the value of fund shares is not guaranteed and will fluctuate. * Corporate bonds are considered higher risk than government bonds but normally offer a higher yield and are subject to ...
Introduction to Risk, Return and the Opportunity Cost of Capital
... today’s investors expect the same “normal” rates of return as in the past, you would set rm at 11.7%, the average of past market returns. Do you believe that investors would be content to hold common stocks offering an expected return of 11.7% when Treasury bills were offering 15% – as they did in 1 ...
... today’s investors expect the same “normal” rates of return as in the past, you would set rm at 11.7%, the average of past market returns. Do you believe that investors would be content to hold common stocks offering an expected return of 11.7% when Treasury bills were offering 15% – as they did in 1 ...
Some Lessons from Capital Market History
... • Efficient markets do not mean that you can’t make money • They do mean that, on average, you will earn a return that is appropriate for the risk undertaken and there is not a bias in prices that can be exploited to earn excess returns • Market efficiency will not protect you from wrong choices if ...
... • Efficient markets do not mean that you can’t make money • They do mean that, on average, you will earn a return that is appropriate for the risk undertaken and there is not a bias in prices that can be exploited to earn excess returns • Market efficiency will not protect you from wrong choices if ...
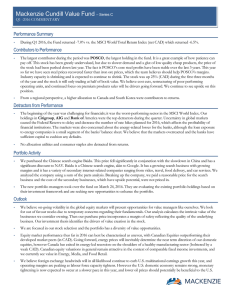
Mackenzie Cundill Value Fund – Series C
... Please read the prospectus before investing. The indicated rates of return are the historical annual compounded total returns as of March 31, 2016 including changes in unit value and reinvestment of all distributions and does not take into account sales, redemption, distribution, or optional charges ...
... Please read the prospectus before investing. The indicated rates of return are the historical annual compounded total returns as of March 31, 2016 including changes in unit value and reinvestment of all distributions and does not take into account sales, redemption, distribution, or optional charges ...
TopicsInAnalysis
... Does certainty equivalent depend on mean and variance? What does Barry Schwartz think of all this? 8. Uncertain future payments (uncertainty and time) Expected values of cash flows Higher discount rates as a proxy for uncertainty (Bringing in the lawyers: “We agree that the truth is between 3.2% and ...
... Does certainty equivalent depend on mean and variance? What does Barry Schwartz think of all this? 8. Uncertain future payments (uncertainty and time) Expected values of cash flows Higher discount rates as a proxy for uncertainty (Bringing in the lawyers: “We agree that the truth is between 3.2% and ...
Expected Return Standard Deviation Increasing Utility
... Example: Suppose that the value of the Best Candy stock is sensitive to the price of sugar. In years when world sugar crops are low, the price of sugar increases and Best Candy suffers considerable ...
... Example: Suppose that the value of the Best Candy stock is sensitive to the price of sugar. In years when world sugar crops are low, the price of sugar increases and Best Candy suffers considerable ...
Institute of Actuaries of India Subject CT8 – Financial Economics INDICATIVE SOLUTIONS
... Rf is the risk free rate, RM is the expected market return and β is the covariance of the return of the risky stock (or well diversified portfolio) with the market, divided by the market variance. For portfolio 1 we have, 0.09 = Rf + 0.88*(RM-Rf), so 0.09= 0.12Rf +0.88RM For portfolio 2 we have, 0.0 ...
... Rf is the risk free rate, RM is the expected market return and β is the covariance of the return of the risky stock (or well diversified portfolio) with the market, divided by the market variance. For portfolio 1 we have, 0.09 = Rf + 0.88*(RM-Rf), so 0.09= 0.12Rf +0.88RM For portfolio 2 we have, 0.0 ...
US Equities
... figures use trailing five-year earnings. Past performance is no guarantee of future results. You cannot invest directly in an index. Stocks represented by total returns of S&P 500 Index including reinvestment of dividends and interest income. S&P earnings estimates used for Q1 2013. Source: Standard ...
... figures use trailing five-year earnings. Past performance is no guarantee of future results. You cannot invest directly in an index. Stocks represented by total returns of S&P 500 Index including reinvestment of dividends and interest income. S&P earnings estimates used for Q1 2013. Source: Standard ...
investment portfolio management. objectives and constraints
... will be composed of three types of assets-common stocks, high-grade corporate bonds, and a risk-free asset-but the appropriate proportions need to be determined. Through simulation, it can be shown to the investor how portfolios with various combinations of these three types of assets would have per ...
... will be composed of three types of assets-common stocks, high-grade corporate bonds, and a risk-free asset-but the appropriate proportions need to be determined. Through simulation, it can be shown to the investor how portfolios with various combinations of these three types of assets would have per ...
Trade Log - Portfolio Strategies Investment Managers
... your principal back sooner than the stated maturity, extensions risk, the opposite of prepayment risk, and interest rate risk. Government bonds and Treasury bills are guaranteed by the U.S. Government as to the timely payment of principal and interest and, if held to maturity, offer a fixed rate of ...
... your principal back sooner than the stated maturity, extensions risk, the opposite of prepayment risk, and interest rate risk. Government bonds and Treasury bills are guaranteed by the U.S. Government as to the timely payment of principal and interest and, if held to maturity, offer a fixed rate of ...
Portfolio Diversification and Asset Allocation
... There are literally hundreds of separate and distinct asset classes available and more are constantly being proposed. There are varying levels of risk and reward for each. Putting the right asset classes together to meet your goals is key in building a suitable portfolio to meet your needs. Making a ...
... There are literally hundreds of separate and distinct asset classes available and more are constantly being proposed. There are varying levels of risk and reward for each. Putting the right asset classes together to meet your goals is key in building a suitable portfolio to meet your needs. Making a ...
The Oak Financial Times - Oak Financial Group, Inc.
... therefore it is important to get the timing for action accurate. It is possible that interest rates may rise this year, however, if they do it will be at a gradual level as the Fed cannot afford to be wrong and lose their credibility. We have positioned our clients’ accounts in a manner where our ac ...
... therefore it is important to get the timing for action accurate. It is possible that interest rates may rise this year, however, if they do it will be at a gradual level as the Fed cannot afford to be wrong and lose their credibility. We have positioned our clients’ accounts in a manner where our ac ...
CLTL - PowerShares Treasury Collateral Portfolio fund in
... Smart Beta represents an alternative and selection index based methodology that seeks to outperform a benchmark or reduce portfolio risk, or both in active or passive vehicles. Smart beta funds may underperform cap-weighted benchmarks and increase portfolio risk. Risk Information There are risks inv ...
... Smart Beta represents an alternative and selection index based methodology that seeks to outperform a benchmark or reduce portfolio risk, or both in active or passive vehicles. Smart beta funds may underperform cap-weighted benchmarks and increase portfolio risk. Risk Information There are risks inv ...
class9n4 - Duke University
... Compare the Yreynor Measure for a particular fund to that of the market (or appropriate benchmark): ...
... Compare the Yreynor Measure for a particular fund to that of the market (or appropriate benchmark): ...
Problem-Solving A* and Beyond
... To SOLVE a problem: If the current state is the goal state, then we’re done. If not, first REDUCE the difference between the current state and goal state to produce a new current state. Then SOLVE the problem from the (presumably better) current state and the original goal. To REDUCE the differenc ...
... To SOLVE a problem: If the current state is the goal state, then we’re done. If not, first REDUCE the difference between the current state and goal state to produce a new current state. Then SOLVE the problem from the (presumably better) current state and the original goal. To REDUCE the differenc ...
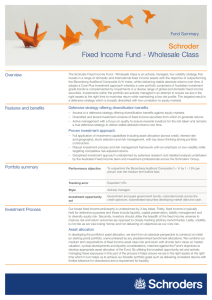
Schroder Fixed Income Fund - Wholesale Class Fund Summary Overview
... Our broad fixed income philosophy is underpinned by 3 key ideas. Firstly, fixed income is typically held for defensive purposes and these include liquidity, capital preservation, liability management and to diversify equity risk. Secondly, investors should utilise the breadth of the fixed income uni ...
... Our broad fixed income philosophy is underpinned by 3 key ideas. Firstly, fixed income is typically held for defensive purposes and these include liquidity, capital preservation, liability management and to diversify equity risk. Secondly, investors should utilise the breadth of the fixed income uni ...
practice
... A. use of several factors instead of a single market index to explain the risk-return relationship b. identification of anticipated changes in production, inflation and term structure as key factors in explaining the risk-return relationship c. superior measurement of the risk-free rate of return ov ...
... A. use of several factors instead of a single market index to explain the risk-return relationship b. identification of anticipated changes in production, inflation and term structure as key factors in explaining the risk-return relationship c. superior measurement of the risk-free rate of return ov ...
Seeing the positive - The Business Times
... rates in the coming months, it is by no means tightening monetary conditions. This means a “lower for longer” global interest rate environment will remain. Today, around US$10 trillion of debt outstanding globally suffers from negative yields. Asian fixed income is an asset class that still offers po ...
... rates in the coming months, it is by no means tightening monetary conditions. This means a “lower for longer” global interest rate environment will remain. Today, around US$10 trillion of debt outstanding globally suffers from negative yields. Asian fixed income is an asset class that still offers po ...
The Capital Asset Pricing model is based on the relationship
... The Capital Asset Pricing model is based on the relationship between a stocks return and the overall market return. The “beta” of a given stock is the slope coefficient, B of the linear regression which is in the form Y = A + BX + where Y is the stock’s return and X is the corresponding market ...
... The Capital Asset Pricing model is based on the relationship between a stocks return and the overall market return. The “beta” of a given stock is the slope coefficient, B of the linear regression which is in the form Y = A + BX + where Y is the stock’s return and X is the corresponding market ...
Expected Return
... For Portfolio A, the ratio of risk premium to beta is: (10% 4%)/1 = 6% The ratio for Portfolio E is higher: (9% 4%)/(0.6) = 8.33% This implies that an arbitrage opportunity exists. For instance, you can create a Portfolio G with beta equal to 1.0 (the same as the beta for Portfolio A) by taking ...
... For Portfolio A, the ratio of risk premium to beta is: (10% 4%)/1 = 6% The ratio for Portfolio E is higher: (9% 4%)/(0.6) = 8.33% This implies that an arbitrage opportunity exists. For instance, you can create a Portfolio G with beta equal to 1.0 (the same as the beta for Portfolio A) by taking ...
How the Market Works… and What It Means for Your Portfolio
... The market is considered “efficient” – not perfect, but sufficiently efficient that wise investors will recognize they cannot expect to regularly exploit mispricings Everything currently knowable is already incorporated into prices - stock prices move only in response to new information unexpect ...
... The market is considered “efficient” – not perfect, but sufficiently efficient that wise investors will recognize they cannot expect to regularly exploit mispricings Everything currently knowable is already incorporated into prices - stock prices move only in response to new information unexpect ...
FINANCIAL RISK MANAGEMENT
... FINANCIAL RISK MANAGEMENT Course Objective: This course will focus on variety of risks faced by financial managers and the tools available for managing these risks. Particularly, we shall focus on credit risk, interest rate and liquidity risks, market risk, foreign exchange risk and country risk. We ...
... FINANCIAL RISK MANAGEMENT Course Objective: This course will focus on variety of risks faced by financial managers and the tools available for managing these risks. Particularly, we shall focus on credit risk, interest rate and liquidity risks, market risk, foreign exchange risk and country risk. We ...
Beta (finance)

In finance, the beta (β) of an investment is a measure of the risk arising from exposure to general market movements as opposed to idiosyncratic factors. The market portfolio of all investable assets has a beta of exactly 1. A beta below 1 can indicate either an investment with lower volatility than the market, or a volatile investment whose price movements are not highly correlated with the market. An example of the first is a treasury bill: the price does not go up or down a lot, so it has a low beta. An example of the second is gold. The price of gold does go up and down a lot, but not in the same direction or at the same time as the market.A beta greater than one generally means that the asset both is volatile and tends to move up and down with the market. An example is a stock in a big technology company. Negative betas are possible for investments that tend to go down when the market goes up, and vice versa. There are few fundamental investments with consistent and significant negative betas, but some derivatives like equity put options can have large negative betas.Beta is important because it measures the risk of an investment that cannot be reduced by diversification. It does not measure the risk of an investment held on a stand-alone basis, but the amount of risk the investment adds to an already-diversified portfolio. In the capital asset pricing model, beta risk is the only kind of risk for which investors should receive an expected return higher than the risk-free rate of interest.The definition above covers only theoretical beta. The term is used in many related ways in finance. For example, the betas commonly quoted in mutual fund analyses generally measure the risk of the fund arising from exposure to a benchmark for the fund, rather than from exposure to the entire market portfolio. Thus they measure the amount of risk the fund adds to a diversified portfolio of funds of the same type, rather than to a portfolio diversified among all fund types.Beta decay refers to the tendency for a company with a high beta coefficient (β > 1) to have its beta coefficient decline to the market beta. It is an example of regression toward the mean.