Egyptian Architecture
... repeatedly pounding balls of very hard rock (dolerite) along seams in the harder stones such ...
... repeatedly pounding balls of very hard rock (dolerite) along seams in the harder stones such ...
File
... 22. In terms of Greek development, we refer to this time as the Greek __________________ Age. They lost writing, sophisticated art, palace administration systems, but still worshipped many of the same __________________. The Greek lands saw a huge decrease in __________________________________ as pe ...
... 22. In terms of Greek development, we refer to this time as the Greek __________________ Age. They lost writing, sophisticated art, palace administration systems, but still worshipped many of the same __________________. The Greek lands saw a huge decrease in __________________________________ as pe ...
Egyptian Number System
... Long ago, a civilization arose called Egypt. Egypt was located along the Nile River where there was very fertile land. Ancient Egyptians had a civilized life and invented many useful items for everyday use. Ancient Egyptians developed a writing system with pictures, called hieroglyphs. They used the ...
... Long ago, a civilization arose called Egypt. Egypt was located along the Nile River where there was very fertile land. Ancient Egyptians had a civilized life and invented many useful items for everyday use. Ancient Egyptians developed a writing system with pictures, called hieroglyphs. They used the ...
How Was the Great Pyramid Built?
... What Happened to the Great Temple of Ramses II? The Great Temple of Ramses II at Abu Simbel was one of the most incredible architectural achievements of the New Kingdom. Probably the most outstanding features of the temple are the four enormous statues of Ramses, some of which are more than six stor ...
... What Happened to the Great Temple of Ramses II? The Great Temple of Ramses II at Abu Simbel was one of the most incredible architectural achievements of the New Kingdom. Probably the most outstanding features of the temple are the four enormous statues of Ramses, some of which are more than six stor ...
Chapter 2:i The Nile Valley
... New Kingdom that the rulers of Egypt first began using the title pharaoh.* [Image source: http://www.narmer.pl/gen/ima/g17-18en.gif] ...
... New Kingdom that the rulers of Egypt first began using the title pharaoh.* [Image source: http://www.narmer.pl/gen/ima/g17-18en.gif] ...
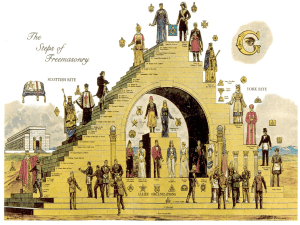
Freemasons
... Sumerian civilization, where it was associated with the sun God and moon Goddess (one early appearance dates to 2100 BCE), and later, with Goddesses Tanit and even Diana. The symbol remained in near constant use, and was eventually adopted into the battle-standard of the Ottoman Dynasty, who are mai ...
... Sumerian civilization, where it was associated with the sun God and moon Goddess (one early appearance dates to 2100 BCE), and later, with Goddesses Tanit and even Diana. The symbol remained in near constant use, and was eventually adopted into the battle-standard of the Ottoman Dynasty, who are mai ...
Early Humans and First Civilizations Powerpoint
... surplus labor and resources over large areas Early states were of ten led by a ruler whose source of power was believed to be divine or had divine support and/or who was supported by the military As states grew and competed for land and resources – some ...
... surplus labor and resources over large areas Early states were of ten led by a ruler whose source of power was believed to be divine or had divine support and/or who was supported by the military As states grew and competed for land and resources – some ...
Woodward Academy Lower School Library
... 'More than one thousand years after the pyramids were built, Egypt reached its apogee. In the time that is now known as the New Kingdom, spectacular conquest and unimaginable wealth came to Egypt's Empire. These are the pharaohs that made Egypt the greatest nation in the ancient World.' (PBS) Read a ...
... 'More than one thousand years after the pyramids were built, Egypt reached its apogee. In the time that is now known as the New Kingdom, spectacular conquest and unimaginable wealth came to Egypt's Empire. These are the pharaohs that made Egypt the greatest nation in the ancient World.' (PBS) Read a ...
royal portraits of the twelfth dynasty
... their ancient land from ruin and injected new cently been placed on exhibition (ill. p. 122). Since the men portrayed were all members of vigor into a civilization grown tired and an art grown smug and empty with the passing cen- one family-father and son in direct succession turies. The new dynasty ...
... their ancient land from ruin and injected new cently been placed on exhibition (ill. p. 122). Since the men portrayed were all members of vigor into a civilization grown tired and an art grown smug and empty with the passing cen- one family-father and son in direct succession turies. The new dynasty ...
We The People American Voices “Here is not merely a
... receiving power from the hawk god, Horus, a sky god who had the power to overcome evil. ...
... receiving power from the hawk god, Horus, a sky god who had the power to overcome evil. ...
Egyptian Social Structure Egyptian society was structured like a
... Egyptian Social Structure Egyptian society was structured like a pyramid. At the top were the gods, such as Ra, Osiris, and Isis. Egyptians believed that the gods controlled the universe. Therefore, it was important to keep them happy. They could make the Nile overflow, cause famine, or even bring d ...
... Egyptian Social Structure Egyptian society was structured like a pyramid. At the top were the gods, such as Ra, Osiris, and Isis. Egyptians believed that the gods controlled the universe. Therefore, it was important to keep them happy. They could make the Nile overflow, cause famine, or even bring d ...
Chapter Excerpt
... peoples. This civilization appears to be the second-oldest in Africa (after Egypt). Either the people were Egyptian or heavily influenced by Egyptians at a very early period in the development of the society. They appear to have spoken NiloSaharan languages. The area in which they lived is called Nu ...
... peoples. This civilization appears to be the second-oldest in Africa (after Egypt). Either the people were Egyptian or heavily influenced by Egyptians at a very early period in the development of the society. They appear to have spoken NiloSaharan languages. The area in which they lived is called Nu ...
File - World History Ms. Petrie
... • Supplies could also be painted on the walls of the tomb. – It was believed that these objects would come to life when it was time. The Tomb • The mummy was taken to the tomb • The organs were kept in jars stored in a large chest. – There were four jars, each one holding a different organ and prote ...
... • Supplies could also be painted on the walls of the tomb. – It was believed that these objects would come to life when it was time. The Tomb • The mummy was taken to the tomb • The organs were kept in jars stored in a large chest. – There were four jars, each one holding a different organ and prote ...
dvxghj8js3
... the delta area of the Nile river. Upper Land (Egypt) - was the name for the territories located up the river, beyond the city of Amarna. “While the labelling of "Upper" and "Lower" might seem counterintuitive, with Upper Egypt in the south and Lower Egypt in the north on modern maps, the terminology ...
... the delta area of the Nile river. Upper Land (Egypt) - was the name for the territories located up the river, beyond the city of Amarna. “While the labelling of "Upper" and "Lower" might seem counterintuitive, with Upper Egypt in the south and Lower Egypt in the north on modern maps, the terminology ...
Egyptian Presentation
... – This sculpture serves as a historical record of events surrounding Narmer’s conquest of lower Egypt. – The relief is divided into registers to denote the separate scenes of the event, and the figures are depicted in hieratic scale to show their level of importance. – Narmer is shown holding the ...
... – This sculpture serves as a historical record of events surrounding Narmer’s conquest of lower Egypt. – The relief is divided into registers to denote the separate scenes of the event, and the figures are depicted in hieratic scale to show their level of importance. – Narmer is shown holding the ...
Ancient Egypt A Time Of The Pyramid
... your breath away. Today, the valley of the Nile has an open air museum so people can witness these grand monuments. Obsessed with the afterlife, Egypt’s rulers of 4,500 years ago glorified themselves in stone, thereby laying the foundation of the first great nation-state. A Pyramid is an enormous ma ...
... your breath away. Today, the valley of the Nile has an open air museum so people can witness these grand monuments. Obsessed with the afterlife, Egypt’s rulers of 4,500 years ago glorified themselves in stone, thereby laying the foundation of the first great nation-state. A Pyramid is an enormous ma ...
The Nile River provided fresh water and fertile land for those living
... Lebanon Mountains rose steeply from the coast. The southern part of this range gave way to the lower hills of Galilee. The Jordan River flowed down from a mountain range through the middle of Canaan, heading south through the Sea of Galilee to the Dead Sea. The land around the narrow river valley in ...
... Lebanon Mountains rose steeply from the coast. The southern part of this range gave way to the lower hills of Galilee. The Jordan River flowed down from a mountain range through the middle of Canaan, heading south through the Sea of Galilee to the Dead Sea. The land around the narrow river valley in ...
bibliography - 1HistoryProject
... important and without any of them, the civilisation would fall. All these features contribute in helping a civilisation to prosper. Some examples include a stable government, geographic features, popular religious beliefs and even a variety of occupations. How great a civilisation is mainly depends ...
... important and without any of them, the civilisation would fall. All these features contribute in helping a civilisation to prosper. Some examples include a stable government, geographic features, popular religious beliefs and even a variety of occupations. How great a civilisation is mainly depends ...
A Short History of Egypt Part I: From the Predynastic Period to the
... earthenware pottery, but no evidence indicates relations with people outside the Nile valley.1 Naqada II culture, on the other hand, shows signs of relations and “cultural boundaries” with the Nubians to the south, and it is during this phase that the Two Lands developed as aggregates of the smaller ...
... earthenware pottery, but no evidence indicates relations with people outside the Nile valley.1 Naqada II culture, on the other hand, shows signs of relations and “cultural boundaries” with the Nubians to the south, and it is during this phase that the Two Lands developed as aggregates of the smaller ...
Grade 9 Egyptian Art
... his architect, Imhotep (the first time the name of an artist has been recorded in history) designed a new kind of tomb at Saqqara. It was made by stacking successively smaller mastabas one on top of another like a ‘stairway to heaven’ and so, it is called a step pyramid. The pyramid did not stand al ...
... his architect, Imhotep (the first time the name of an artist has been recorded in history) designed a new kind of tomb at Saqqara. It was made by stacking successively smaller mastabas one on top of another like a ‘stairway to heaven’ and so, it is called a step pyramid. The pyramid did not stand al ...
the pyramids - Mr. Dowling
... to Giza. Historians estimate that it took over 100,000 workers more than twenty years to build the Great Pyramid. The ancient Egyptians did not have large animals to help them carry the massive stones, and at the time of the construction of the Great Pyramid, the Egyptians had not yet discovered the ...
... to Giza. Historians estimate that it took over 100,000 workers more than twenty years to build the Great Pyramid. The ancient Egyptians did not have large animals to help them carry the massive stones, and at the time of the construction of the Great Pyramid, the Egyptians had not yet discovered the ...
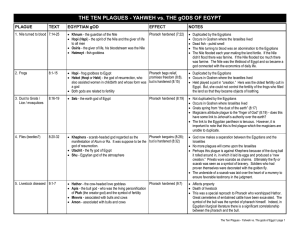
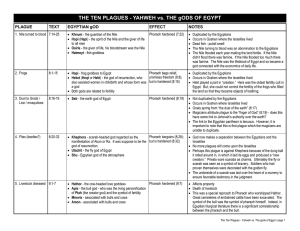
The Plagues Against Egypt
... who could not help the Egyptian army pursue Israel into the desert. The cruel sea was believed to be a manifestation of Seth. The last plague is not only against the supreme god of Egypt, Pharaoh himself, but also against the future pharaoh, his son, the very next god (Horus) of Egypt. The futur ...
... who could not help the Egyptian army pursue Israel into the desert. The cruel sea was believed to be a manifestation of Seth. The last plague is not only against the supreme god of Egypt, Pharaoh himself, but also against the future pharaoh, his son, the very next god (Horus) of Egypt. The futur ...
THE TEN PLAGUES - YAHWEH vs. THE gODS OF EGYPT
... who could not help the Egyptian army pursue Israel into the desert. The cruel sea was believed to be a manifestation of Seth. • The last plague is not only against the supreme god of Egypt, Pharaoh himself, but also against the future pharaoh, his son, the very next god (Horus) of Egypt. • The futur ...
... who could not help the Egyptian army pursue Israel into the desert. The cruel sea was believed to be a manifestation of Seth. • The last plague is not only against the supreme god of Egypt, Pharaoh himself, but also against the future pharaoh, his son, the very next god (Horus) of Egypt. • The futur ...
Document
... Scribes traveled throughout Egypt keeping records of great and small details. Only boys became scribes and they began their study around the age of 10. They chanted passages aloud to improve reading skills. Then they spent hours writing out lessons and stories over and over. If their attention wande ...
... Scribes traveled throughout Egypt keeping records of great and small details. Only boys became scribes and they began their study around the age of 10. They chanted passages aloud to improve reading skills. Then they spent hours writing out lessons and stories over and over. If their attention wande ...