Name: Date:______ Period:___ Map of Ancient Egypt GUIDED
... a preserving process called (7)________________. Through this process, they learned much about the human body and became skilled at using herbs and drugs to treat different (8)________________. Many of the important organs were stored in _____________ jars.(to be provided in class) Because the after ...
... a preserving process called (7)________________. Through this process, they learned much about the human body and became skilled at using herbs and drugs to treat different (8)________________. Many of the important organs were stored in _____________ jars.(to be provided in class) Because the after ...
Flocabulary - Ancient Egypt
... Upper and Lower, we're divided up, Yep, until Pharaoh Menes united us. In 3100 BC, he said, I want my son to be pharaoh, After me, I'll start a ________. King Tut, died before he got old, ...
... Upper and Lower, we're divided up, Yep, until Pharaoh Menes united us. In 3100 BC, he said, I want my son to be pharaoh, After me, I'll start a ________. King Tut, died before he got old, ...
Egypt_Notes - Groupfusion.net
... on a paper called papyrus – We were able to discover what the hieroglyphics meant when Champollion cracked the code of the Rosetta Stone ...
... on a paper called papyrus – We were able to discover what the hieroglyphics meant when Champollion cracked the code of the Rosetta Stone ...
Egyptian Civilization
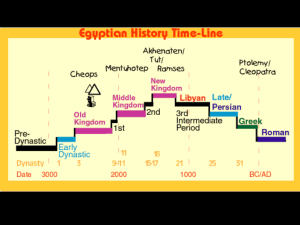
... The Old Kingdom, also known as the pyramid age, reigned from 2700 BCE and 2200 BCE Old Kingdom capital chosen by Narmer was Memphis This period was when Narmer united the upper and lower kingdoms The old Kingdom built the great pyramid and the sphinx Egypt was ruled by a strong government in this pe ...
... The Old Kingdom, also known as the pyramid age, reigned from 2700 BCE and 2200 BCE Old Kingdom capital chosen by Narmer was Memphis This period was when Narmer united the upper and lower kingdoms The old Kingdom built the great pyramid and the sphinx Egypt was ruled by a strong government in this pe ...
Polish archaeologists discovered a tomb in Egypt
... The discovery was made within the so-called Dry Moat, in the rock-hewn gigantic depression which surrounded the pyramid of Djoser at a distance of approximately 200 m. Archaeologists had long wondered whether the high rock "dry moat" walls could contain several floors of tombs from the successive ph ...
... The discovery was made within the so-called Dry Moat, in the rock-hewn gigantic depression which surrounded the pyramid of Djoser at a distance of approximately 200 m. Archaeologists had long wondered whether the high rock "dry moat" walls could contain several floors of tombs from the successive ph ...
Chpt. 2 prentice hall world history
... Each soul had to pass a test in order to win eternal life. Turn to a new partner & come up w/a 2-3 sentence response describing what the “fateful test” involved. ...
... Each soul had to pass a test in order to win eternal life. Turn to a new partner & come up w/a 2-3 sentence response describing what the “fateful test” involved. ...
Chapter 4 Sections 1 and 2
... • During the summer months when the fields were flooded the Egyptians cut granite and limestone blocks from quarries up the Nile and floated them across the river • Huge mud and brick ramps were built so that workers could pull the blocks to where they would be placed on the pyramid ...
... • During the summer months when the fields were flooded the Egyptians cut granite and limestone blocks from quarries up the Nile and floated them across the river • Huge mud and brick ramps were built so that workers could pull the blocks to where they would be placed on the pyramid ...
Study Guide for Unit 2: Ancient Egypt Study Guide for Unit 2
... 5. What were the primary responsibilities of government officials? What privileges did government officials have? 6. How were government and religion intertwined in Egyptian society? 7. Why did Egyptians preserve bodies through embalming? 8. How were scribes educated? What work did they do? 9. What ...
... 5. What were the primary responsibilities of government officials? What privileges did government officials have? 6. How were government and religion intertwined in Egyptian society? 7. Why did Egyptians preserve bodies through embalming? 8. How were scribes educated? What work did they do? 9. What ...
Summary: Ancient Egypt
... civilization. The first ruler of ancient Egypt came to power around 3100 B.C.E. Each year the river flooded and left soil along its banks. Egyptians learned to control the floods and use the land to grow crops. Boats carried people and goods on the Nile. Egyptians traded for things they did not have ...
... civilization. The first ruler of ancient Egypt came to power around 3100 B.C.E. Each year the river flooded and left soil along its banks. Egyptians learned to control the floods and use the land to grow crops. Boats carried people and goods on the Nile. Egyptians traded for things they did not have ...
Egypt: The Middle Kingdom
... During this generally peaceful time trade picked up dramatically. Many resources which before had been unused were now being exploited such as the cultivation of crops, mines which produced gold and quarries that were dug for building projects. During the entire Middle Kingdom many building projects ...
... During this generally peaceful time trade picked up dramatically. Many resources which before had been unused were now being exploited such as the cultivation of crops, mines which produced gold and quarries that were dug for building projects. During the entire Middle Kingdom many building projects ...
SAMPLE TEST ANSWERS
... Old Kingdom - these answers are arranged to show a progression to the best answer. 1. This was the first age of the Egyptian empire. It was important because it was the beginning of Egyptian history, which would last 3,000 years. 2. The Old Kingdom was the first of three historical periods in Ancien ...
... Old Kingdom - these answers are arranged to show a progression to the best answer. 1. This was the first age of the Egyptian empire. It was important because it was the beginning of Egyptian history, which would last 3,000 years. 2. The Old Kingdom was the first of three historical periods in Ancien ...
LIFE IN ANCIENT EGYPT
... Banquets with dancing girls and musicians. Board games, athletics and family hunting expeditions. The Peasants and Agriculture The yearly agricultural cycle. A close look at the tools and methods used in the cultivation of soil, sowing of grain, irrigation and the shaduf, and ...
... Banquets with dancing girls and musicians. Board games, athletics and family hunting expeditions. The Peasants and Agriculture The yearly agricultural cycle. A close look at the tools and methods used in the cultivation of soil, sowing of grain, irrigation and the shaduf, and ...
File
... victorious unification of upper and lower Egypt. • One of first historical artworks • EVERY image shows Narmer’s POWER. ...
... victorious unification of upper and lower Egypt. • One of first historical artworks • EVERY image shows Narmer’s POWER. ...
This is Jeopardy - Town of Mansfield, CT
... People for 500 • His tomb was the only complete one ever found. • Who is Tutankhamen? Why this was important. Gave information to historians/scientists about Egyptian burial practices ...
... People for 500 • His tomb was the only complete one ever found. • Who is Tutankhamen? Why this was important. Gave information to historians/scientists about Egyptian burial practices ...
AncientEgypt-general 1
... to rule Egypt where she forged a relationship with Marc Antony Her suicide in 30 B.C.E. brought to an end the last chapter in the 3,000-year story of Ancient Egypt ...
... to rule Egypt where she forged a relationship with Marc Antony Her suicide in 30 B.C.E. brought to an end the last chapter in the 3,000-year story of Ancient Egypt ...
Notes- Chapter 5
... As the centuries passed, Egyptians came to believe that the afterlife was not only for pharaohs. All people—rich and poor—could hope for eternal life with the help of the god Osiris. As a result, the process of embalming emerged so that Egyptians could protect bodies for the afterlife. Before a body ...
... As the centuries passed, Egyptians came to believe that the afterlife was not only for pharaohs. All people—rich and poor—could hope for eternal life with the help of the god Osiris. As a result, the process of embalming emerged so that Egyptians could protect bodies for the afterlife. Before a body ...
ancient egypt
... The flooding of the Nile rendered the narrow strip of land on either side of the river extremely fertile. INTENSIVE AGRICULTURE was practiced by the majority of the peasant population. who played a vital role within the country's STRICT HIERARHICAL SOCIETY. As the flood waters receded, SOWING and ...
... The flooding of the Nile rendered the narrow strip of land on either side of the river extremely fertile. INTENSIVE AGRICULTURE was practiced by the majority of the peasant population. who played a vital role within the country's STRICT HIERARHICAL SOCIETY. As the flood waters receded, SOWING and ...
Egypt
... “Gift of the Nile” The Ancient Egyptian Civilization was located along the Nile River in northern Africa. Egypt was known as the “Gift of the Nile.” The Nile River is the main reason that a civilization started here. Without the Nile Egypt would be an empty desert. The Nile River Valley is the only ...
... “Gift of the Nile” The Ancient Egyptian Civilization was located along the Nile River in northern Africa. Egypt was known as the “Gift of the Nile.” The Nile River is the main reason that a civilization started here. Without the Nile Egypt would be an empty desert. The Nile River Valley is the only ...
Old and Middle Kingdoms
... Obverse of a Narmer Palette facsimileBelow the bovine heads thought to represent the cow goddess Bat, who was the patron deity of the seventh nome of Upper Egypt, flanking the serekh of Narmer.[11] Below that is what appears to be a procession, with Narmer depicted at almost the full height of the r ...
... Obverse of a Narmer Palette facsimileBelow the bovine heads thought to represent the cow goddess Bat, who was the patron deity of the seventh nome of Upper Egypt, flanking the serekh of Narmer.[11] Below that is what appears to be a procession, with Narmer depicted at almost the full height of the r ...
Characteristics of Ancient Egyptian Art
... • Only temples and tombs have survived. Their walls were immensely thick and built using durable materials like stone • The belief in existence beyond death (reincarnation) resulted in existing architecture of utmost impressiveness and permanence. ...
... • Only temples and tombs have survived. Their walls were immensely thick and built using durable materials like stone • The belief in existence beyond death (reincarnation) resulted in existing architecture of utmost impressiveness and permanence. ...
Ancient Egypt
... c. Often shown holding the Ankh, the key of life 2. Anubis--god of mummification a. Head of a jackal b. Tail of a lion c. Body of a man 3. Osiris--god of the dead 4. Isis--wife of Osiris B. Monotheism – a belief in one God 1. Aten – the sun god a. Creator of the world b. Affected the world through h ...
... c. Often shown holding the Ankh, the key of life 2. Anubis--god of mummification a. Head of a jackal b. Tail of a lion c. Body of a man 3. Osiris--god of the dead 4. Isis--wife of Osiris B. Monotheism – a belief in one God 1. Aten – the sun god a. Creator of the world b. Affected the world through h ...
EGYPT
... • Kingship was a divine institution and pharaohs had absolute power – Belief that the pharaoh was a god in human form – Egypt was a theocracy, a state ruled by a religious figure • Surrounded by a well-established bureaucracy – Bureaucracy = a highly structured organization, often governmental, mana ...
... • Kingship was a divine institution and pharaohs had absolute power – Belief that the pharaoh was a god in human form – Egypt was a theocracy, a state ruled by a religious figure • Surrounded by a well-established bureaucracy – Bureaucracy = a highly structured organization, often governmental, mana ...
The Glories of Egypt - Renton School District
... Egypt and their Environment 1) The Egyptians were considered one of the most advanced civilizations of the ancient world. They were able to develop into such an admired empire because they had a lot of time to spend time on the arts, technology, architecture, music, dance, religion, and leisure time ...
... Egypt and their Environment 1) The Egyptians were considered one of the most advanced civilizations of the ancient world. They were able to develop into such an admired empire because they had a lot of time to spend time on the arts, technology, architecture, music, dance, religion, and leisure time ...
Egypt Extension with Valley of the Kings
... Egypt Extension with Valley of the Kings 5 days / 4 nights (depending on flight connections) Day 1 – Arrival in Cairo Transfer to Ben Gurion Airport, for the flight to Cairo International Airport. We meet the touring representative after passport control and board our bus for a transfer to the Hotel ...
... Egypt Extension with Valley of the Kings 5 days / 4 nights (depending on flight connections) Day 1 – Arrival in Cairo Transfer to Ben Gurion Airport, for the flight to Cairo International Airport. We meet the touring representative after passport control and board our bus for a transfer to the Hotel ...