Thoracic Cage
... - There are twelve ribs on each side classified as: A: True ribs --------- Upper seven ribs (their anterior end is attached to the sternum). B: False ribs --------- Lower five ribs (they are not attached anteriorly to the sternum). - The lower two ribs are called the floating ribs because they are f ...
... - There are twelve ribs on each side classified as: A: True ribs --------- Upper seven ribs (their anterior end is attached to the sternum). B: False ribs --------- Lower five ribs (they are not attached anteriorly to the sternum). - The lower two ribs are called the floating ribs because they are f ...
The superficial veins of the lower limb begin as the dorsal venous
... Arising from the dorsal venous network (arch) on the dorsum of the hand are the two most important superficial veins: the cephalic and basilic veins. The cephalic vein ascends along the lateral aspect of the forearm. (This side of your arm is considered "cephalic" because the limbs develop projecti ...
... Arising from the dorsal venous network (arch) on the dorsum of the hand are the two most important superficial veins: the cephalic and basilic veins. The cephalic vein ascends along the lateral aspect of the forearm. (This side of your arm is considered "cephalic" because the limbs develop projecti ...
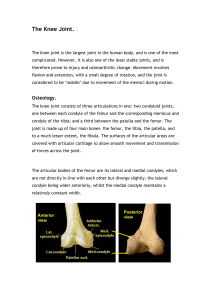
The Knee Joint - Judith Brown CPD
... ligament of Wrisberg, passing upward and medially to insert into the medial condyle of the femur, immediately behind the attachment of the posterior cruciate ligament. Occasionally a small fasciculus passes forward to be inserted into the lateral part of the anterior cruciate ligament, known as the ...
... ligament of Wrisberg, passing upward and medially to insert into the medial condyle of the femur, immediately behind the attachment of the posterior cruciate ligament. Occasionally a small fasciculus passes forward to be inserted into the lateral part of the anterior cruciate ligament, known as the ...
Occipitalization of atlas with other associated anomalies of skull
... cal on the two sides. Plain X-rays revealed no evidence of a joint cavity (Fig. 3). On both the sides, the inferior articular facets were almost oval in shape, with a narrow anterior extension. The facets were relatively smooth and flat, directed anteromedially along the long axis and downwards and ...
... cal on the two sides. Plain X-rays revealed no evidence of a joint cavity (Fig. 3). On both the sides, the inferior articular facets were almost oval in shape, with a narrow anterior extension. The facets were relatively smooth and flat, directed anteromedially along the long axis and downwards and ...
0025_SFX 1 07 text_final.indd - Australian Sonographers Association
... manage and the footprints are smaller. The use of an offset (stand off) is advisable for imaging superficial structures and aids contact in hard-to-access areas such as the lateral malleolus. A thick coupling gel may be used as it acts as an offset and does not run. In general, the examination shoul ...
... manage and the footprints are smaller. The use of an offset (stand off) is advisable for imaging superficial structures and aids contact in hard-to-access areas such as the lateral malleolus. A thick coupling gel may be used as it acts as an offset and does not run. In general, the examination shoul ...
Concise Guide to HUMAN ANATOMY 2
... Face and eyes are directed forward . Hands are by both sides with palms directed forwards . Feet are pointed forwards so that the hells and greater toes together . 2. The terms Anterior-------- front or belly side Posterior-------- back side Superior-------- upper part Inferior-------- lower part La ...
... Face and eyes are directed forward . Hands are by both sides with palms directed forwards . Feet are pointed forwards so that the hells and greater toes together . 2. The terms Anterior-------- front or belly side Posterior-------- back side Superior-------- upper part Inferior-------- lower part La ...
by collateral ligaments. A synovial membrane lines the fibrous
... other than pure extension and flexion. Since raising the foot produces a tightening of the ligaments of the articular socket the natural position of rest is that assumed by the foot depending in a position of partial flexion with the maximum relaxation of the joint ligaments. The second noteworthy f ...
... other than pure extension and flexion. Since raising the foot produces a tightening of the ligaments of the articular socket the natural position of rest is that assumed by the foot depending in a position of partial flexion with the maximum relaxation of the joint ligaments. The second noteworthy f ...
African Journal of Herpetology 56:39-75
... unknown, although Angolosaurus skoogi previously was proposed as the sister taxon to mainland African gerrhosaurids. Many details of the cranial osteology of A. skoogi are also unknown because of the rarity in museum collections and elusive lifestyle of this dune-dwelling lizard, endemic to the Nami ...
... unknown, although Angolosaurus skoogi previously was proposed as the sister taxon to mainland African gerrhosaurids. Many details of the cranial osteology of A. skoogi are also unknown because of the rarity in museum collections and elusive lifestyle of this dune-dwelling lizard, endemic to the Nami ...
Semester 1, 2016/17 - University of Bolton
... a. Spinous process of T2-T5, intervening supraspinous ligament, inserts into medial border of scapula between base of its spine and its inferior angle b. Spinous process of C7-T1, intervening supraspinous ligament, inserts into medial border of scapula at the base of its spine. c. Spinous process of ...
... a. Spinous process of T2-T5, intervening supraspinous ligament, inserts into medial border of scapula between base of its spine and its inferior angle b. Spinous process of C7-T1, intervening supraspinous ligament, inserts into medial border of scapula at the base of its spine. c. Spinous process of ...
preview only - World Health Webinars
... exact spinal segments Solonen (1957): SIJ predominantly innervated by nerves L4-S1 Bradley (1974): fine fibres innervating the joint from L5 to S3 Grobb (1995): branches to the joint from posterior rami S1-S4 Willard et al 1998: small communicating branches from L5, as well S1-S2 into the ed ...
... exact spinal segments Solonen (1957): SIJ predominantly innervated by nerves L4-S1 Bradley (1974): fine fibres innervating the joint from L5 to S3 Grobb (1995): branches to the joint from posterior rami S1-S4 Willard et al 1998: small communicating branches from L5, as well S1-S2 into the ed ...
L 20- Anatomt of Basal ganglia and connections
... giving the striated appearance hence, the name corpus striatum. ...
... giving the striated appearance hence, the name corpus striatum. ...
1 2. Endoscopic Anatomy of the Paranasal Sinuses Anatomical
... point in the bony wall of the anterior sphenoidal sinus can be found and perforated lying a little more than 1 cm above and 0 .5 cm medially. This point can also be palpated 1 cm above the dome of the choana paramedially. The sphenoidal ostium lies higher and somewhat more medial. It is seldom suita ...
... point in the bony wall of the anterior sphenoidal sinus can be found and perforated lying a little more than 1 cm above and 0 .5 cm medially. This point can also be palpated 1 cm above the dome of the choana paramedially. The sphenoidal ostium lies higher and somewhat more medial. It is seldom suita ...
Axillary artery
... Lower lateral cutaneous nerve of the arm supplies the skin over the lateral and anterior aspects of the lower part of the arm Posterior cutaneous nerve of the forearm runs down the middle of the back of the forearm as far as the ...
... Lower lateral cutaneous nerve of the arm supplies the skin over the lateral and anterior aspects of the lower part of the arm Posterior cutaneous nerve of the forearm runs down the middle of the back of the forearm as far as the ...
Arthroscopic Capsular Plication And Capsular
... is begun. The anterior-superior lateral portal is localized with a spinal needle, the skin incision is made and a disposable cannula (at least 5.5mm inner diameter) is introduced into the glenohumeral joint. While this cannula will usually be anterior to the biceps tendon, it can be introduced throu ...
... is begun. The anterior-superior lateral portal is localized with a spinal needle, the skin incision is made and a disposable cannula (at least 5.5mm inner diameter) is introduced into the glenohumeral joint. While this cannula will usually be anterior to the biceps tendon, it can be introduced throu ...
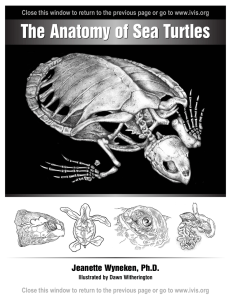
Muscle Anatomy - The Anatomy of Sea Turtles by Jeanette
... As they apply to sea turtles, these functions are as follows. Flexion bends one part relative to another at a joint; extension straightens those parts. Protraction moves one part (usually a limb) out and forward; retraction moves that part in and back. Abduction moves a part away from the ventral su ...
... As they apply to sea turtles, these functions are as follows. Flexion bends one part relative to another at a joint; extension straightens those parts. Protraction moves one part (usually a limb) out and forward; retraction moves that part in and back. Abduction moves a part away from the ventral su ...
Sample
... ● In terms of surface anatomy, the lateral prominence (distal fibula) is the lateral malleolus, medial prominence (distal tibia) is the medial malleolus (A). ● The talus articulates with the calcaneus to form the subtalar joint; articulation between talus and navicular is talonavicular joint; articu ...
... ● In terms of surface anatomy, the lateral prominence (distal fibula) is the lateral malleolus, medial prominence (distal tibia) is the medial malleolus (A). ● The talus articulates with the calcaneus to form the subtalar joint; articulation between talus and navicular is talonavicular joint; articu ...
Trachea and bronchial tree
... The trachea terminates at the level of T 4 by dividing into right and left main bronchi which are asymmetrical. - When a foreign body enters the trachea it passes through the right main bronchus. ...
... The trachea terminates at the level of T 4 by dividing into right and left main bronchi which are asymmetrical. - When a foreign body enters the trachea it passes through the right main bronchus. ...
Non-Muscular-Anatomy-Teaching-Pack-5
... Insert to the whole length of the sustentaculum tali of the calcaneus Primary function is to control medial distraction and calcaneal eversion Anterior parts limit plantarflexion Posterior parts limit dorsiflexion Plantar calcaneonavicular (spring) ligament Short thick wide ligament Conn ...
... Insert to the whole length of the sustentaculum tali of the calcaneus Primary function is to control medial distraction and calcaneal eversion Anterior parts limit plantarflexion Posterior parts limit dorsiflexion Plantar calcaneonavicular (spring) ligament Short thick wide ligament Conn ...
The Nasal Cavity
... Originate from the facial artery on the front of the face Superior labial gives an alar branch supplies the region around the naris and a septal branch supplies anterior regions of the nasal septum. ...
... Originate from the facial artery on the front of the face Superior labial gives an alar branch supplies the region around the naris and a septal branch supplies anterior regions of the nasal septum. ...
Anomalous Branching Pattern of the Popliteal Artery (PA): A Case
... The Popliteal Artery (PA), which is the continuation of the Femoral artery, crosses the popliteal fossa at the distal border of popliteus; it divides into the Anterior and Posterior Tibial arteries. The Posterior Tibial Artery (PTA) divides into terminal branches proximal to popliteus, in which case ...
... The Popliteal Artery (PA), which is the continuation of the Femoral artery, crosses the popliteal fossa at the distal border of popliteus; it divides into the Anterior and Posterior Tibial arteries. The Posterior Tibial Artery (PTA) divides into terminal branches proximal to popliteus, in which case ...
The cerebellum. A
... Clinical notes and function Each cerebellar hemisphere is connected by nervous pathways principally with the same side of the body; thus, a lesion in one cerebellar hemisphere gives rise to signs and symptoms that are limited to the same side of the body The essential function of the cerebellum is ...
... Clinical notes and function Each cerebellar hemisphere is connected by nervous pathways principally with the same side of the body; thus, a lesion in one cerebellar hemisphere gives rise to signs and symptoms that are limited to the same side of the body The essential function of the cerebellum is ...
The Nasal Cavity
... Originate from the facial artery on the front of the face Superior labial gives an alar branch supplies the region around the naris and a septal branch supplies anterior regions of the nasal septum. lateral nasal arteries supply blood of the external nose Alar branches pass around the lateral margin ...
... Originate from the facial artery on the front of the face Superior labial gives an alar branch supplies the region around the naris and a septal branch supplies anterior regions of the nasal septum. lateral nasal arteries supply blood of the external nose Alar branches pass around the lateral margin ...
The upper limb
... Action: supinator of forearm, flexor of elbow joint, weak flexor of should joint Pronator teres Origin: medical epicondyle of humerus and deep fascia of forearm Insertion: middle of lateral surface of radius Action: pronation of forearm and flexion of elbow ...
... Action: supinator of forearm, flexor of elbow joint, weak flexor of should joint Pronator teres Origin: medical epicondyle of humerus and deep fascia of forearm Insertion: middle of lateral surface of radius Action: pronation of forearm and flexion of elbow ...
Medial maxillectomy - Vula
... Figure 23: Liga clips being applied to anterior ethmoidal artery (AEA) Now strip along the floor of the orbit in an extraperiosteal plane. Take special care not to tear the periosteum at the inferior orbital margin at the attachment of the orbital septum so as to avoid entering the orbital fat and c ...
... Figure 23: Liga clips being applied to anterior ethmoidal artery (AEA) Now strip along the floor of the orbit in an extraperiosteal plane. Take special care not to tear the periosteum at the inferior orbital margin at the attachment of the orbital septum so as to avoid entering the orbital fat and c ...
Drosophila embryogenesis

Drosophila embryogenesis, the process by which Drosophila (fruit fly) embryos form, is a favorite model system for geneticists and developmental biologists studying embryogenesis. The small size, short generation time, and large brood size make it ideal for genetic studies. Transparent embryos facilitate developmental studies. Drosophila melanogaster was introduced into the field of genetic experiments by Thomas Hunt Morgan in 1909.