Name: Chemistry Honors Date: Period: ____ Reduction/Oxidation
... 2. Would you use an oxidizing agent or reducing agent in order for the following reactions to occur? a. ClO3- ...
... 2. Would you use an oxidizing agent or reducing agent in order for the following reactions to occur? a. ClO3- ...
(MgCl2 and CaCl2): Osmotic Pressure Calculations
... between a Ca2+ ion and oxygen atoms in a theoretical study of Ca2+ binding with Parvalbumin provided evidence of how the charge in the center of the ion by itself is not sufficient to keep the Ca2+ ion stable in its binding site.34 Another theoretical study of Ca2+ binding in Calbindin reported that a ...
... between a Ca2+ ion and oxygen atoms in a theoretical study of Ca2+ binding with Parvalbumin provided evidence of how the charge in the center of the ion by itself is not sufficient to keep the Ca2+ ion stable in its binding site.34 Another theoretical study of Ca2+ binding in Calbindin reported that a ...
Acids and Bases - vortexlauncher
... the same, pH=pKa. When you choose an acid for a buffer solution, it is best to pick an acid with a pKa that is close to the desired pH. That way you can have almost equal amounts of acid and conjugate base in the solution, which will make the buffer as flexible as possible in neutralizing both added ...
... the same, pH=pKa. When you choose an acid for a buffer solution, it is best to pick an acid with a pKa that is close to the desired pH. That way you can have almost equal amounts of acid and conjugate base in the solution, which will make the buffer as flexible as possible in neutralizing both added ...
Multiplets in Polymer Gels. Rare Earth Metal Ions Luminescence Study
... ca. 15%. In methanol solutions under the same conditions the decay curves for the mixture Eu(NO3)3/Tb(NO3)3 are fairly close to that for Tb(NO3)3 alone. This suggests that in the gel some of the RE cations are held by the polymer network in close molecular-scale proximity to one another indicating o ...
... ca. 15%. In methanol solutions under the same conditions the decay curves for the mixture Eu(NO3)3/Tb(NO3)3 are fairly close to that for Tb(NO3)3 alone. This suggests that in the gel some of the RE cations are held by the polymer network in close molecular-scale proximity to one another indicating o ...
Chemistry 11
... Polyatomic Compounds Continued / The Addition of Hydrogen In lesson six the radicals based on the oxy acids were formed when all of the hydrogens were removed. These acids however, hang on to one or two of their hydrogens. This will still create a radical whose charge will be equal to the total numb ...
... Polyatomic Compounds Continued / The Addition of Hydrogen In lesson six the radicals based on the oxy acids were formed when all of the hydrogens were removed. These acids however, hang on to one or two of their hydrogens. This will still create a radical whose charge will be equal to the total numb ...
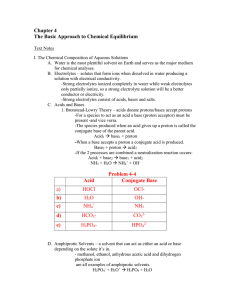
Chapter 4
... I. The Chemical Composition of Aqueous Solutions A. Water is the most plentiful solvent on Earth and serves as the major medium for chemical analyses. B. Electrolytes – solutes that form ions when dissolved in water producing a solution with electrical conductivity. -Strong electrolytes ionized comp ...
... I. The Chemical Composition of Aqueous Solutions A. Water is the most plentiful solvent on Earth and serves as the major medium for chemical analyses. B. Electrolytes – solutes that form ions when dissolved in water producing a solution with electrical conductivity. -Strong electrolytes ionized comp ...
THE s -BLOCK ELEMENTS OCK ELEMENTS THE s
... 9. The solubility of metal halides depends on their nature, lattice enthalpy and hydration enthalpy of the individual ions. Amongst fluorides of alkali metals, the lowest solubility of LiF in water is due to (i) ...
... 9. The solubility of metal halides depends on their nature, lattice enthalpy and hydration enthalpy of the individual ions. Amongst fluorides of alkali metals, the lowest solubility of LiF in water is due to (i) ...
APPENDIX 2 1 ASSESSMENT OF STUDENT LEARNING BROAD
... from the solid? Molarity and normality can be done for either type of solution, but % is for solutions prepared from solids only and 10x is for dilutions only How are these calculations done? Students should be able to solve either for mass or volume for any type of solution given its concentration ...
... from the solid? Molarity and normality can be done for either type of solution, but % is for solutions prepared from solids only and 10x is for dilutions only How are these calculations done? Students should be able to solve either for mass or volume for any type of solution given its concentration ...
Chapter 15
... An ideal solution exists when all intermolecular forces are of comparable strength, ΔH(soln) = 0. When solute–solvent intermolecular forces are somewhat stronger than other intermolecular forces, ΔH(soln) < 0. When solute–solvent intermolecular forces are somewhat weaker than other intermolecular fo ...
... An ideal solution exists when all intermolecular forces are of comparable strength, ΔH(soln) = 0. When solute–solvent intermolecular forces are somewhat stronger than other intermolecular forces, ΔH(soln) < 0. When solute–solvent intermolecular forces are somewhat weaker than other intermolecular fo ...
Strong and weak acids and bases
... • have more H+ ions, hence lower pH • higher conductivity • react more vigorously with metals, metal oxides, metal carbonates and bicarbonates • have a more (-)∆H of neutralization (more heat) • dangerous ...
... • have more H+ ions, hence lower pH • higher conductivity • react more vigorously with metals, metal oxides, metal carbonates and bicarbonates • have a more (-)∆H of neutralization (more heat) • dangerous ...
Europium(III) and terbium(III) trans-2
... its position in the lanthanide series (ionic radii 0.95 Eu(III) vs. 0.92 Tb(III) Å). The structure is completed by two hydration water molecules, one of which appears depleted with an occupation factor of approximately 0.60. No hydrogen atoms could be found on these water molecules, but the presenc ...
... its position in the lanthanide series (ionic radii 0.95 Eu(III) vs. 0.92 Tb(III) Å). The structure is completed by two hydration water molecules, one of which appears depleted with an occupation factor of approximately 0.60. No hydrogen atoms could be found on these water molecules, but the presenc ...
Activity (chemistry) - Chemical Engineering
... The difference between activity and other measures of composition arises because molecules in nonideal gases or solutions interact with each other, either to attract or to repel each other. The activity of an ion is particularly influenced by its surroundings. Activities should be used to define equ ...
... The difference between activity and other measures of composition arises because molecules in nonideal gases or solutions interact with each other, either to attract or to repel each other. The activity of an ion is particularly influenced by its surroundings. Activities should be used to define equ ...
PDF (chapter_8)
... and the data acquisition system used in this investigation were based on designs previously described by Hill and co-workers17,29 and have been described in detail by Johnson et al.14. The drift length of the ion mobility spectrometer was 13.65 cm and was operated in the positive mode. A drift volta ...
... and the data acquisition system used in this investigation were based on designs previously described by Hill and co-workers17,29 and have been described in detail by Johnson et al.14. The drift length of the ion mobility spectrometer was 13.65 cm and was operated in the positive mode. A drift volta ...
Ionic Strength and Electrostatic Effects in
... Department of Chemical Engineering, McGill University, ...
... Department of Chemical Engineering, McGill University, ...
chapter 13 solubility.notebook
... 1. Learn how to manage big amounts of information. 2. Set up a review plan to follow each day. Make it small (15 min) because you are more likely to stick with that. 3. Sign up for the AP Question of the Day ...
... 1. Learn how to manage big amounts of information. 2. Set up a review plan to follow each day. Make it small (15 min) because you are more likely to stick with that. 3. Sign up for the AP Question of the Day ...
Solubility Equilibria
... The pH. It is another example of applying Le Chatelier’s principle in solubility reactions. o Dissolution of ionic compounds containing OH ions are directly affected by the pH of the solution they are dissolved in. Increasing the pH by adding OH ...
... The pH. It is another example of applying Le Chatelier’s principle in solubility reactions. o Dissolution of ionic compounds containing OH ions are directly affected by the pH of the solution they are dissolved in. Increasing the pH by adding OH ...
Electronic and Electrochemical Properties of Platinum(H) and
... waves are observed. Compounds 2-5 could be oxidized in a single step in the potential range 1.05-l .40 V (Table I; Figure la, b). For compound 1 three oxidation waves were observed (0.87, 1.17 and 1.31 V), the relative intensity varied with the number of cycles (vide infra). All the oxidations are c ...
... waves are observed. Compounds 2-5 could be oxidized in a single step in the potential range 1.05-l .40 V (Table I; Figure la, b). For compound 1 three oxidation waves were observed (0.87, 1.17 and 1.31 V), the relative intensity varied with the number of cycles (vide infra). All the oxidations are c ...
AP Chemistry
... to isolate and test for the presence of one or more of the "group 1" cations (Ag+, Pb2+ and Hg22+) in an unknown. Step 1: Add 2 drops of 6 M HCl to 20 drops of the known solution in a small test tube. Place in a boiling water bath (250 mL beaker half filled with tap water) for 2 minutes and stir occ ...
... to isolate and test for the presence of one or more of the "group 1" cations (Ag+, Pb2+ and Hg22+) in an unknown. Step 1: Add 2 drops of 6 M HCl to 20 drops of the known solution in a small test tube. Place in a boiling water bath (250 mL beaker half filled with tap water) for 2 minutes and stir occ ...
Chapter 3 Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations How
... cannot readily be determined from its constituent elements because the same combination of elements may form many different molecular compounds, each with a different formula. – Nitrogen and oxygen form all of the following ...
... cannot readily be determined from its constituent elements because the same combination of elements may form many different molecular compounds, each with a different formula. – Nitrogen and oxygen form all of the following ...
conductometric and potentiometric determination of the dissociation
... Conductivity measurements are performed always while the stirrer is turned off, after calming of the solution. The electrical conductivity of deionised water should be two orders of magnitude lower than determined later conductivities of acid solutions – one can then assume that it is within the lim ...
... Conductivity measurements are performed always while the stirrer is turned off, after calming of the solution. The electrical conductivity of deionised water should be two orders of magnitude lower than determined later conductivities of acid solutions – one can then assume that it is within the lim ...
Chemistry Review - Hicksville Public Schools
... The ability to conduct electricity depends on the concentration of ions. 3. Arrhenius acids yield H+(aq) ions as the only positive ion in solution. H+(aq) ions may also be written as H3O+(aq) ions (hydronium ions). 4. Arrhenius bases yield OH-(aq) ions as the only negative ion in solution. Organ ...
... The ability to conduct electricity depends on the concentration of ions. 3. Arrhenius acids yield H+(aq) ions as the only positive ion in solution. H+(aq) ions may also be written as H3O+(aq) ions (hydronium ions). 4. Arrhenius bases yield OH-(aq) ions as the only negative ion in solution. Organ ...
Solutions
... substances that do not break up into ions (i.e. sugar, alcohols CxHyOH) Do not conduct an electric current (no mobile ions) Non-electrolytes have a dissociation factor (d.f.) of 1. C12H22O11 C12H22O11 (aq) 1 mole ...
... substances that do not break up into ions (i.e. sugar, alcohols CxHyOH) Do not conduct an electric current (no mobile ions) Non-electrolytes have a dissociation factor (d.f.) of 1. C12H22O11 C12H22O11 (aq) 1 mole ...
Role of Pressure in Transport of F
... all atoms and F- ion is highly reactive nucleophilic reagent and generally forms strong bonds with many Lewis acids in the gas phase [4]. Association reaction of F- with BF3 produces very stable BF4- ion. This reaction proceeds either with radiative or collisional stabilisation both with similar int ...
... all atoms and F- ion is highly reactive nucleophilic reagent and generally forms strong bonds with many Lewis acids in the gas phase [4]. Association reaction of F- with BF3 produces very stable BF4- ion. This reaction proceeds either with radiative or collisional stabilisation both with similar int ...
Ionic compound

In chemistry, an ionic compound is a chemical compound in which ions are held together in a structure by electrostatic forces termed ionic bonds. The positively charged ions are called cations and the negatively charged ions are called anions. These can be simple ions such as the sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl−) in sodium chloride, or polyatomic species such as the carbonate ion (CO32−) in calcium carbonate. Individual ions within an ionic compound usually have multiple nearest neighbours, so are not considered to be part of molecules, but instead part of a continuous three-dimensional network, usually in a crystalline structure.Ionic compounds typically have high melting and boiling points, and are hard and brittle. As solids they are almost always electrically insulating, but when melted or dissolved they become highly conductive, because the ions are mobilized.Ionic compounds without the acidic hydrogen ion (H+), or the basic ions hydroxide (OH−) or oxide (O2−), are also known as salts and can be formed by acid-base reactions. Ionic compounds containing hydrogen ions are classified as acids and compounds containing hydroxide or oxide ions are classified as bases.