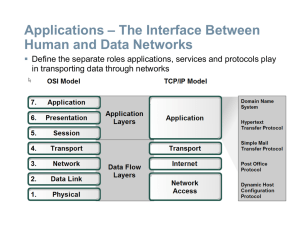
Lecture19 - The University of Texas at Dallas
... • Moves information between two hosts that are not physically connected • Uses logical addressing ...
... • Moves information between two hosts that are not physically connected • Uses logical addressing ...
Semester 3 Chapter 1 - IIS Windows Server
... A node needing to transmit listens for activity on the media. If there is none, it transmits. The node continues to listen. A collision is detected by a spike in voltage (a bit can only be a 0 or a 1--it cannot be a 2) The node generates a jam signal to tell all devices to stop transmitting for a ra ...
... A node needing to transmit listens for activity on the media. If there is none, it transmits. The node continues to listen. A collision is detected by a spike in voltage (a bit can only be a 0 or a 1--it cannot be a 2) The node generates a jam signal to tell all devices to stop transmitting for a ra ...
Network Layer (Congestion and QoS)
... occasional lapses is QoS. Also, apps might not know what its CPU requirements are. Hence routers must convert a set of specifications to resource requirements and then decide whether to accept or reject the flow. ...
... occasional lapses is QoS. Also, apps might not know what its CPU requirements are. Hence routers must convert a set of specifications to resource requirements and then decide whether to accept or reject the flow. ...
Liverpool HEP - Site Report June 2010 John Bland, Robert Fay
... • Nodes are 3GHz P4, 1-1.5GB RAM, 120GB disk – 5.32 HEPSPEC06 • 2 racks (80 nodes) shared with other departments • 18 racks (~700 nodes) primarily for LCG jobs • 1 rack (40 nodes) for general purpose local batch processing • 3 racks retired (Dell nodes replaced with other hardware) ...
... • Nodes are 3GHz P4, 1-1.5GB RAM, 120GB disk – 5.32 HEPSPEC06 • 2 racks (80 nodes) shared with other departments • 18 racks (~700 nodes) primarily for LCG jobs • 1 rack (40 nodes) for general purpose local batch processing • 3 racks retired (Dell nodes replaced with other hardware) ...
PowerPoint Title
... They offer alternatives to the last-kilometer wireline network Beyond the last-kilometer, both rely on similar network connections and transmission support infrastructure. – For 3G, the wireless link is from the end-user device to the ...
... They offer alternatives to the last-kilometer wireline network Beyond the last-kilometer, both rely on similar network connections and transmission support infrastructure. – For 3G, the wireless link is from the end-user device to the ...
Slide 1
... – multi-port device that directs data between networks and nodes using logical addressing, – switches devices that connect to LANs where multiple paths exist, determining best path. – Used to interconnect LANs and WANs – Each port can be configured for a unique network address – Can connect differen ...
... – multi-port device that directs data between networks and nodes using logical addressing, – switches devices that connect to LANs where multiple paths exist, determining best path. – Used to interconnect LANs and WANs – Each port can be configured for a unique network address – Can connect differen ...
CMPT 880: Internet Architectures and Protocols
... ISPs get their address space from ICANN ICANN: Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers allocates addresses, manages DNS and assigns domain names ...
... ISPs get their address space from ICANN ICANN: Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers allocates addresses, manages DNS and assigns domain names ...
Lektion 1-Introduktion
... An old name for routers is gateways Forward packets between networks (route and switch) Transform packets as necessary to meet standards for each network A Windows PC can act as a router if it has more than one NIC, and IP forwarding is enabled in the networking settings. ...
... An old name for routers is gateways Forward packets between networks (route and switch) Transform packets as necessary to meet standards for each network A Windows PC can act as a router if it has more than one NIC, and IP forwarding is enabled in the networking settings. ...
ppt
... Allow distributed management Allow host attachment with a low level of effort Be cost effective ...
... Allow distributed management Allow host attachment with a low level of effort Be cost effective ...
IPv4 to IPv6 Migration strategies
... Will provide larger availability of mobile networks It is good for mobile networks for its low cost, Higher speed of deployment For wireless, larger IP address is required. ...
... Will provide larger availability of mobile networks It is good for mobile networks for its low cost, Higher speed of deployment For wireless, larger IP address is required. ...
A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e
... Networking Adapters and Ports (cont’d.) • WI-FI wireless adapters – 802.11b/g/n connections use a variety of devices – Laptops sold today have antenna embedded inside Figure 17-16 Four different types of wireless network adapters: (a) wireless NIC that fits in a PCI slot; (b) onboard wireless with ...
... Networking Adapters and Ports (cont’d.) • WI-FI wireless adapters – 802.11b/g/n connections use a variety of devices – Laptops sold today have antenna embedded inside Figure 17-16 Four different types of wireless network adapters: (a) wireless NIC that fits in a PCI slot; (b) onboard wireless with ...
CMPT 880: Internet Architectures and Protocols
... ISPs get their address space from ICANN ICANN: Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers allocates addresses, manages DNS and assigns domain names ...
... ISPs get their address space from ICANN ICANN: Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers allocates addresses, manages DNS and assigns domain names ...
CCNA 1 Module 6 Ethernet Fundamentals
... Nodes monitor the bus (or Ether) to determine if it is busy. A node wishing to send data waits for an idle condition then transmits its message. Collisions can occur when two nodes transmit at the same time, thus nodes must monitor the cable when they transmit. When a collision occurs, both nodes st ...
... Nodes monitor the bus (or Ether) to determine if it is busy. A node wishing to send data waits for an idle condition then transmits its message. Collisions can occur when two nodes transmit at the same time, thus nodes must monitor the cable when they transmit. When a collision occurs, both nodes st ...
Internet Programming - Seneca
... This sends discrete messages rather than a stream of bytes Each message can be sent to a different computer UDP is much more efficient than TCP/IP UDP is used for sending audio and video ...
... This sends discrete messages rather than a stream of bytes Each message can be sent to a different computer UDP is much more efficient than TCP/IP UDP is used for sending audio and video ...
Slide 1
... Layer 3 is not concerned with or even aware of the type of data contained inside of a packet. This responsibility is the role of the upper layers as required. Unreliable: IP does not have the capability or responsibility to manage, and recover from, undelivered or corrupt packets. TCP’s resp ...
... Layer 3 is not concerned with or even aware of the type of data contained inside of a packet. This responsibility is the role of the upper layers as required. Unreliable: IP does not have the capability or responsibility to manage, and recover from, undelivered or corrupt packets. TCP’s resp ...
Chapter 15 Local Area Networks
... • Order of magnitude increase in performance compared to software-based router • Flow-based switch tries to enhance performance by identifying flows of IP packets —Same source and destination —Done by observing ongoing traffic or using a special flow label in packet header (IPv6) ...
... • Order of magnitude increase in performance compared to software-based router • Flow-based switch tries to enhance performance by identifying flows of IP packets —Same source and destination —Done by observing ongoing traffic or using a special flow label in packet header (IPv6) ...
7. Medium Access Control Sublayer (17.3.) File
... Classic Ethernet (4) – Performance Efficient for large frames, even with many senders • Degrades for small frames (and long LANs) ...
... Classic Ethernet (4) – Performance Efficient for large frames, even with many senders • Degrades for small frames (and long LANs) ...
Chapter 15 Local Area Networks
... • Order of magnitude increase in performance compared to software-based router • Flow-based switch tries to enhance performance by identifying flows of IP packets —Same source and destination —Done by observing ongoing traffic or using a special flow label in packet header (IPv6) ...
... • Order of magnitude increase in performance compared to software-based router • Flow-based switch tries to enhance performance by identifying flows of IP packets —Same source and destination —Done by observing ongoing traffic or using a special flow label in packet header (IPv6) ...
ch10.ppt
... • Client/server model (domain) – Access to network resources controlled by an NOS – Server is called a domain controller ...
... • Client/server model (domain) – Access to network resources controlled by an NOS – Server is called a domain controller ...
Application Layer Functionality and Protocols
... Managing TCP Sessions Describe the mechanisms in TCP that manage the interrelationship between window size, data loss and congestion during a session ...
... Managing TCP Sessions Describe the mechanisms in TCP that manage the interrelationship between window size, data loss and congestion during a session ...
Client-Server Architectures and the Internet
... Protocols at this level transmit data in a network representation that is independent of the representations used in individual computers, which may differ. Encryption is also performed in this layer, if required. At this level reliability and adaptation are performed, such as detection of failures ...
... Protocols at this level transmit data in a network representation that is independent of the representations used in individual computers, which may differ. Encryption is also performed in this layer, if required. At this level reliability and adaptation are performed, such as detection of failures ...
ppt
... • ISO and the ITU are huge standards bodies that handle the world-wide telephone system and other global standards • The Internet protocols and reference model were created by a small group of about a dozen researchers – It is easy to see why the standards organizations might be confident that they ...
... • ISO and the ITU are huge standards bodies that handle the world-wide telephone system and other global standards • The Internet protocols and reference model were created by a small group of about a dozen researchers – It is easy to see why the standards organizations might be confident that they ...