Lecture 14
... Using a common syntax. If necessary, the data are converted to a form expected by the destination. This may include a different character code, the use of encryption, and/or compression. Segmenting the data. TCP may break the data block into a number of segments, keeping track of their sequence. Eac ...
... Using a common syntax. If necessary, the data are converted to a form expected by the destination. This may include a different character code, the use of encryption, and/or compression. Segmenting the data. TCP may break the data block into a number of segments, keeping track of their sequence. Eac ...
Lecture 20: Transport layer
... reorder or duplicate (if the sender sends only once). In addition, packets will either get to the receiver or get lost. – When two hosts are connected by a network, packets can be duplicated, delayed, lost, reordered. – Implication: The problems to be addressed in the transport layer are very simila ...
... reorder or duplicate (if the sender sends only once). In addition, packets will either get to the receiver or get lost. – When two hosts are connected by a network, packets can be duplicated, delayed, lost, reordered. – Implication: The problems to be addressed in the transport layer are very simila ...
Chapter 9b IPv6 Subnetting
... the configuration. The network administrator has already configured some commands on the routers. Do not to erase or modify those configurations. Your task is to complete the IPv4 and IPv6 addressing scheme, implement IPv4 and IPv6 addressing, and verify connectivity. ...
... the configuration. The network administrator has already configured some commands on the routers. Do not to erase or modify those configurations. Your task is to complete the IPv4 and IPv6 addressing scheme, implement IPv4 and IPv6 addressing, and verify connectivity. ...
Network Models
... The layers in the TCP/IP protocol suite do not exactly match those in the OSI model. The original TCP/IP protocol suite was defined as having four layers: host-tonetwork, internet, transport, and application. However, when TCP/IP is compared to OSI, we can say that the TCP/IP protocol suite is made ...
... The layers in the TCP/IP protocol suite do not exactly match those in the OSI model. The original TCP/IP protocol suite was defined as having four layers: host-tonetwork, internet, transport, and application. However, when TCP/IP is compared to OSI, we can say that the TCP/IP protocol suite is made ...
Cisco Systems Networking Academy S2 C 11
... • When topology changes routers must recompute routes (disrupts routing) • Time to reconvergence varies with routing protocols ...
... • When topology changes routers must recompute routes (disrupts routing) • Time to reconvergence varies with routing protocols ...
The Network Layer
... Implementation of Connectionless Service Implementation of Connection-Oriented Service Comparison of Virtual-Circuit and Datagram Subnets ...
... Implementation of Connectionless Service Implementation of Connection-Oriented Service Comparison of Virtual-Circuit and Datagram Subnets ...
The Network Layer
... Implementation of Connectionless Service Implementation of Connection-Oriented Service Comparison of Virtual-Circuit and Datagram Subnets ...
... Implementation of Connectionless Service Implementation of Connection-Oriented Service Comparison of Virtual-Circuit and Datagram Subnets ...
Heterogeneity-aware Ad hoc Networking
... The newly proposed scheme for AODV for efficient operation in presence of unidirectional links – Whenever a node detects a unidirectional link to its neighbor, it blacklists that neighbor from which a link is unidirectional. – Later when the node receives a RREQ from one of the nodes in its blacklis ...
... The newly proposed scheme for AODV for efficient operation in presence of unidirectional links – Whenever a node detects a unidirectional link to its neighbor, it blacklists that neighbor from which a link is unidirectional. – Later when the node receives a RREQ from one of the nodes in its blacklis ...
Internetworking and Internet Global Addresses
... ⇒ restricted within the same LAN (a RARP server is needed for each network) ...
... ⇒ restricted within the same LAN (a RARP server is needed for each network) ...
LAB02-Network_Connectivity
... utility NBTSTAT since the logged on account name is part of the naming information maintained locally by NBT. NBT runs on each Windows PC and functions as a local naming agent for TCP/IP. If a network address is not locally cached, NBT gets the information from a WINS server or the LMHOST file. NBTS ...
... utility NBTSTAT since the logged on account name is part of the naming information maintained locally by NBT. NBT runs on each Windows PC and functions as a local naming agent for TCP/IP. If a network address is not locally cached, NBT gets the information from a WINS server or the LMHOST file. NBTS ...
UDP—User Datagram Protocol - Department of Computer and
... DNS, RTP, SNMP based on the destination port # in the header. i.e., UDP can support multiple applications in the same end systems. – (Optionally) check the integrity of entire UDP. (recall IP only checks the integrity of IP header.) • If source does not want to compute checksum, fill checksum with a ...
... DNS, RTP, SNMP based on the destination port # in the header. i.e., UDP can support multiple applications in the same end systems. – (Optionally) check the integrity of entire UDP. (recall IP only checks the integrity of IP header.) • If source does not want to compute checksum, fill checksum with a ...
Application and Circuit Gateways
... Many application clients can be configured to use a specific ALG (proxy) by the end user ...
... Many application clients can be configured to use a specific ALG (proxy) by the end user ...
Architektura software defined data center
... taking/restoring a checkpoint. Restoring a checkpoint is like restoring a clean backup of the server. Linux: Linux virtual machines flush their file system buffers to create a file system consistent checkpoint. Production as default: New virtual machines will use production checkpoints with a fallba ...
... taking/restoring a checkpoint. Restoring a checkpoint is like restoring a clean backup of the server. Linux: Linux virtual machines flush their file system buffers to create a file system consistent checkpoint. Production as default: New virtual machines will use production checkpoints with a fallba ...
Introduction - Ceng Anadolu
... – no need to be allocated range of addresses from ISP: - just one IP address is used for all devices – can change addresses of devices in local network without notifying outside world – can change ISP without changing addresses of devices in local network – devices inside local net not explicitly ad ...
... – no need to be allocated range of addresses from ISP: - just one IP address is used for all devices – can change addresses of devices in local network without notifying outside world – can change ISP without changing addresses of devices in local network – devices inside local net not explicitly ad ...
Networks - Faculty - Genesee Community College
... The Network layer encapsulation allows the Transport layer contents to be passed to the destination within a network or on another network entirely. Communication between networks is facilitated by a process called routing. Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to: ...
... The Network layer encapsulation allows the Transport layer contents to be passed to the destination within a network or on another network entirely. Communication between networks is facilitated by a process called routing. Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to: ...
Chapter 36
... Networking technologies, such as Ethernet, Token Ring and FDDI provide a data link layer function, that is, they allow a reliable connection between one node and another on the same network. They do not provide for inter-networking where data can be transferred from one network to another or one net ...
... Networking technologies, such as Ethernet, Token Ring and FDDI provide a data link layer function, that is, they allow a reliable connection between one node and another on the same network. They do not provide for inter-networking where data can be transferred from one network to another or one net ...
Basics of Networking
... Basics of Networking Class B - This class is used for medium-sized networks. A good example is a large college campus. IP addresses with a first octet from 128 to 191 are part of this class. Class B addresses also include the second octet as part of the Net identifier. ...
... Basics of Networking Class B - This class is used for medium-sized networks. A good example is a large college campus. IP addresses with a first octet from 128 to 191 are part of this class. Class B addresses also include the second octet as part of the Net identifier. ...
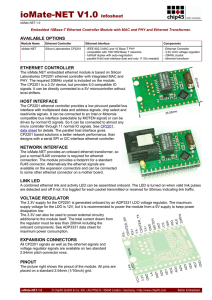
ioMate-NET V1.0 Infosheet
... CHIP45 products lacking protective enclosures are subject to damage by ESD and, hence, may only be unpacked, handled or operated in environments in which sufficient precautionary measures have been taken in respect to ESD-dangers. It is also necessary that only appropriately trained personnel (such ...
... CHIP45 products lacking protective enclosures are subject to damage by ESD and, hence, may only be unpacked, handled or operated in environments in which sufficient precautionary measures have been taken in respect to ESD-dangers. It is also necessary that only appropriately trained personnel (such ...
DS-CH3 - RU - Ryerson University
... Protocols at this level transmit data in a network representation that is independent of the representations used in individual computers, which may differ. Encryption is also performed in this layer, if required. At this level reliability and adaptation are performed, such as detection of failures ...
... Protocols at this level transmit data in a network representation that is independent of the representations used in individual computers, which may differ. Encryption is also performed in this layer, if required. At this level reliability and adaptation are performed, such as detection of failures ...
Dealing with multiple clients
... continuing with 10BASE-T, was designed for point-to-point links only and all termination was built into the device. This changed hubs from a specialist device used at the center of large networks to a device that every twisted pair-based network with more than two machines had to use. The tree struc ...
... continuing with 10BASE-T, was designed for point-to-point links only and all termination was built into the device. This changed hubs from a specialist device used at the center of large networks to a device that every twisted pair-based network with more than two machines had to use. The tree struc ...
3rd Edition: Chapter 4
... range of addresses not needed from ISP: just one IP address for all devices can change addresses of devices in local network ...
... range of addresses not needed from ISP: just one IP address for all devices can change addresses of devices in local network ...
429-07a-TCPIP
... Make a call to the “resolver” (or, in most PCs, the “stub resolver”) to get a numeric address. The answer may come from local storage, or may itself require a network transmission using the Domain Name System (DNS) protocols. The name space and the address space are unrelated, except that they ...
... Make a call to the “resolver” (or, in most PCs, the “stub resolver”) to get a numeric address. The answer may come from local storage, or may itself require a network transmission using the Domain Name System (DNS) protocols. The name space and the address space are unrelated, except that they ...