Data Structures
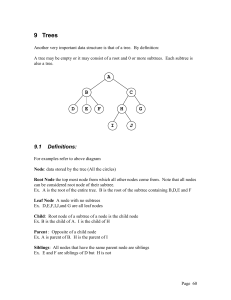
... Tree ... a linked list of nodes each of which give rise to multiple sub-nodes all emanating from a single node ...
... Tree ... a linked list of nodes each of which give rise to multiple sub-nodes all emanating from a single node ...
Data Structures
... 12.2 The ArrayList and LinkedList Classes 12.3 Example: A Stack Application and Class 12.4 Example: A Queue Class 12.5 An Introduction to Trees Part of the Picture: Data Structures 12.6 Graphical/Internet Java: A PolygonSketcher Class ...
... 12.2 The ArrayList and LinkedList Classes 12.3 Example: A Stack Application and Class 12.4 Example: A Queue Class 12.5 An Introduction to Trees Part of the Picture: Data Structures 12.6 Graphical/Internet Java: A PolygonSketcher Class ...
1. The memory address of the first element of an array is called A
... 43. The space factor when determining the efficiency of algorithm is measured by A. Counting the maximum memory needed by the algorithm B. Counting the minimum memory needed by the algorithm C. Counting the average memory needed by the algorithm D. Counting the maximum disk space needed by the algo ...
... 43. The space factor when determining the efficiency of algorithm is measured by A. Counting the maximum memory needed by the algorithm B. Counting the minimum memory needed by the algorithm C. Counting the average memory needed by the algorithm D. Counting the maximum disk space needed by the algo ...
Algorithms and data structures—topic summary
... various calculations such as determining the size and height of trees. As one application, we consider ropes: full binary trees where each child is either a string or is itself another rope. The rope defines a string formed by the concatenation of the children. 5.2 Perfect binary trees A perfect bin ...
... various calculations such as determining the size and height of trees. As one application, we consider ropes: full binary trees where each child is either a string or is itself another rope. The rope defines a string formed by the concatenation of the children. 5.2 Perfect binary trees A perfect bin ...
Trees, Binary search trees
... • A binary tree is a tree in which no node has more than two children, and every child is either a left child or a right child, even if it's the only child its parent has. ...
... • A binary tree is a tree in which no node has more than two children, and every child is either a left child or a right child, even if it's the only child its parent has. ...
lecture 6
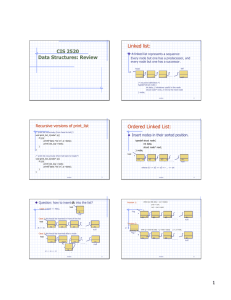
... • A list L is a linear sequence of elements. • The first element of the list is the head and the last is the tail. When both are null, the list is empty • Each element has a predecessor and a successor • The list operations are: ...
... • A list L is a linear sequence of elements. • The first element of the list is the head and the last is the tail. When both are null, the list is empty • Each element has a predecessor and a successor • The list operations are: ...
Lecture 16 Student Notes
... A suffix tree is a compressed trie built on all |T | suffixes of T , with $ appended. For example, if our text is the string T = banana$, then our suffix tree will be built on {banana$, anana$, nana$, ana$, na$, a$}. The suffix starting at the ith index is denoted T [i :]. For a non-leaf node of the suffix tr ...
... A suffix tree is a compressed trie built on all |T | suffixes of T , with $ appended. For example, if our text is the string T = banana$, then our suffix tree will be built on {banana$, anana$, nana$, ana$, na$, a$}. The suffix starting at the ith index is denoted T [i :]. For a non-leaf node of the suffix tr ...
Modeling Bill-Of-Material with Tree Data Structure: Case Study in
... Figure xx indicates that the structure of BOM resembles a tree. Therefore, the data structure of the BOM is best represented by the tree data structure. A tree structure is a way of representing the hierarchical nature of a structure in a graphical form. It is named a "tree structure" because the gr ...
... Figure xx indicates that the structure of BOM resembles a tree. Therefore, the data structure of the BOM is best represented by the tree data structure. A tree structure is a way of representing the hierarchical nature of a structure in a graphical form. It is named a "tree structure" because the gr ...
Chapter 2: Introduction to Microprocessor
... Linked List is a linear Data structure. Linked List contains list of nodes. Each node contains two parts: 1. Data Part 2. Address of Next Node (Link to next node in the list) The nodes in the linked list represents in terms of structures. aman 101 ...
... Linked List is a linear Data structure. Linked List contains list of nodes. Each node contains two parts: 1. Data Part 2. Address of Next Node (Link to next node in the list) The nodes in the linked list represents in terms of structures. aman 101 ...
Binary Trees
... • There are many kinds of trees – Every binary tree is a tree – Every list is kind of a tree (think of “next” as the one child) • There are many kinds of binary trees – Every binary search tree is a binary tree – Later: A binary heap is a different kind of binary tree • A tree can be balanced or not ...
... • There are many kinds of trees – Every binary tree is a tree – Every list is kind of a tree (think of “next” as the one child) • There are many kinds of binary trees – Every binary search tree is a binary tree – Later: A binary heap is a different kind of binary tree • A tree can be balanced or not ...
Data Structures
... of list. Much slower than ArrayList for access by position and iterating over. Uses a hash table. Requires that stored objects override hashCode() and equals(). Uses a doubly linked list as well as a hash table. This allows elements to be iterated over in insertion order rather than unpredictable or ...
... of list. Much slower than ArrayList for access by position and iterating over. Uses a hash table. Requires that stored objects override hashCode() and equals(). Uses a doubly linked list as well as a hash table. This allows elements to be iterated over in insertion order rather than unpredictable or ...
Basic Element of Data Structures like linked list, stack and queue
... into n≥0 disjoint set.T1, T2,.. Tn, where each of these subset is a tree. The set set.T1, T2,.. Tn are called the sub tree of the root. ...
... into n≥0 disjoint set.T1, T2,.. Tn, where each of these subset is a tree. The set set.T1, T2,.. Tn are called the sub tree of the root. ...
Quadtree
A quadtree is a tree data structure in which each internal node has exactly four children. Quadtrees are most often used to partition a two-dimensional space by recursively subdividing it into four quadrants or regions. The regions may be square or rectangular, or may have arbitrary shapes. This data structure was named a quadtree by Raphael Finkel and J.L. Bentley in 1974. A similar partitioning is also known as a Q-tree. All forms of quadtrees share some common features: They decompose space into adaptable cells Each cell (or bucket) has a maximum capacity. When maximum capacity is reached, the bucket splits The tree directory follows the spatial decomposition of the quadtree.