CS 261 – Recitation 1 - Classes
... • Takes O(log N) time for searching, insertion, and deletion ...
... • Takes O(log N) time for searching, insertion, and deletion ...
binary search tree
... The depth of an “average” binary tree is considerably smaller than N, even though in the worst case, the depth can be as large as N – 1. Worst-case binary tree ...
... The depth of an “average” binary tree is considerably smaller than N, even though in the worst case, the depth can be as large as N – 1. Worst-case binary tree ...
Lecture No. 41 - Taleem-E
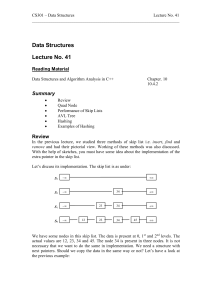
... Let’s analyze this data structure and see how much time is required for search and deletion process. The analysis is probability-based and needs lot of time. We will do this in some other course. Let’s discuss about the performance of the skip list regarding insert, find and remove methods. In a ski ...
... Let’s analyze this data structure and see how much time is required for search and deletion process. The analysis is probability-based and needs lot of time. We will do this in some other course. Let’s discuss about the performance of the skip list regarding insert, find and remove methods. In a ski ...
Building Trees
... Initially trees may be unbalanced Worst case, they may be so-called leftspine (or right-spine) trees, i.e. no different from linear lists, but more costly to process ...
... Initially trees may be unbalanced Worst case, they may be so-called leftspine (or right-spine) trees, i.e. no different from linear lists, but more costly to process ...
ppt - Dave Reed
... tricky, since removing an internal node means rerouting pointers must maintain binary tree structure ...
... tricky, since removing an internal node means rerouting pointers must maintain binary tree structure ...
ppt
... A regular queue is a first-in and first-out data structure. Elements are appended to the end of the queue and are removed from the beginning of the queue. In a priority queue, elements are assigned with priorities. When accessing elements, the element with the highest priority is removed first. A pr ...
... A regular queue is a first-in and first-out data structure. Elements are appended to the end of the queue and are removed from the beginning of the queue. In a priority queue, elements are assigned with priorities. When accessing elements, the element with the highest priority is removed first. A pr ...
thm01 - persistent ds_1
... • Make a copy of the node before changing it to point to the new child. Cascade the change back until root is reached. Restructuring costs O(height_of_tree) per update operation • Every modification creates a new root • Maintain an array of roots indexed by timestamp. ...
... • Make a copy of the node before changing it to point to the new child. Cascade the change back until root is reached. Restructuring costs O(height_of_tree) per update operation • Every modification creates a new root • Maintain an array of roots indexed by timestamp. ...
Search Trees for Strings
... Search Trees for Strings A balanced binary search tree is a powerful data structure that stores a set of objects and supports many operations including: Insert and Delete. Lookup: Find if a given object is in the set, and if it is, possibly return some data associated with the object. Range query: F ...
... Search Trees for Strings A balanced binary search tree is a powerful data structure that stores a set of objects and supports many operations including: Insert and Delete. Lookup: Find if a given object is in the set, and if it is, possibly return some data associated with the object. Range query: F ...
continued
... A node contains two references (to left and right child nodes) A node contains a data field The data field has type Comparable, so that you can compare the values in order to place them in the correct position in the binary search tree ...
... A node contains two references (to left and right child nodes) A node contains a data field The data field has type Comparable, so that you can compare the values in order to place them in the correct position in the binary search tree ...
Programming for GCSE - Teaching London Computing
... • Where do lists and dictionaries come from? • Understand the problem • Introduce the following data structures ...
... • Where do lists and dictionaries come from? • Understand the problem • Introduce the following data structures ...
Scalable Classification Algorithms
... Choose overall split from the attribute and split point with the lowest GINI ...
... Choose overall split from the attribute and split point with the lowest GINI ...
Laboratory 6: Binary trees I. THEORETICAL ASPECTS
... 10. The current node cannot be inserted into the binary tree. In this situation we have to call the equivalence function. Tree traversal Tree traversal is a form of graph traversal and refers to the process of visiting (examining or updating) each node in a tree data structure, exactly once, in a sy ...
... 10. The current node cannot be inserted into the binary tree. In this situation we have to call the equivalence function. Tree traversal Tree traversal is a form of graph traversal and refers to the process of visiting (examining or updating) each node in a tree data structure, exactly once, in a sy ...
B+ Tree example
... No, because all B+ trees are inherently balanced, which make it easy for us to manipulate the data. ...
... No, because all B+ trees are inherently balanced, which make it easy for us to manipulate the data. ...
Lecture 15 Student Notes
... rightmost element of the tree created so far. For example, if we have a tree for which the subarray [2, 4, 5] has been inserted, and the next element is 3, then insertion has the following result: ...
... rightmost element of the tree created so far. For example, if we have a tree for which the subarray [2, 4, 5] has been inserted, and the next element is 3, then insertion has the following result: ...
PowerPoint 2007
... A collection of elements (values or variables), each identified by at least one array index or key ...
... A collection of elements (values or variables), each identified by at least one array index or key ...
Chapter11-OSedition7Final
... • transfers data in and out as a stream of bytes • no block structure • terminals, printers, communications ports, and most other devices that are not secondary storage are examples ...
... • transfers data in and out as a stream of bytes • no block structure • terminals, printers, communications ports, and most other devices that are not secondary storage are examples ...
Chapter 11 I/O Management and Disk Scheduling
... • transfers data in and out as a stream of bytes • no block structure • terminals, printers, communications ports, and most other devices that are not secondary storage are examples ...
... • transfers data in and out as a stream of bytes • no block structure • terminals, printers, communications ports, and most other devices that are not secondary storage are examples ...
B-tree
In computer science, a B-tree is a tree data structure that keeps data sorted and allows searches, sequential access, insertions, and deletions in logarithmic time. The B-tree is a generalization of a binary search tree in that a node can have more than two children (Comer 1979, p. 123). Unlike self-balancing binary search trees, the B-tree is optimized for systems that read and write large blocks of data. B-trees are a good example of a data structure for external memory. It is commonly used in databases and filesystems.