pptx - The University of Texas at Arlington
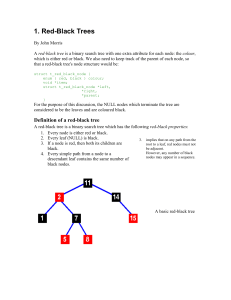
... • If Y is the parent of X, then X is called a child of Y. – The root has no parents. – Every other node, except for the root, has exactly one parent. ...
... • If Y is the parent of X, then X is called a child of Y. – The root has no parents. – Every other node, except for the root, has exactly one parent. ...
Binary Search Trees
... Time: Running time is O(h), where h is the height of the tree. For both the TREE-SUCCESSOR and TREE-PREDECESSOR procedures, in both cases, we visit nodes on a path down the tree or up the tree. ...
... Time: Running time is O(h), where h is the height of the tree. For both the TREE-SUCCESSOR and TREE-PREDECESSOR procedures, in both cases, we visit nodes on a path down the tree or up the tree. ...
ICS 220 – Data Structures and Algorithms
... • B+ Trees are variations on a B-Tree, where the internal nodes are simply indexes allowing quicker searching of the tree. • The values stored in index nodes are repeated in the leaf nodes – Essentially all data is stored in leaf nodes, with indexes used to point to the correct leaf. ...
... • B+ Trees are variations on a B-Tree, where the internal nodes are simply indexes allowing quicker searching of the tree. • The values stored in index nodes are repeated in the leaf nodes – Essentially all data is stored in leaf nodes, with indexes used to point to the correct leaf. ...
Trees
... Decision procedures (Hayne’s manual for repairing a car) The local sewage system As a data structure (for storing information) As an ephemeral structure, as in combinatorial search (backtracking) Your family tree. ...
... Decision procedures (Hayne’s manual for repairing a car) The local sewage system As a data structure (for storing information) As an ephemeral structure, as in combinatorial search (backtracking) Your family tree. ...
Proofs, Recursion and Analysis of Algorithms
... algorithm that solves the search problem for an n-element list by comparing the target element x to the list items must do at least └log n┘ + 1 comparisons in the worst case. Since binary search does no more work than this required minimum amount, binary search is an optimal algorithm in its worst-c ...
... algorithm that solves the search problem for an n-element list by comparing the target element x to the list items must do at least └log n┘ + 1 comparisons in the worst case. Since binary search does no more work than this required minimum amount, binary search is an optimal algorithm in its worst-c ...