Dynamic FM-Index for a Collection of Texts with
... Sequence-based indices allow to search efficiently for any substring within the text. Classical examples of such sequence-based indices are the suffix tree and the suffix array. The problem with these indices is that they require space several times the text size in addition to the text itself. Thus ...
... Sequence-based indices allow to search efficiently for any substring within the text. Classical examples of such sequence-based indices are the suffix tree and the suffix array. The problem with these indices is that they require space several times the text size in addition to the text itself. Thus ...
Hashing hash functions collision resolution
... no effective alternative for unordered keys faster for simple keys (a few arithmetic ops versus lg N compares) (Java) better system support for strings [cached hashcode] does your hash function produce random values for your key type?? ...
... no effective alternative for unordered keys faster for simple keys (a few arithmetic ops versus lg N compares) (Java) better system support for strings [cached hashcode] does your hash function produce random values for your key type?? ...
Optimizing Hash-Array Mapped Tries for Fast and Lean Immutable
... to functional/object-oriented programming such as practiced by Scala1 and Clojure2 programmers. With the advance of functional language constructs in Java 8 and functional APIs such as the stream processing API [6], immutable collections become more relevant to Java as well. Immutability for collect ...
... to functional/object-oriented programming such as practiced by Scala1 and Clojure2 programmers. With the advance of functional language constructs in Java 8 and functional APIs such as the stream processing API [6], immutable collections become more relevant to Java as well. Immutability for collect ...
A practical scalable distributed B-tree.
... Sinfonia is a data sharing service that, like our B-tree, is composed of a client library and a set of servers called memory nodes (see Figure 2). Each memory node exports a linear address space without any structure imposed by Sinfonia. Sinfonia ensures the memory nodes are fault-tolerant, offering ...
... Sinfonia is a data sharing service that, like our B-tree, is composed of a client library and a set of servers called memory nodes (see Figure 2). Each memory node exports a linear address space without any structure imposed by Sinfonia. Sinfonia ensures the memory nodes are fault-tolerant, offering ...
Hierarchical range queries on encrypted data
... outsourced data. One is to de ne a privacy policy between the data creator and the entity storing the data. Another one is to present an access control mechanism for the data manipulation. After taking a closer look at these methods, none of them provides su cient guarantees of protecting the stored ...
... outsourced data. One is to de ne a privacy policy between the data creator and the entity storing the data. Another one is to present an access control mechanism for the data manipulation. After taking a closer look at these methods, none of them provides su cient guarantees of protecting the stored ...
Lab 6g Searching and Sorting An Integer List
... IntegerList(int size)—creates a new list of size elements. Elements are initialized to 0. void randomize()—fills the list with random integers between 1 and 100, inclusive. void print()—prints the array elements and indices int search(int target)—looks for value target in the list using a linear (al ...
... IntegerList(int size)—creates a new list of size elements. Elements are initialized to 0. void randomize()—fills the list with random integers between 1 and 100, inclusive. void print()—prints the array elements and indices int search(int target)—looks for value target in the list using a linear (al ...
Interfaces
... "natural ordering" of objects. For strings, it is alphabetic ordering. For Double and Integer it is what we already know: 3 < 4 and 1.2 > 1.1, for example. In the case of BankAccount, we will see that one BankAccount can be made to be "less than" another when its ID precedes the other's ID alphabeti ...
... "natural ordering" of objects. For strings, it is alphabetic ordering. For Double and Integer it is what we already know: 3 < 4 and 1.2 > 1.1, for example. In the case of BankAccount, we will see that one BankAccount can be made to be "less than" another when its ID precedes the other's ID alphabeti ...
Linked Lists
... In array implementation of the linked lists a fixed set of nodes represented by an array is established at the beginning of the execution A pointer to a node is represented by the relative position of the node within the array. In array implementation, it is not possible to determine the number of n ...
... In array implementation of the linked lists a fixed set of nodes represented by an array is established at the beginning of the execution A pointer to a node is represented by the relative position of the node within the array. In array implementation, it is not possible to determine the number of n ...
External Memory Three-Sided Range Reporting and Top
... trees are essentially just balanced heap-ordered binary trees where the root stores the point with minimum y-value and the remaining points are distributed among the left and right children so that all points in the left subtree have smaller x-value than points in the right subtree. Frederickson [10 ...
... trees are essentially just balanced heap-ordered binary trees where the root stores the point with minimum y-value and the remaining points are distributed among the left and right children so that all points in the left subtree have smaller x-value than points in the right subtree. Frederickson [10 ...
CS2007Ch12C
... All previous searching techniques require a specified amount of time (O(logn) or O(n)) Time usually depends on number of elements (n) stored in the table In some situations searching should be almost instantaneous -- how? ...
... All previous searching techniques require a specified amount of time (O(logn) or O(n)) Time usually depends on number of elements (n) stored in the table In some situations searching should be almost instantaneous -- how? ...
public boolean - Pitt Computer Science
... the actual methods however they want An interface variable can be used to reference any object that implements that interface • However, only the interface methods are accessible through the interface reference ...
... the actual methods however they want An interface variable can be used to reference any object that implements that interface • However, only the interface methods are accessible through the interface reference ...
ws0708-lecture-12-PersistentDS
... • Creates a set of search trees, one per update, having different roots but sharing common subtrees • Copy only the nodes in which changes are made, such that any node in the current version that contains a pointer to a node must itself be copied • In our linked data structure, each node contains po ...
... • Creates a set of search trees, one per update, having different roots but sharing common subtrees • Copy only the nodes in which changes are made, such that any node in the current version that contains a pointer to a node must itself be copied • In our linked data structure, each node contains po ...
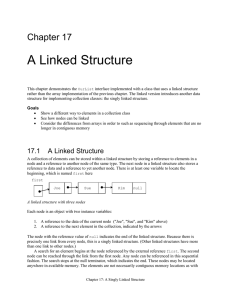
Chapter17
... item, 23, is added Copyright © 2014, 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley ...
... item, 23, is added Copyright © 2014, 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley ...
Abstract Efficient Data Structures for Tamper-Evident Logging
... Tamper-evident logs are fundamentally different: An untrusted logger is the sole author of the log and is responsible for both building and signing it. A log is a dynamic data structure, with the author signing a stream of commitments, a new commitment each time a new event is added to the log. Each ...
... Tamper-evident logs are fundamentally different: An untrusted logger is the sole author of the log and is responsible for both building and signing it. A log is a dynamic data structure, with the author signing a stream of commitments, a new commitment each time a new event is added to the log. Each ...
Data Representation and Linear Structures
... 3.1. A shortcoming of the LinearList class is the need to predict the maximum possible size of the list. One possible improvement is to start the MaxSize with 1, then double the size whenever a need arises, create a new list with the doubled size, copy over the values, finally delete the original li ...
... 3.1. A shortcoming of the LinearList class is the need to predict the maximum possible size of the list. One possible improvement is to start the MaxSize with 1, then double the size whenever a need arises, create a new list with the doubled size, copy over the values, finally delete the original li ...
Binary search tree
In computer science, binary search trees (BST), sometimes called ordered or sorted binary trees, are a particular type of containers: data structures that store ""items"" (such as numbers, names and etc.) in memory. They allow fast lookup, addition and removal of items, and can be used to implement either dynamic sets of items, or lookup tables that allow finding an item by its key (e.g., finding the phone number of a person by name).Binary search trees keep their keys in sorted order, so that lookup and other operations can use the principle of binary search: when looking for a key in a tree (or a place to insert a new key), they traverse the tree from root to leaf, making comparisons to keys stored in the nodes of the tree and deciding, based on the comparison, to continue searching in the left or right subtrees. On average, this means that each comparison allows the operations to skip about half of the tree, so that each lookup, insertion or deletion takes time proportional to the logarithm of the number of items stored in the tree. This is much better than the linear time required to find items by key in an (unsorted) array, but slower than the corresponding operations on hash tables.They are a special case of the more general B-tree with order equal to two.