MEADE INSTRUCTION MANUAL
... old. Many of them had telescope no bigger than the one you are using right now. Galileo, who is one of the first astronomers to use a telescope, discovered four of the moons of Jupiter with a telescope about the same size as yours (and his didn’t even focus very well!). OBSERVING Observe during the ...
... old. Many of them had telescope no bigger than the one you are using right now. Galileo, who is one of the first astronomers to use a telescope, discovered four of the moons of Jupiter with a telescope about the same size as yours (and his didn’t even focus very well!). OBSERVING Observe during the ...
February - Amateur Telescope Makers of Boston
... time, for when I first started really noticing Jupiter was rising around midnight or so and I was seeing it as I stepped out for my last look up before retiring to bed. If I happened to get up in the middle of the night and happened to go out for a quick look there was Jupiter staring, no - glaring ...
... time, for when I first started really noticing Jupiter was rising around midnight or so and I was seeing it as I stepped out for my last look up before retiring to bed. If I happened to get up in the middle of the night and happened to go out for a quick look there was Jupiter staring, no - glaring ...
Document
... The scientific and engineering discipline whereby the performance of an optical signal is improved by using information about the environment through which it passes AO Deals with the control of light in a real time closed loop and is a subset of active optics. ...
... The scientific and engineering discipline whereby the performance of an optical signal is improved by using information about the environment through which it passes AO Deals with the control of light in a real time closed loop and is a subset of active optics. ...
The production and updating of experimental results
... were indeed moons orbiting Jupiter with a constant period. The assumption was borne out, not only by the quantitative measurements but also by the more qualitative observation that the satellites occasionally disappeared from view as they passed behind or in front of the parent planet or moved into ...
... were indeed moons orbiting Jupiter with a constant period. The assumption was borne out, not only by the quantitative measurements but also by the more qualitative observation that the satellites occasionally disappeared from view as they passed behind or in front of the parent planet or moved into ...
v A v A
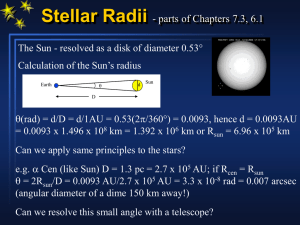
... (angular diameter of a dime 150 km away!) Can we resolve this small angle with a telescope? ...
... (angular diameter of a dime 150 km away!) Can we resolve this small angle with a telescope? ...
Highlights of the Month - Bridgend Astronomical Society
... and is caused by the obscuration of light from distant stars by a lane of dust in our local spiral arm. the dust comes from elements such as carbon which have been built up in stars and ejected into space in explosions that give rise to objects such as the planetary nebula M57 described above. Deneb ...
... and is caused by the obscuration of light from distant stars by a lane of dust in our local spiral arm. the dust comes from elements such as carbon which have been built up in stars and ejected into space in explosions that give rise to objects such as the planetary nebula M57 described above. Deneb ...
Document
... objective of focal length 1200 mm using two different eyepieces with focal lengths of: (a) 25 mm (b) 10 mm (a) Magnification = 1200/25 = 48x (b) Magnification = 1200/10 = 120x ...
... objective of focal length 1200 mm using two different eyepieces with focal lengths of: (a) 25 mm (b) 10 mm (a) Magnification = 1200/25 = 48x (b) Magnification = 1200/10 = 120x ...
40-04135 8 Page Manual Template
... and planets. Read about astronomers of old. Many of them had telescope no bigger than the one you are using right now. Galileo, who is one of the first astronomers to use a telescope, discovered four of the moons of Jupiter with a telescope about the same size as yours (and his didn’t even focus ver ...
... and planets. Read about astronomers of old. Many of them had telescope no bigger than the one you are using right now. Galileo, who is one of the first astronomers to use a telescope, discovered four of the moons of Jupiter with a telescope about the same size as yours (and his didn’t even focus ver ...
May - Hawaiian Astronomical Society
... the solar system was not always appreciated. Until spacecraft and astronauts started visiting the Moon, it was widely believed that volcanic processes were responsible for at least some of the craters seen on the Moon through telescopes. Meteor (or Barringer) Crater in Arizona was at first thought t ...
... the solar system was not always appreciated. Until spacecraft and astronauts started visiting the Moon, it was widely believed that volcanic processes were responsible for at least some of the craters seen on the Moon through telescopes. Meteor (or Barringer) Crater in Arizona was at first thought t ...
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS
... gamma-rays. Thus, gamma-ray astronomy is expected to reveal astronomical objects where special conditions obtain for the acceleration of particles to high energies. The processes that lead to the production of gamma-rays in the astrophysical context are (1) nuclear excitation followed by deexcitatio ...
... gamma-rays. Thus, gamma-ray astronomy is expected to reveal astronomical objects where special conditions obtain for the acceleration of particles to high energies. The processes that lead to the production of gamma-rays in the astrophysical context are (1) nuclear excitation followed by deexcitatio ...
telestar instruction manual
... interesting. But look again. There is much information that is revealed in stars. The first thing you will notice is that not all stars are the same colors. See if you can find blue, orange, yellow, white and red stars. The color of stars sometimes can tell you about the age of a star and the temper ...
... interesting. But look again. There is much information that is revealed in stars. The first thing you will notice is that not all stars are the same colors. See if you can find blue, orange, yellow, white and red stars. The color of stars sometimes can tell you about the age of a star and the temper ...
Astronomy 102, Spring 2003 Solutions to Review Problems
... d, the distance, in order to calculate L. For mass, if it’s a binary star, you can measure the period of the orbit without knowing the distance, but again to get the physical semi-major axis of the orbit from the angular separation of the two stars, you need to know the distance to the system. Prope ...
... d, the distance, in order to calculate L. For mass, if it’s a binary star, you can measure the period of the orbit without knowing the distance, but again to get the physical semi-major axis of the orbit from the angular separation of the two stars, you need to know the distance to the system. Prope ...
telestar instruction manual
... astronomers of old. Many of them had telescope no bigger than the one you are using right now. Galileo, who is one of the first astronomers to use a telescope, discovered four of the moons of Jupiter with a telescope about the same size as yours (and his didn’t even focus very well!). OBSERVING Obse ...
... astronomers of old. Many of them had telescope no bigger than the one you are using right now. Galileo, who is one of the first astronomers to use a telescope, discovered four of the moons of Jupiter with a telescope about the same size as yours (and his didn’t even focus very well!). OBSERVING Obse ...
telescope field of view
... 1. [1 pt] A) Why do stars appear to move towards the south if the telescope moves towards north? (Hint: will stars in the eyepiece actually be further north or south after moving? Another hint: which way do stars appear to move in your eyes’ fields of view if you look up?) B) Give another, non-teles ...
... 1. [1 pt] A) Why do stars appear to move towards the south if the telescope moves towards north? (Hint: will stars in the eyepiece actually be further north or south after moving? Another hint: which way do stars appear to move in your eyes’ fields of view if you look up?) B) Give another, non-teles ...
Object A
... Refraction depends on the wavelength— violet light is bent more than red. Dispersion: the resulting spreading out of the wavelengths of light. Causes chromatic aberration in lenses, which can be fixed by a compound lens. ...
... Refraction depends on the wavelength— violet light is bent more than red. Dispersion: the resulting spreading out of the wavelengths of light. Causes chromatic aberration in lenses, which can be fixed by a compound lens. ...
Fundamentals - Indiana University
... • Flux measures how bright a star is. In optical astronomy, this is measured in magnitudes, a logarithmic measure of flux. • Intensity: If a source is extended, its surface brightness varies across its extent. The surface brightness is the intensity, the amount of flux that originates from unit soli ...
... • Flux measures how bright a star is. In optical astronomy, this is measured in magnitudes, a logarithmic measure of flux. • Intensity: If a source is extended, its surface brightness varies across its extent. The surface brightness is the intensity, the amount of flux that originates from unit soli ...
High Resolution Imaging of Satellites with Ground-Based
... and future missions, developing high resolution imaging capability is crucial to adequately support these endeavors. Ground-based satellite imaging is limited by atmospheric turbulence that degrades the resolution and by fast apparent satellite motion that makes them impossible to track with convent ...
... and future missions, developing high resolution imaging capability is crucial to adequately support these endeavors. Ground-based satellite imaging is limited by atmospheric turbulence that degrades the resolution and by fast apparent satellite motion that makes them impossible to track with convent ...
the printable Hartness House Workshop Schedule in pdf
... Robo-AO is the first and only fully automated adaptive optics laser guide star adaptive optics (AO) instrument. It was developed as an instrument for 1-3m robotic telescopes, in order to take advantage of their availability to pursue large survey programs and target of opportunity observations that ...
... Robo-AO is the first and only fully automated adaptive optics laser guide star adaptive optics (AO) instrument. It was developed as an instrument for 1-3m robotic telescopes, in order to take advantage of their availability to pursue large survey programs and target of opportunity observations that ...
Coordinate Systems for Astronomy or: How to get
... The Earth turns once on its axis in 23 hours 56 minutes and 04 seconds. This is called a sidereal day. Stars rise at the same time each sidereal day. However we set our watches to a length of day matching the mean solar day. The Earth has to turn for an extra ~1o to get the Sun back to the same plac ...
... The Earth turns once on its axis in 23 hours 56 minutes and 04 seconds. This is called a sidereal day. Stars rise at the same time each sidereal day. However we set our watches to a length of day matching the mean solar day. The Earth has to turn for an extra ~1o to get the Sun back to the same plac ...
Series Telescopes INSTRUCTION MANUAL
... Since putting your head in front of the telescope to look at the image with an eyepiece would keep the reflector from working, a flat mirror called a diagonal intercepts the light and points it out the side of the tube at right angles to the tube. The eyepiece is placed there for easy viewing. Newto ...
... Since putting your head in front of the telescope to look at the image with an eyepiece would keep the reflector from working, a flat mirror called a diagonal intercepts the light and points it out the side of the tube at right angles to the tube. The eyepiece is placed there for easy viewing. Newto ...
Introduction and first data set
... the sky. They are similar to the jet-like features extending from the Southern Blue Spot (SBS). They vary enormously in brightness and size, though the larger ones tend to be brighter. Faint fuzzballs greatly outnumber the bright ones. Most fuzzballs are brighter and bigger than the LMS. ...
... the sky. They are similar to the jet-like features extending from the Southern Blue Spot (SBS). They vary enormously in brightness and size, though the larger ones tend to be brighter. Faint fuzzballs greatly outnumber the bright ones. Most fuzzballs are brighter and bigger than the LMS. ...
Extremely Large Telescopes
... • 60m could reach mH~29 in 100hrs (depending on source size) • Spectroscopy at z>10 hard even for 100m The Universe at z=6.1 (Gnedin 2000) Neutral H, ionising intensity (z), gas density, gas temperature ...
... • 60m could reach mH~29 in 100hrs (depending on source size) • Spectroscopy at z>10 hard even for 100m The Universe at z=6.1 (Gnedin 2000) Neutral H, ionising intensity (z), gas density, gas temperature ...
Word - Wichita State University
... Over the years many interesting things have happened at the Observatory. Here are just a few. One evening a five or six year old girl discovered Saturn on her own with a small telescope and rushed back inside to get a staff member to go back outside with her so he could see what she had done. Anothe ...
... Over the years many interesting things have happened at the Observatory. Here are just a few. One evening a five or six year old girl discovered Saturn on her own with a small telescope and rushed back inside to get a staff member to go back outside with her so he could see what she had done. Anothe ...
5th
... The last day of Xplora Science Teachers Conference, before the SkyWatch 2006 Contest award ceremony a new D-Space service presented. Dr. Ioannis Papamastorakis demonstrated the use of robotic telescopes by remotely operate a telescope located in Skinakas Observatory in Crete, using a web page. There ...
... The last day of Xplora Science Teachers Conference, before the SkyWatch 2006 Contest award ceremony a new D-Space service presented. Dr. Ioannis Papamastorakis demonstrated the use of robotic telescopes by remotely operate a telescope located in Skinakas Observatory in Crete, using a web page. There ...
VISIT TO NORMAN LOCKYER OBSERVATORY IN SIDMOUTH
... Jupiter is now well past its best, but still stands out in the South to South-west at nightfall Its brightness falls slightly from magnitude -1.9 to -1.8 whilst its angular size drops from 35 to 32.5 arc seconds. Jupiter starts the month in Cancer but moves into Leo on the 9th of June in its eastwar ...
... Jupiter is now well past its best, but still stands out in the South to South-west at nightfall Its brightness falls slightly from magnitude -1.9 to -1.8 whilst its angular size drops from 35 to 32.5 arc seconds. Jupiter starts the month in Cancer but moves into Leo on the 9th of June in its eastwar ...
History of the telescope

The earliest known working telescopes appeared in 1608 and are credited to Hans Lippershey. Among many others who claimed to have made the discovery were Zacharias Janssen, a spectacle-maker in Middelburg, and Jacob Metius of Alkmaar. The design of these early refracting telescopes consisted of a convex objective lens and a concave eyepiece. Galileo used this design the following year. In 1611, Johannes Kepler described how a telescope could be made with a convex objective lens and a convex eyepiece lens and by 1655 astronomers such as Christiaan Huygens were building powerful but unwieldy Keplerian telescopes with compound eyepieces. Hans Lippershey is the earliest person documented to have applied for a patent for the device.Isaac Newton is credited with building the first ""practical"" reflector in 1668 with a design that incorporated a small flat diagonal mirror to reflect the light to an eyepiece mounted on the side of the telescope. Laurent Cassegrain in 1672 described the design of a reflector with a small convex secondary mirror to reflect light through a central hole in the main mirror.The achromatic lens, which greatly reduced color aberrations in objective lenses and allowed for shorter and more functional telescopes, first appeared in a 1733 telescope made by Chester Moore Hall, who did not publicize it. John Dollond learned of Hall's invention and began producing telescopes using it in commercial quantities, starting in 1758.Important developments in reflecting telescopes were John Hadley's production of larger paraboloidal mirrors in 1721; the process of silvering glass mirrors introduced by Léon Foucault in 1857; and the adoption of long lasting aluminized coatings on reflector mirrors in 1932. Almost all of the large optical research telescopes used today are reflectors.The era of radio telescopes (along with radio astronomy) was born with Karl Guthe Jansky's serendipitous discovery of an astronomical radio source in 1931. Many types of telescopes were developed in the 20th century for a wide range of wavelengths from radio to gamma-rays.