Matrix Algebra
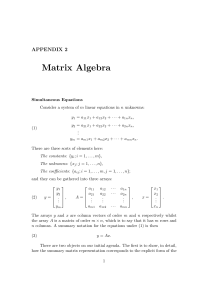
... matrix of (2), we write A = [aij ]. Likewise, we can write y = [yi ] and x = [xj ] for the vectors. In fact, the vectors y and x may be regarded as degenerate matrices of orders m × 1 and n × 1 respectively. The purpose of this is to avoid having to enunciate rules of vector algebra alongside those ...
... matrix of (2), we write A = [aij ]. Likewise, we can write y = [yi ] and x = [xj ] for the vectors. In fact, the vectors y and x may be regarded as degenerate matrices of orders m × 1 and n × 1 respectively. The purpose of this is to avoid having to enunciate rules of vector algebra alongside those ...
Why study matrix groups?
... (see Section 8.6). Weeks writes, “Matrix groups model possible shapes for the universe. Conceptually one thinks of the universe as a single multi-connected space, but when cosmologists roll up their sleeves to work on such models they find it far easier to represent them as a simply connected space u ...
... (see Section 8.6). Weeks writes, “Matrix groups model possible shapes for the universe. Conceptually one thinks of the universe as a single multi-connected space, but when cosmologists roll up their sleeves to work on such models they find it far easier to represent them as a simply connected space u ...
Document
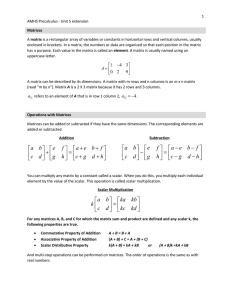
... column with the constants, it is called the augmented matrix. Often the constants are separated with a line. ...
... column with the constants, it is called the augmented matrix. Often the constants are separated with a line. ...
Hamming scheme H(d, n) Let d, n ∈ N and Σ = {0,1,...,n − 1}. The
... The matrices E0, . . . , Ed are called primitive idempotents of the associative scheme A. Schur (or Hadamard) product of matrices is an entry-wise product. denoted by “◦”. Since Ai ◦ Aj = δij Ai, the BM-algebra is closed for Schur product. The matrices Ai are pairwise othogonal idempotents for Schur ...
... The matrices E0, . . . , Ed are called primitive idempotents of the associative scheme A. Schur (or Hadamard) product of matrices is an entry-wise product. denoted by “◦”. Since Ai ◦ Aj = δij Ai, the BM-algebra is closed for Schur product. The matrices Ai are pairwise othogonal idempotents for Schur ...
Linear Algebra and Matrices
... analysis and solution of systems of linear equations (i.e. GLMs). • The determinant is a function that associates a scalar det(A) to every square matrix A. – Input is nxn matrix – Output is a single number (real or complex) called the ...
... analysis and solution of systems of linear equations (i.e. GLMs). • The determinant is a function that associates a scalar det(A) to every square matrix A. – Input is nxn matrix – Output is a single number (real or complex) called the ...
Module 4 : Solving Linear Algebraic Equations Section 3 : Direct
... Thus, the solution procedure for solving this system of equations involving a special type of upper triangular matrix is particularly simple. However, the trouble is that most of the problems encountered in real applications do not have such special form. Now, suppose we want to solve a system of eq ...
... Thus, the solution procedure for solving this system of equations involving a special type of upper triangular matrix is particularly simple. However, the trouble is that most of the problems encountered in real applications do not have such special form. Now, suppose we want to solve a system of eq ...
QUANTUM GROUPS AND HADAMARD MATRICES Introduction A
... (1) ξ(h) is the magic basis given by ξ ij = hj /hi . (2) P (h) is the magic unitary given by P ij = P (ξij ). (3) πh is the representation given by πh (uij ) = Pij . (4) A(h) is the quantum permutation algebra associated to π. In other words, associated to h are the rank one projections P (h j /hi ) ...
... (1) ξ(h) is the magic basis given by ξ ij = hj /hi . (2) P (h) is the magic unitary given by P ij = P (ξij ). (3) πh is the representation given by πh (uij ) = Pij . (4) A(h) is the quantum permutation algebra associated to π. In other words, associated to h are the rank one projections P (h j /hi ) ...
3.1 15. Let S denote the set of all the infinite sequences
... To see this first note that all elements of the set described by (c) can be written in the form p(x) = ax3 + bx2 + cx where a, b, c are real numbers. The first condition is satisfied becuase if we take any element in the set described by (c) which I will represent by p(x) = ax3 + bx2 + cx and multip ...
... To see this first note that all elements of the set described by (c) can be written in the form p(x) = ax3 + bx2 + cx where a, b, c are real numbers. The first condition is satisfied becuase if we take any element in the set described by (c) which I will represent by p(x) = ax3 + bx2 + cx and multip ...
![arXiv:math/0403252v1 [math.HO] 16 Mar 2004](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017716978_1-976b7d80197f8d34f66860694a7698bb-300x300.png)