Separating Doubly Nonnegative and Completely
... For X ∈ Sn let G(X) denote the undirected graph on vertices {1, . . . , n} with edges {{i 6= j} | Xij 6= 0}. Definition 1. Let G be an undirected graph on n vertices. Then G is called a CP graph if any matrix X ∈ Dn with G(X) = G also has X ∈ Cn. The main result on CP graphs is the following: Propo ...
... For X ∈ Sn let G(X) denote the undirected graph on vertices {1, . . . , n} with edges {{i 6= j} | Xij 6= 0}. Definition 1. Let G be an undirected graph on n vertices. Then G is called a CP graph if any matrix X ∈ Dn with G(X) = G also has X ∈ Cn. The main result on CP graphs is the following: Propo ...
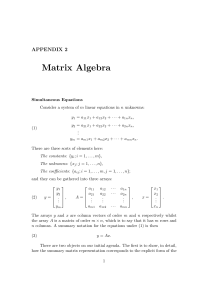
APPENDIX Matrix Algebra
... of A and pressing Ctrl-C), clicking where you want AT located (i.e. the cell at the upper left corner of AT) and then selecting Home/Paste/ and choosing the Transpose option. ...
... of A and pressing Ctrl-C), clicking where you want AT located (i.e. the cell at the upper left corner of AT) and then selecting Home/Paste/ and choosing the Transpose option. ...
Transformations - tandrageemaths
... X= -5 How far has it moved up the y axis? Y= 3 So the translation is (-5,3) ...
... X= -5 How far has it moved up the y axis? Y= 3 So the translation is (-5,3) ...
Revisions in Linear Algebra
... A linear function f is a mathematical function in which the variables appear only in the rst degree, are multiplied by constants, and are combined only by addition and subtraction. A linear equation is of the form f (x, y, · · · ) = 0 ...
... A linear function f is a mathematical function in which the variables appear only in the rst degree, are multiplied by constants, and are combined only by addition and subtraction. A linear equation is of the form f (x, y, · · · ) = 0 ...
5-3 Unit Circle Exact Values (Degrees)
... While we can use our sandbox trigonometry to find values on the unit circle, we will generally have to round those values. However there are some exact value coordinates on the unit circle, such as the coordinates at angle rotations of 0°. 90°, 180°, 270°, and 360° (and all their multiples). 16a. ...
... While we can use our sandbox trigonometry to find values on the unit circle, we will generally have to round those values. However there are some exact value coordinates on the unit circle, such as the coordinates at angle rotations of 0°. 90°, 180°, 270°, and 360° (and all their multiples). 16a. ...
LINEAR DEPENDENCE AND RANK
... Another theorem of linear algebra provides a way to evaluate whether a consistent set of equations has an infinite number of solutions: a consistent system of n equations in n unknowns has a unique solution if the rank of the coefficient matrix is equal to its order, where r(A) = n. In the example h ...
... Another theorem of linear algebra provides a way to evaluate whether a consistent set of equations has an infinite number of solutions: a consistent system of n equations in n unknowns has a unique solution if the rank of the coefficient matrix is equal to its order, where r(A) = n. In the example h ...