Parasites and Parasitism (CAMB 549)
... chemotherapy represents the major strategy for treating and controlling helminth infections. However, lack of drug options and emergence of parasite drug resistance are huge problems, and new drugs are urgently needed. We will explore current anthelmintic drug targets, and prospects for development ...
... chemotherapy represents the major strategy for treating and controlling helminth infections. However, lack of drug options and emergence of parasite drug resistance are huge problems, and new drugs are urgently needed. We will explore current anthelmintic drug targets, and prospects for development ...
Animal Disease And Parasite Susceptibility
... parasites susceptibility? What breed influence in cattle might effect this? Can it have negative impacts as well? ...
... parasites susceptibility? What breed influence in cattle might effect this? Can it have negative impacts as well? ...
8.L.1.1 Warm-Up Questions
... 139. What is the main purpose of a hand sanitizer? To promote viral contamination To reduce the number of virus strands To increase cell production on one’s hands To decrease the bacteria found on one’s hands ...
... 139. What is the main purpose of a hand sanitizer? To promote viral contamination To reduce the number of virus strands To increase cell production on one’s hands To decrease the bacteria found on one’s hands ...
Protozoal Diseases of Wildlife
... live in blood, lymph, and tissue spaces transmitted from host-host by blood-feeding arthropods most important genera: Trypanosoma and Leishmania. infection in mammalian hosts occurs – through the bite of the infected arthropod – through contamination of the host's mucus membranes or abraded skin by ...
... live in blood, lymph, and tissue spaces transmitted from host-host by blood-feeding arthropods most important genera: Trypanosoma and Leishmania. infection in mammalian hosts occurs – through the bite of the infected arthropod – through contamination of the host's mucus membranes or abraded skin by ...
20130822150015301
... evolved to increase R0. Reduced larval mortality & increased adult body size leads to high fecundity ...
... evolved to increase R0. Reduced larval mortality & increased adult body size leads to high fecundity ...
Slide ()
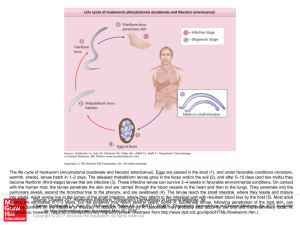
... The life cycle of hookworm (Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus). Eggs are passed in the stool (1), and under favorable conditions (moisture, warmth, shade), larvae hatch in 1–2 days. The released rhabditiform larvae grow in the feces and/or the soil (2), and after 5–10 days (and two molts) ...
... The life cycle of hookworm (Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus). Eggs are passed in the stool (1), and under favorable conditions (moisture, warmth, shade), larvae hatch in 1–2 days. The released rhabditiform larvae grow in the feces and/or the soil (2), and after 5–10 days (and two molts) ...
“living together” Symbiosis Phoresis
... development occurs. • Paratenic host - transport host, but parasites do not develop in this host. • Reservoir host - any animal that carries an infection that can serve as a source of infection to human and other ...
... development occurs. • Paratenic host - transport host, but parasites do not develop in this host. • Reservoir host - any animal that carries an infection that can serve as a source of infection to human and other ...
BSC 361
... Inflammation-host immune response that is includes increased localized temperature, increased permeability of the capillaries, increased blood flow. Leukocyte-any "white blood cell" Lymphocytes-T-cells and B-cells PMN's=polymorphonuclear luekocytes-includes neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils Mon ...
... Inflammation-host immune response that is includes increased localized temperature, increased permeability of the capillaries, increased blood flow. Leukocyte-any "white blood cell" Lymphocytes-T-cells and B-cells PMN's=polymorphonuclear luekocytes-includes neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils Mon ...
Life cycle
... does not reach sexual maturity, parasites often can undergo asexual reproduction in this type of host. ...
... does not reach sexual maturity, parasites often can undergo asexual reproduction in this type of host. ...
RESEARCH ABSTRACT FORM
... -acetylgalactosaminyl (GalNAc) residues. Lectins and antibodies specific for ...
... -acetylgalactosaminyl (GalNAc) residues. Lectins and antibodies specific for ...
Unit 2 PPT 11 (Macroparasites and microparasites)
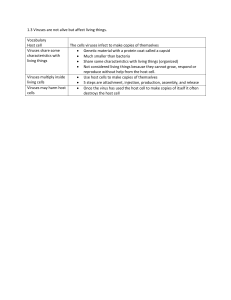
... inside a host cell. Viruses contain genetic material in the form of DNA or RNA, packaged in a protective protein coat. • Some viruses have a lipid membrane surround derived from host cell materials. The outer surface of a virus contains antigens that a host cell may or may not be able to detect as f ...
... inside a host cell. Viruses contain genetic material in the form of DNA or RNA, packaged in a protective protein coat. • Some viruses have a lipid membrane surround derived from host cell materials. The outer surface of a virus contains antigens that a host cell may or may not be able to detect as f ...
Commensalism, mutualism, and parasitism are three
... because the parasite needs the host to complete its reproductive cycle by spreading to another host. The reproductive cycles of parasites are often very complex, sometimes requiring more than one host species. A tapeworm is a parasite that causes disease in humans when contaminated, undercooked meat ...
... because the parasite needs the host to complete its reproductive cycle by spreading to another host. The reproductive cycles of parasites are often very complex, sometimes requiring more than one host species. A tapeworm is a parasite that causes disease in humans when contaminated, undercooked meat ...
Notes - MIT Biology
... type III and it works, KO from type II and it doesn’t) e. 1,756 known host genes are regulated by GRA15 Toxoplasma growth is largely controlled by the Immunity-Related GTPases (mice die if they don’t have these and are infected) a. GRA15 induces IL-12 production, which activates a pathway that creat ...
... type III and it works, KO from type II and it doesn’t) e. 1,756 known host genes are regulated by GRA15 Toxoplasma growth is largely controlled by the Immunity-Related GTPases (mice die if they don’t have these and are infected) a. GRA15 induces IL-12 production, which activates a pathway that creat ...
Summaries of Infectious Diseases
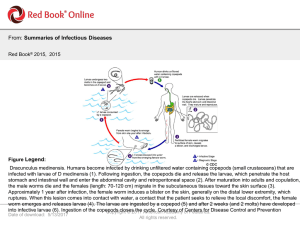
... infected with larvae of D medinensis (1). Following ingestion, the copepods die and release the larvae, which penetrate the host stomach and intestinal wall and enter the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space (2). After maturation into adults and copulation, the male worms die and the females ( ...
... infected with larvae of D medinensis (1). Following ingestion, the copepods die and release the larvae, which penetrate the host stomach and intestinal wall and enter the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space (2). After maturation into adults and copulation, the male worms die and the females ( ...
Schistosoma mansoni

Schistosoma mansoni is a significant parasite of humans, a trematode that is one of the major agents of the disease schistosomiasis which is one type of helminthiasis, a neglected tropical disease. The schistosomiasis caused by Schistosoma mansoni is intestinal schistosomiasis.Schistosomes are atypical trematodes in that the adult stages have two sexes (dioecious) and are located in blood vessels of the definitive host. Most other trematodes are hermaphroditic and are found in the intestinal tract or in organs, such as the liver. The lifecycle of schistosomes includes two hosts: a definitive host (i.e. human) where the parasite undergoes sexual reproduction, and a single intermediate snail host where there are a number of asexual reproductive stages.S. mansoni is named after Sir Patrick Manson, who first identified it in Formosa (now Taiwan).