Introduction to Environmentally Transmitted Pathogens, Part 1
... – 1) methods for measuring the health of groups and for determining the attributes and exposures that influence health; – 2) study of the occurrence of disease in its natural habitat rather than the controlled environment of the laboratory (exception: clinical trials); and – 3) methods for the quant ...
... – 1) methods for measuring the health of groups and for determining the attributes and exposures that influence health; – 2) study of the occurrence of disease in its natural habitat rather than the controlled environment of the laboratory (exception: clinical trials); and – 3) methods for the quant ...
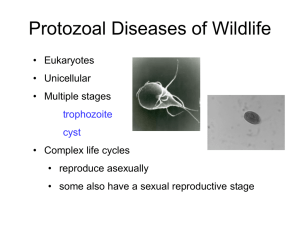
Protozoal Diseases of Wildlife
... The common feature of all members is the presence of an apical complex in one or more stages of the life cycle. – Acts like a drill bit, and secretes enzymes that allow the parasite to enter other cells ...
... The common feature of all members is the presence of an apical complex in one or more stages of the life cycle. – Acts like a drill bit, and secretes enzymes that allow the parasite to enter other cells ...
Female Reproductive System
... External Female Reproductive Organs • Mons Pubis: rounded mound of fatty tissue located directly over the pubic bone • Labia Majora: fatter outer folds on either side of the vaginal opening • Labia Minora: small folds of skin which contain oil glands and blood vessels • Vaginal Opening: opening for ...
... External Female Reproductive Organs • Mons Pubis: rounded mound of fatty tissue located directly over the pubic bone • Labia Majora: fatter outer folds on either side of the vaginal opening • Labia Minora: small folds of skin which contain oil glands and blood vessels • Vaginal Opening: opening for ...
Introduction to Biotechnology
... Fundamental process of Viral infection in a host cell: maintain reservoir –a place to live and multiply before infection enter host contact and enter susceptible cells replicate within cells release from host (immediate or delayed) ...
... Fundamental process of Viral infection in a host cell: maintain reservoir –a place to live and multiply before infection enter host contact and enter susceptible cells replicate within cells release from host (immediate or delayed) ...
microbiology ch 12 [9-4
... o Hyaluronic acid capsule allows GAS to bind to host HA receptor (CD44) found on surface of pharyngeal epithelial cells and skin keratinocytes o Adhere to host ECM molecules surrounding host tissue (fibronectin and laminin) using ECM adhesins (lipoteichoic acid, SfbI (Fba), and serum opacity factor) ...
... o Hyaluronic acid capsule allows GAS to bind to host HA receptor (CD44) found on surface of pharyngeal epithelial cells and skin keratinocytes o Adhere to host ECM molecules surrounding host tissue (fibronectin and laminin) using ECM adhesins (lipoteichoic acid, SfbI (Fba), and serum opacity factor) ...
Are vector borne diseases more virulent?
... • Nucleoprotein sequences cluster together by host group • Hemagglutinin sequences do not • The gene phylogenies are not congruent! ...
... • Nucleoprotein sequences cluster together by host group • Hemagglutinin sequences do not • The gene phylogenies are not congruent! ...
Impaired pneumococcal polyamine transport effects on host and
... Division of Infectious Diseases, University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, MS, 39216. ...
... Division of Infectious Diseases, University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, MS, 39216. ...
Teacher Answer Key - Ecology Unit Plan
... malaria parasites in its saliva when it bites a human) 3. Which sex of mosquito drinks a blood meal? (Female) Parasite Game: 4. What two places in the human body must the malaria parasite go in order to reproduce? (Liver and red blood cell) 5. Draw what the malaria parasite looks like before it ente ...
... malaria parasites in its saliva when it bites a human) 3. Which sex of mosquito drinks a blood meal? (Female) Parasite Game: 4. What two places in the human body must the malaria parasite go in order to reproduce? (Liver and red blood cell) 5. Draw what the malaria parasite looks like before it ente ...
Neospora factsheet.
... that results in abortion and stillbirth. Neospora parasites cause problems in the placenta, brain and sometimes other organs in the developing foetus. A recent survey of aborting cattle within Scotland, conducted by scientists at Moredun in collaboration with SACVS, showed that 16% of aborted foetus ...
... that results in abortion and stillbirth. Neospora parasites cause problems in the placenta, brain and sometimes other organs in the developing foetus. A recent survey of aborting cattle within Scotland, conducted by scientists at Moredun in collaboration with SACVS, showed that 16% of aborted foetus ...
Schistosoma mansoni

Schistosoma mansoni is a significant parasite of humans, a trematode that is one of the major agents of the disease schistosomiasis which is one type of helminthiasis, a neglected tropical disease. The schistosomiasis caused by Schistosoma mansoni is intestinal schistosomiasis.Schistosomes are atypical trematodes in that the adult stages have two sexes (dioecious) and are located in blood vessels of the definitive host. Most other trematodes are hermaphroditic and are found in the intestinal tract or in organs, such as the liver. The lifecycle of schistosomes includes two hosts: a definitive host (i.e. human) where the parasite undergoes sexual reproduction, and a single intermediate snail host where there are a number of asexual reproductive stages.S. mansoni is named after Sir Patrick Manson, who first identified it in Formosa (now Taiwan).