Pinworms Division of Disease Control What Do I Need To Know?
... Symptoms usually are noticed one to two months after infection. How are pinworms spread? Humans are the only known source of pinworms; pets and other animals do not have pinworms. People become infected when they eat the eggs of the worm. The worm matures inside the person and the adult female crawl ...
... Symptoms usually are noticed one to two months after infection. How are pinworms spread? Humans are the only known source of pinworms; pets and other animals do not have pinworms. People become infected when they eat the eggs of the worm. The worm matures inside the person and the adult female crawl ...
Antimalarial drugs
... 1-The antifolate agent pyrimethamine is frequently employed to effect a radical cure as a blood schizonticide. 2-It also acts as a strong sporonticide in the mosquito's gut when the mosquito ingests it with the blood of the human host. Mechanisim of action: Pyrimethamine inhibits plasmodial dihydrof ...
... 1-The antifolate agent pyrimethamine is frequently employed to effect a radical cure as a blood schizonticide. 2-It also acts as a strong sporonticide in the mosquito's gut when the mosquito ingests it with the blood of the human host. Mechanisim of action: Pyrimethamine inhibits plasmodial dihydrof ...
B-cells
... B.10A - describe the interactions that occur among systems that perform the functions of regulation, nutrient absorption, reproduction, and defense from injury or illness in animals ...
... B.10A - describe the interactions that occur among systems that perform the functions of regulation, nutrient absorption, reproduction, and defense from injury or illness in animals ...
Lecture #4
... – NEGATIVE: progeny of infected individuals less fit; – POSITIVE; progeny more resistant (shown with herbivory) ...
... – NEGATIVE: progeny of infected individuals less fit; – POSITIVE; progeny more resistant (shown with herbivory) ...
Medical Bacteriology ( 460 MIC) lecture 1 Bacterial
... The bacteria is capable of causing disease to the host. This type of a symbiotic association may become pathogenic and damage to the host. Some pathogenic bacteria live as normal flora of humans while waiting for an opportunity to cause disease. Other non-indigenous pathogens generally always cause ...
... The bacteria is capable of causing disease to the host. This type of a symbiotic association may become pathogenic and damage to the host. Some pathogenic bacteria live as normal flora of humans while waiting for an opportunity to cause disease. Other non-indigenous pathogens generally always cause ...
Portal hypertension - Medically fit for exams
... o Is the radius that is affected in portal hypertension, with decreased width of blood vessels for blood to pass through – leads to ‘backing up’ Can be split into pre-hepatic, intra-hepatic and post-hepatic causes Pre-hepatic o Splenomegaly, leading to increased flow from the spleen (overwhelming po ...
... o Is the radius that is affected in portal hypertension, with decreased width of blood vessels for blood to pass through – leads to ‘backing up’ Can be split into pre-hepatic, intra-hepatic and post-hepatic causes Pre-hepatic o Splenomegaly, leading to increased flow from the spleen (overwhelming po ...
Appendix A: Glossary of Medical Terms
... nerve injuries, whereupon it acts as a transmitter on the effector organ; it is hydrolyzed into choline and acetic acid by acetylcholinesterase before a second impulse may be transmitted. Active immunization -The act of artificially stimulating the body to develop antibodies against infectious disea ...
... nerve injuries, whereupon it acts as a transmitter on the effector organ; it is hydrolyzed into choline and acetic acid by acetylcholinesterase before a second impulse may be transmitted. Active immunization -The act of artificially stimulating the body to develop antibodies against infectious disea ...
Appendix A: Glossary of Medical Terms
... nerve injuries, whereupon it acts as a transmitter on the effector organ; it is hydrolyzed into choline and acetic acid by acetylcholinesterase before a second impulse may be transmitted. Active immunization -The act of artificially stimulating the body to develop antibodies against infectious disea ...
... nerve injuries, whereupon it acts as a transmitter on the effector organ; it is hydrolyzed into choline and acetic acid by acetylcholinesterase before a second impulse may be transmitted. Active immunization -The act of artificially stimulating the body to develop antibodies against infectious disea ...
Jackie Lester Yasmin Lutz
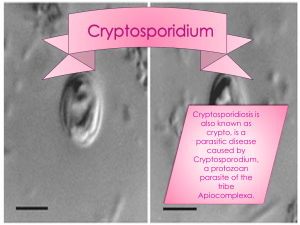
... parasitic disease that was first described in the United States in 1953. •Recently, two ...
... parasitic disease that was first described in the United States in 1953. •Recently, two ...
EXIT
... Lampreys are primitive fish with limited digestive systems. They attach to and feed on the body fluids of fish with more advanced digestive systems, often leading to the death of the host fish. This relationship is an example of… ...
... Lampreys are primitive fish with limited digestive systems. They attach to and feed on the body fluids of fish with more advanced digestive systems, often leading to the death of the host fish. This relationship is an example of… ...
Host Microbe Interactions
... Disruption of tissues or organs caused by microbes or their products The Progress of Infection Pathogen: A microbe whose relationship with its host is parasitic Results in infection and disease Type and severity of infection depend on both the pathogenicity of the organism and the condition of the h ...
... Disruption of tissues or organs caused by microbes or their products The Progress of Infection Pathogen: A microbe whose relationship with its host is parasitic Results in infection and disease Type and severity of infection depend on both the pathogenicity of the organism and the condition of the h ...
Schistosoma mansoni

Schistosoma mansoni is a significant parasite of humans, a trematode that is one of the major agents of the disease schistosomiasis which is one type of helminthiasis, a neglected tropical disease. The schistosomiasis caused by Schistosoma mansoni is intestinal schistosomiasis.Schistosomes are atypical trematodes in that the adult stages have two sexes (dioecious) and are located in blood vessels of the definitive host. Most other trematodes are hermaphroditic and are found in the intestinal tract or in organs, such as the liver. The lifecycle of schistosomes includes two hosts: a definitive host (i.e. human) where the parasite undergoes sexual reproduction, and a single intermediate snail host where there are a number of asexual reproductive stages.S. mansoni is named after Sir Patrick Manson, who first identified it in Formosa (now Taiwan).