Document
... How much data can a TCP sender have outstanding in the network? How much data should TCP retransmit when an error occurs? Just selectively repeat the missing ...
... How much data can a TCP sender have outstanding in the network? How much data should TCP retransmit when an error occurs? Just selectively repeat the missing ...
Chapter 11 n` 12
... number of the first byte in the segment • HLen (or, Data Offset): Number of 32-bit words in the TCP header. The typical value is 5 (20 bytes of header, if Options are not used) • Window: indicates the number of bytes the receiver is prepared to accept from the sender (called rwnd). This reflects fre ...
... number of the first byte in the segment • HLen (or, Data Offset): Number of 32-bit words in the TCP header. The typical value is 5 (20 bytes of header, if Options are not used) • Window: indicates the number of bytes the receiver is prepared to accept from the sender (called rwnd). This reflects fre ...
slides ppt
... • Let xr be the mean bandwidth of flow r [pkts/sec] Let y be the total bandwidth of all flows [pkts/sec] Let C be the total available capacity [pkts/sec] • TCP and the network act so as to solve maximise r U(xr) - P(y,C) over xr0 where y=r xr ...
... • Let xr be the mean bandwidth of flow r [pkts/sec] Let y be the total bandwidth of all flows [pkts/sec] Let C be the total available capacity [pkts/sec] • TCP and the network act so as to solve maximise r U(xr) - P(y,C) over xr0 where y=r xr ...
Solving this Traffic Management Problem... and the Next... and the
... • it’s not just what the Internet can do for you it’s what you can do for the Internet • others have independently identified this as the problem or proposed solutions • we have a fully spec’d proposal to fix IP (re-ECN) ...
... • it’s not just what the Internet can do for you it’s what you can do for the Internet • others have independently identified this as the problem or proposed solutions • we have a fully spec’d proposal to fix IP (re-ECN) ...
The TCP/IP reference model and OSI reference model IPv4 vs. IPv6
... IPv4 vs. IPv6: Much of the information within this tool is intended for use with IP version 4 (IPv4), the current IP standard. IP version 6 (IPv6) is on the horizon, however, and you should understand the differences between it and IPv4. To help you do so, we've included a section comparing IPv6 and ...
... IPv4 vs. IPv6: Much of the information within this tool is intended for use with IP version 4 (IPv4), the current IP standard. IP version 6 (IPv6) is on the horizon, however, and you should understand the differences between it and IPv4. To help you do so, we've included a section comparing IPv6 and ...
Poster - The University of Manchester
... Transporting VLBI Constant Bit Rate Data with TCP/IP TCP is a byte-stream transport layer protocol that guarantees reliable, in-order, and non-duplicated delivery data from sender to receiver. It uses acknowledgments (ACK) from the receiver to slide a window (Cwnd) over the data to regulate the tran ...
... Transporting VLBI Constant Bit Rate Data with TCP/IP TCP is a byte-stream transport layer protocol that guarantees reliable, in-order, and non-duplicated delivery data from sender to receiver. It uses acknowledgments (ACK) from the receiver to slide a window (Cwnd) over the data to regulate the tran ...
Network Coding and Reliable Communications Group
... By taking into account the time-out period and exponential back-offs: ...
... By taking into account the time-out period and exponential back-offs: ...
Study of Transport Layer Protocol for InterPlaNetary Internet
... history as a means of predicting RTT. The RTT for transmitted segment N could be much larger than segment N-1 if there happened to be a loss of connectivity. LTP calculate a first approximation of RTT by simply doubling the known one-way light time to the destination and adding an arbitrary margin f ...
... history as a means of predicting RTT. The RTT for transmitted segment N could be much larger than segment N-1 if there happened to be a loss of connectivity. LTP calculate a first approximation of RTT by simply doubling the known one-way light time to the destination and adding an arbitrary margin f ...
Congestion control principles
... use the network as efficiently as possible, that is, attain the highest possible throughput while maintaining a low loss ratio and small delay. • Congestion must be avoided because it leads to queue growth and queue growth leads to delay and loss. therefore, the term ‘congestion avoidance’ is someti ...
... use the network as efficiently as possible, that is, attain the highest possible throughput while maintaining a low loss ratio and small delay. • Congestion must be avoided because it leads to queue growth and queue growth leads to delay and loss. therefore, the term ‘congestion avoidance’ is someti ...
Slides
... it takes long time for sender to recovery to original cwnd after it being halved due to a packet loss. HSTCP, TCP-Westwood, FAST, Quick-Start, Explicit Transport Error Notification, eXplicit Control Protocol (XCP)… Inefficiency in wireless networks: current TCP implementations are unable to ...
... it takes long time for sender to recovery to original cwnd after it being halved due to a packet loss. HSTCP, TCP-Westwood, FAST, Quick-Start, Explicit Transport Error Notification, eXplicit Control Protocol (XCP)… Inefficiency in wireless networks: current TCP implementations are unable to ...
Chapter3 Transport Layer4
... • Initial rate = 20 kbps • Available bandwidth may be >> MSS/RTT • Desirable to quickly ramp up to respectable rate • Increase rate exponentially until first loss event or when threshold reached • Double cwnd every RTT • Done by increasing cwnd for every ACK received ...
... • Initial rate = 20 kbps • Available bandwidth may be >> MSS/RTT • Desirable to quickly ramp up to respectable rate • Increase rate exponentially until first loss event or when threshold reached • Double cwnd every RTT • Done by increasing cwnd for every ACK received ...
Assignment #4 - comp
... c) Contrary to what was said in the class about the active/passive close of TCP connections, an HTTP server in fact performs an active close and an HTTP client performs a passive close. There are a few good reasons for this design. However, point out one disadvantage of this design. 7. This question ...
... c) Contrary to what was said in the class about the active/passive close of TCP connections, an HTTP server in fact performs an active close and an HTTP client performs a passive close. There are a few good reasons for this design. However, point out one disadvantage of this design. 7. This question ...
No Slide Title - comp
... – Initial Sequence Numbers (ISN), which are the first SNs used by the two sides. – The SYN segment also advertises window size (buffer available for receiving data). – Each side may optionally announce the Maximum Segment Size (MSS) it expects to receive. • If the destination IP address is local, se ...
... – Initial Sequence Numbers (ISN), which are the first SNs used by the two sides. – The SYN segment also advertises window size (buffer available for receiving data). – Each side may optionally announce the Maximum Segment Size (MSS) it expects to receive. • If the destination IP address is local, se ...
Lect15
... retransmission to achieve reliable data delivery • Recipient sends acknowledgment control messages (ACK) to sender to verify successful receipt of data • Sender sets timer when data transmitted; if timer expires before acknowledgment arrives, sender retransmits (with new timer) IP ...
... retransmission to achieve reliable data delivery • Recipient sends acknowledgment control messages (ACK) to sender to verify successful receipt of data • Sender sets timer when data transmitted; if timer expires before acknowledgment arrives, sender retransmits (with new timer) IP ...
Transport Layer Issue in Wireless Ad Hoc and Sensor Networking
... TCP Operation Problem Statement TCP Feedback Ad hoc TCP ...
... TCP Operation Problem Statement TCP Feedback Ad hoc TCP ...
TamVu_TCP_lec_DR13 - Winlab
... Decrease the congestion window multiplicatively, immediately cwnd = cwnd/2 cwnd in bytes ...
... Decrease the congestion window multiplicatively, immediately cwnd = cwnd/2 cwnd in bytes ...
computer networks - Technicalsymposium
... Network Interface Cards (NIC) are working as repeaters. No starting or ending point. Each node will repeat any signal that is on the network regardless its destination. The destination station recognizes its address and copies the frame into a local buffer. The frame continues to circulate until it ...
... Network Interface Cards (NIC) are working as repeaters. No starting or ending point. Each node will repeat any signal that is on the network regardless its destination. The destination station recognizes its address and copies the frame into a local buffer. The frame continues to circulate until it ...
EECP 0442
... But TCP/IP was designed as a Wide-area-network ("WAN"), able to continue to function, even if part of the network was not operating ( damaged or destroyed). ...
... But TCP/IP was designed as a Wide-area-network ("WAN"), able to continue to function, even if part of the network was not operating ( damaged or destroyed). ...
pptx - CSE Labs User Home Pages
... • How to adjust sending rates dynamically? – AIMD (additive increase & multiplicative decrease): • no packet loss in one RTT: W W+1 • packet loss in one RTT: W W/2 ...
... • How to adjust sending rates dynamically? – AIMD (additive increase & multiplicative decrease): • no packet loss in one RTT: W W+1 • packet loss in one RTT: W W/2 ...
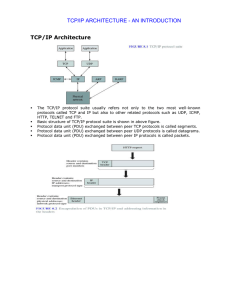
TCP/IP Architecture TCP/IP ARCHITECTURE
... o First 24 bits identify NIC manufacturer; second 24 bits are serial number o 00:90:27:96:68:07 12 hex numbers ...
... o First 24 bits identify NIC manufacturer; second 24 bits are serial number o 00:90:27:96:68:07 12 hex numbers ...
PowerPoint
... • Fraction of UDP packets is rapidly increasing – Commonly used for multimedia applications – UDP traffic interferes with TCP performance – But, many firewalls do not accept UDP packets ...
... • Fraction of UDP packets is rapidly increasing – Commonly used for multimedia applications – UDP traffic interferes with TCP performance – But, many firewalls do not accept UDP packets ...
1. Foundation
... • Initial Sequence Numbers (ISN), which are the first SNs used by the two sides. • The SYN segment also advertises window size (buffer available for receiving data). • Each side may optionally announce the Maximum Segment Size (MSS) it expects to receive. • If the destination IP address is local, se ...
... • Initial Sequence Numbers (ISN), which are the first SNs used by the two sides. • The SYN segment also advertises window size (buffer available for receiving data). • Each side may optionally announce the Maximum Segment Size (MSS) it expects to receive. • If the destination IP address is local, se ...
TCP/IP Management
... largest size of the send window, or the number of bytes that can be transmitted without an acknowledgment. • A large send window indicates that the network is successfully transmitting large packets without the need for retransmission. • A small send window size means that the system has detected pr ...
... largest size of the send window, or the number of bytes that can be transmitted without an acknowledgment. • A large send window indicates that the network is successfully transmitting large packets without the need for retransmission. • A small send window size means that the system has detected pr ...