TCP Details - CSE - University of South Carolina
... Once the connection is established, data can be sent. Each data segment includes a sequence number identifying the first byte in the segment. Each ACK segment includes a request number indicating what data has been received. (bytes instead of packets) ...
... Once the connection is established, data can be sent. Each data segment includes a sequence number identifying the first byte in the segment. Each ACK segment includes a request number indicating what data has been received. (bytes instead of packets) ...
Part III Network Layer
... Identification,Flags and fragmentation offset- These three fields are related to the fragmentation of the IP datagram when the size of the datagram is larger than the underplaying network ...
... Identification,Flags and fragmentation offset- These three fields are related to the fragmentation of the IP datagram when the size of the datagram is larger than the underplaying network ...
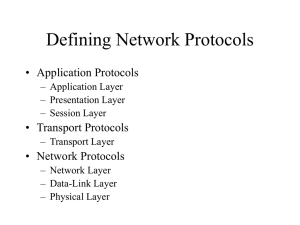
Defining Network Protocols
... • Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol • Assigns IP address, gateway (router) address, name server, netmask, time server, and other configuration information based on a NIC’s MAC address • IP addresses may be fixed or taken from a pool of available addresses • Allows assigning temporary addresses for ...
... • Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol • Assigns IP address, gateway (router) address, name server, netmask, time server, and other configuration information based on a NIC’s MAC address • IP addresses may be fixed or taken from a pool of available addresses • Allows assigning temporary addresses for ...
Introduction to TCP/IP networking
... Link Layer : includes device driver and network interface card Network Layer : handles the movement of packets, i.e. Routing Transport Layer : provides a reliable flow of data between two hosts Application Layer : handles the details of the particular application ...
... Link Layer : includes device driver and network interface card Network Layer : handles the movement of packets, i.e. Routing Transport Layer : provides a reliable flow of data between two hosts Application Layer : handles the details of the particular application ...
Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) RFC 3168
... ECE set ACKs until Receiver gets a TCP-PDU with CWR set from the sender For CWR set TCP-PDU to reach the receiver and get acked takes at least 1 RTT. So any more ECEs received in this time span is for the same instance of congestion ...
... ECE set ACKs until Receiver gets a TCP-PDU with CWR set from the sender For CWR set TCP-PDU to reach the receiver and get acked takes at least 1 RTT. So any more ECEs received in this time span is for the same instance of congestion ...
Computer Networks and Internets
... • Simple sequence numbers enable the client to discard duplicate copies of the same frame • Stop & wait allows one outstanding frame, requires two distinct sequence numbers CS 640 ...
... • Simple sequence numbers enable the client to discard duplicate copies of the same frame • Stop & wait allows one outstanding frame, requires two distinct sequence numbers CS 640 ...
No Slide Title
... Distance learning is applied in these fields: * Providing open learning environments * Offering more information for traditional teaching * Providing continuing education after graduation ...
... Distance learning is applied in these fields: * Providing open learning environments * Offering more information for traditional teaching * Providing continuing education after graduation ...
ppt3
... of a variety of error situations – Out-of-order delivery – Duplicate detection and deletion – Recognizing packet loss and prompting retransmission ...
... of a variety of error situations – Out-of-order delivery – Duplicate detection and deletion – Recognizing packet loss and prompting retransmission ...
Network Security Attacks & Defenses
... – Server needs to keep waiting for ACK y+1 – Server recognizes Client based on IP address/port and y+1 ...
... – Server needs to keep waiting for ACK y+1 – Server recognizes Client based on IP address/port and y+1 ...
local area network
... Introduction to TCP/IP TCP and IP were developed by a Department of Defence (DOD) research project to connect a number different networks designed by different vendors into a network of networks (the "Internet"). It was initially successful because it delivered a few basic services that everyone ne ...
... Introduction to TCP/IP TCP and IP were developed by a Department of Defence (DOD) research project to connect a number different networks designed by different vendors into a network of networks (the "Internet"). It was initially successful because it delivered a few basic services that everyone ne ...
How the TCP/IP Protocol Works
... Packets sent, awaiting ACK • Sender can send 4 packets of data without ACK – When sender gets ACK then can send another packet – Window = unacknowledged packets/bytes – Keeps timer for each packet ...
... Packets sent, awaiting ACK • Sender can send 4 packets of data without ACK – When sender gets ACK then can send another packet – Window = unacknowledged packets/bytes – Keeps timer for each packet ...
dc9798.PDF
... For the network given in Figure Q3.1. Determine the number of possible routes that can be taken when routing between node A and node F (without ever going through the same node twice). ...
... For the network given in Figure Q3.1. Determine the number of possible routes that can be taken when routing between node A and node F (without ever going through the same node twice). ...
UDP—User Datagram Protocol - Department of Computer and
... • TCP establishes connection by setting up variables that are used in two peer TCP entities. Most important variables are initial sequence numbers. • TCP uses Selective Repeat ARQ. • TCP terminates each direction of connection independently, allowing data to continue flowing in one direction after c ...
... • TCP establishes connection by setting up variables that are used in two peer TCP entities. Most important variables are initial sequence numbers. • TCP uses Selective Repeat ARQ. • TCP terminates each direction of connection independently, allowing data to continue flowing in one direction after c ...
What computers talk about and how. COS 116 4/6/2006
... Internet is actually a bunch of connected computers called routers Packets hop from router to router until they reach destination ...
... Internet is actually a bunch of connected computers called routers Packets hop from router to router until they reach destination ...
Network layer
... Physical layer: handle the transmission of raw bits over a communications link Data-link layer: collect a stream of bits into a large aggregate called a frame Network layer: handle routing among nodes within a packetswitched network. Transport layer: implement a process-to-process channel ...
... Physical layer: handle the transmission of raw bits over a communications link Data-link layer: collect a stream of bits into a large aggregate called a frame Network layer: handle routing among nodes within a packetswitched network. Transport layer: implement a process-to-process channel ...
How the TCP/IP Protocol Works
... • App tells TCP to close, TCP sends remaining data & waits for ACK, then sends FIN • Site 2 TCP ACKs FIN, tells its application “end of data” • Site 2 sends FIN when its app closes connection (may be long delay 43 (e.g. require human interaction). ...
... • App tells TCP to close, TCP sends remaining data & waits for ACK, then sends FIN • Site 2 TCP ACKs FIN, tells its application “end of data” • Site 2 sends FIN when its app closes connection (may be long delay 43 (e.g. require human interaction). ...
TCP/IP
... • Developed in the late 1970s to describe basic functionality of networked data communications • Has seven layers • Uses encapsulation to sequentially process data through the layers until it is ready for transmission – Each layer performs some transformation of data such as adding a header or conve ...
... • Developed in the late 1970s to describe basic functionality of networked data communications • Has seven layers • Uses encapsulation to sequentially process data through the layers until it is ready for transmission – Each layer performs some transformation of data such as adding a header or conve ...
Chapter 4 : TCP/IP and OSI
... Internet layer handles tasks similar to network access layer, but between networks rather than between nodes on a network ...
... Internet layer handles tasks similar to network access layer, but between networks rather than between nodes on a network ...
chap01 - cknuckles
... Transport Layer -- End-to-End Service • Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) -- Divides data into packets, verifies arrival on the other end, puts packets back together. TCP connections between two computers called sockets. • User Datagram Protocol (UDP) -- No guarantee of delivery, often single pac ...
... Transport Layer -- End-to-End Service • Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) -- Divides data into packets, verifies arrival on the other end, puts packets back together. TCP connections between two computers called sockets. • User Datagram Protocol (UDP) -- No guarantee of delivery, often single pac ...
Internet and WWW - Computer Science Department
... • In homes, you can connect to a network via a digital subscription line (DSL), a TV cable company, or a phone line. DSL and cable connections are high speed (also called broad band) connections. The phone line is much ...
... • In homes, you can connect to a network via a digital subscription line (DSL), a TV cable company, or a phone line. DSL and cable connections are high speed (also called broad band) connections. The phone line is much ...