Test of New Master
... and converts the data to Radio Frequency. The other Transceiver receives the RF data and converts it back to RS232c ...
... and converts the data to Radio Frequency. The other Transceiver receives the RF data and converts it back to RS232c ...
PPT - Computer Sciences User Pages
... – Yet they can communicate because they use the same protocol • Actually implementations could be different • But must adhere to same specification ...
... – Yet they can communicate because they use the same protocol • Actually implementations could be different • But must adhere to same specification ...
02-Protocol Architecture
... provides a reliable connection for transfer of data between applications a TCP segment is the basic protocol unit TCP tracks segments between entities for duration of each connection ...
... provides a reliable connection for transfer of data between applications a TCP segment is the basic protocol unit TCP tracks segments between entities for duration of each connection ...
Wireless Networks
... connection is over a 64Kbps SCO link. The voice coding scheme is the Continuous Variable Slope Delta (CVSD) Link Manager Protocol (LMP): link setup and control, authentication and encryption Host Controller Interface: provides a uniform method of access to the baseband, control registers, etc throug ...
... connection is over a 64Kbps SCO link. The voice coding scheme is the Continuous Variable Slope Delta (CVSD) Link Manager Protocol (LMP): link setup and control, authentication and encryption Host Controller Interface: provides a uniform method of access to the baseband, control registers, etc throug ...
Ethernet, IP and TCP
... traffic is doing there. • A “bridge” or “switch” is a device that links different LANs together. In normal “promiscuous” mode, it receives signals from all LANs. It will know which MAC address is on which LAN and transmit echo signal to the right LAN. ...
... traffic is doing there. • A “bridge” or “switch” is a device that links different LANs together. In normal “promiscuous” mode, it receives signals from all LANs. It will know which MAC address is on which LAN and transmit echo signal to the right LAN. ...
download
... Repeaters are joined by unidirectional pointto-point links in a ring As a frame circulates past a receiver, the receiver checks its address, and copies those intended for it into a local buffer Frame circulates until it returns to source, which removes it from network ...
... Repeaters are joined by unidirectional pointto-point links in a ring As a frame circulates past a receiver, the receiver checks its address, and copies those intended for it into a local buffer Frame circulates until it returns to source, which removes it from network ...
Protocol Architecture, TCP/IP, and Internet
... attached network • concerned with issues like : – destination address provision – invoking specific services like priority – access to & routing data across a network link between two attached systems ...
... attached network • concerned with issues like : – destination address provision – invoking specific services like priority – access to & routing data across a network link between two attached systems ...
Chapter 14: Local Area Network Technology
... Repeaters are joined by unidirectional pointto-point links in a ring As a frame circulates past a receiver, the receiver checks its address, and copies those intended for it into a local buffer Frame circulates until it returns to source, which removes it from network ...
... Repeaters are joined by unidirectional pointto-point links in a ring As a frame circulates past a receiver, the receiver checks its address, and copies those intended for it into a local buffer Frame circulates until it returns to source, which removes it from network ...
Midterm Review - UTK-EECS
... Network edge: different types of access networks and communication links Network core: packet switching, circuit switching, packet switching vs. circuit switching Delay, loss and throughput: simple calculations using the 4 types of delay, bandwidth, link capacity, packet loss rate, and throughput Pr ...
... Network edge: different types of access networks and communication links Network core: packet switching, circuit switching, packet switching vs. circuit switching Delay, loss and throughput: simple calculations using the 4 types of delay, bandwidth, link capacity, packet loss rate, and throughput Pr ...
Introduction to Transport Layer
... When a packet arrives at a host, it moves up the protocol stack until it reaches the transport layer, e.g., TCP Now, the transport layer needs a way to determine which application the packet needs to be delivered. This is the ...
... When a packet arrives at a host, it moves up the protocol stack until it reaches the transport layer, e.g., TCP Now, the transport layer needs a way to determine which application the packet needs to be delivered. This is the ...
Networking
... write to main memory • It will then modify the descriptor to reflect the received data, DMA write it to memory, and notify the OS that a frame is ready ...
... write to main memory • It will then modify the descriptor to reflect the received data, DMA write it to memory, and notify the OS that a frame is ready ...
Introduction - Jigar Pandya
... In contrast, normal telephone service is based on a circuitswitching technology, in which a dedicated line is allocated for transmission between two parties. Circuit-switching is ideal when data must be transmitted quickly and must arrive in the same order in which it's sent. This is the case wi ...
... In contrast, normal telephone service is based on a circuitswitching technology, in which a dedicated line is allocated for transmission between two parties. Circuit-switching is ideal when data must be transmitted quickly and must arrive in the same order in which it's sent. This is the case wi ...
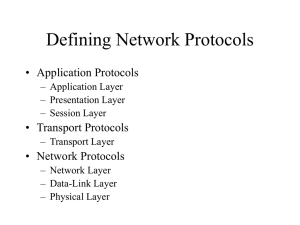
Defining Network Protocols
... • Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol • Assigns IP address, gateway (router) address, name server, netmask, time server, and other configuration information based on a NIC’s MAC address • IP addresses may be fixed or taken from a pool of available addresses • Allows assigning temporary addresses for ...
... • Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol • Assigns IP address, gateway (router) address, name server, netmask, time server, and other configuration information based on a NIC’s MAC address • IP addresses may be fixed or taken from a pool of available addresses • Allows assigning temporary addresses for ...
• Communication: transfer of information between entities
... mechanical, electrical, functional, and procedural characteristics to access the physical medium ...
... mechanical, electrical, functional, and procedural characteristics to access the physical medium ...
TCP/IP Protocol Architecture
... functions across multiple networks for systems attached to different networks using IP protocol implemented in end systems and routers routers connect two networks and relays data between them ...
... functions across multiple networks for systems attached to different networks using IP protocol implemented in end systems and routers routers connect two networks and relays data between them ...
William Stallings Data and Computer Communications
... Both devices may transmit simultaneously or take turns Amount of data sent at one time Data format What to do if an error occurs ...
... Both devices may transmit simultaneously or take turns Amount of data sent at one time Data format What to do if an error occurs ...
Handout
... A protocol is a set of rules that governs how two or more communicating entities in a layer are to interact Messages that can be sent and received Actions that are to be taken when a certain event occurs, e.g. sending or receiving messages, expiry of timers The purpose of a protocol is to provide a ...
... A protocol is a set of rules that governs how two or more communicating entities in a layer are to interact Messages that can be sent and received Actions that are to be taken when a certain event occurs, e.g. sending or receiving messages, expiry of timers The purpose of a protocol is to provide a ...
Chapter 1/Tutorial
... a session between end-user application processes , Communication sessions consist of requests and responses that occur between applications, synchronization, checkpointing. (e.g., Microsoft Word importing a chart from Excel) ISO-SP, OSI session-layer protocol (X.225, ISO 8327) ...
... a session between end-user application processes , Communication sessions consist of requests and responses that occur between applications, synchronization, checkpointing. (e.g., Microsoft Word importing a chart from Excel) ISO-SP, OSI session-layer protocol (X.225, ISO 8327) ...
William Stallings Data and Computer Communications
... Interfacing Data processing devices (or data terminal equipment, DTE) do not (usually) include data transmission facilities Need an interface called data circuit terminating equipment (DCE) e.g. modem, NIC ...
... Interfacing Data processing devices (or data terminal equipment, DTE) do not (usually) include data transmission facilities Need an interface called data circuit terminating equipment (DCE) e.g. modem, NIC ...
ppt - Carnegie Mellon School of Computer Science
... » Needs to buffer and deal with congestion: » More complex switches » Harder to provide good network services (e.g., delay and bandwidth guarantees) ...
... » Needs to buffer and deal with congestion: » More complex switches » Harder to provide good network services (e.g., delay and bandwidth guarantees) ...