CUAHSIHIS2009
... Horsburgh, J. S., D. G. Tarboton, D. R. Maidment and I. Zaslavsky, (2008), A Relational Model for Environmental and Water Resources Data, Water Resour. Res., 44: W05406, doi:10.1029/2007WR006392. ...
... Horsburgh, J. S., D. G. Tarboton, D. R. Maidment and I. Zaslavsky, (2008), A Relational Model for Environmental and Water Resources Data, Water Resour. Res., 44: W05406, doi:10.1029/2007WR006392. ...
link-mac - Zoo
... Source and dest. addresses: 6 bytes Type: indicates the higher layer protocol, mostly IP but ...
... Source and dest. addresses: 6 bytes Type: indicates the higher layer protocol, mostly IP but ...
IEC-60870-5-103 protocol
... • The “DNP 3.0 Basic 4” protocol specification document set was released into the public domain in 1993, and ownership of the protocol was given to the newly formed DNP Users Group in October 1993. • DNP was specifically developed for use in Electrical Utility SCADA Applications. • It is now the dom ...
... • The “DNP 3.0 Basic 4” protocol specification document set was released into the public domain in 1993, and ownership of the protocol was given to the newly formed DNP Users Group in October 1993. • DNP was specifically developed for use in Electrical Utility SCADA Applications. • It is now the dom ...
Chapter 2 - Slide DataComm file - Elearning-KL
... In Figure 2.4, which gives an overall view of the OSI layers. D7 means the data unit at layer 7, D6 means the data unit at layer 6, and so on. The process starts at layer 7 (the application layer), then moves from layer to layer in descending , sequentially order. At each layer, a header or traile ...
... In Figure 2.4, which gives an overall view of the OSI layers. D7 means the data unit at layer 7, D6 means the data unit at layer 6, and so on. The process starts at layer 7 (the application layer), then moves from layer to layer in descending , sequentially order. At each layer, a header or traile ...
Networks and Communication
... – Accept data from higher layers • Split it up into smaller units if need be • Passes these to the network layer • Ensures that the packets all arrive correctly at the destination in the right order • Isolates higher layers from changes in the underlying hardware ...
... – Accept data from higher layers • Split it up into smaller units if need be • Passes these to the network layer • Ensures that the packets all arrive correctly at the destination in the right order • Isolates higher layers from changes in the underlying hardware ...
5 modulasi+encoding.
... Polar, Non Return To Zero Inverted Non return to zero, inverted on ones Constant voltage pulse for duration of bit Data encoded as presence or absence of signal transition at beginning of bit time • Transition (low to high or high to low) denotes a binary 1 • No transition denotes binary 0 • An exam ...
... Polar, Non Return To Zero Inverted Non return to zero, inverted on ones Constant voltage pulse for duration of bit Data encoded as presence or absence of signal transition at beginning of bit time • Transition (low to high or high to low) denotes a binary 1 • No transition denotes binary 0 • An exam ...
Document
... – stations compete for empty slots according to the slotted aloha principle – once a station reserves a slot successfully, this slot is automatically assigned to this station in all following frames as long as the station has data to send – competition for this slots starts again as soon as the slot ...
... – stations compete for empty slots according to the slotted aloha principle – once a station reserves a slot successfully, this slot is automatically assigned to this station in all following frames as long as the station has data to send – competition for this slots starts again as soon as the slot ...
Receiver
... incrementally develop sender, receiver sides of reliable data transfer protocol (rdt) consider only unidirectional data transfer ...
... incrementally develop sender, receiver sides of reliable data transfer protocol (rdt) consider only unidirectional data transfer ...
GPS Data Format NEMA-0183
... receiver) to other devices (PAD) • Query: means for listener (e.g. notebook) to request specified talker sentence from talker (GPS receiver) • Proprietary: means for manufactures to use non-standard sentences for special ...
... receiver) to other devices (PAD) • Query: means for listener (e.g. notebook) to request specified talker sentence from talker (GPS receiver) • Proprietary: means for manufactures to use non-standard sentences for special ...
best-effort service!
... Tokens are placed in bucket at rate r If bucket fills, tokens are discarded Sending a packet of size P uses P tokens If bucket has P tokens, packet sent at max rate, else must wait for tokens to accumulate ...
... Tokens are placed in bucket at rate r If bucket fills, tokens are discarded Sending a packet of size P uses P tokens If bucket has P tokens, packet sent at max rate, else must wait for tokens to accumulate ...
10_Tools_Troubleshooting
... This is an engineer-oriented tool to analyze packets and traffic- often needs interpretation. ...
... This is an engineer-oriented tool to analyze packets and traffic- often needs interpretation. ...
Click Here to Download…
... device simply transmits. The receiving device has to look at the incoming signal and figure out what it is receiving and coordinate and retime its clock to match the incoming signal. Sending data encoded into your signal requires that the sender and receiver are both using the same encoding/decodin ...
... device simply transmits. The receiving device has to look at the incoming signal and figure out what it is receiving and coordinate and retime its clock to match the incoming signal. Sending data encoded into your signal requires that the sender and receiver are both using the same encoding/decodin ...
Networks concepts - EN
... TCAP: Transaction Capabilities Application Part ISUP: ISDN User Part SCCP: Signalling Connection Control Part MTP: Message Transfer Part ...
... TCAP: Transaction Capabilities Application Part ISUP: ISDN User Part SCCP: Signalling Connection Control Part MTP: Message Transfer Part ...
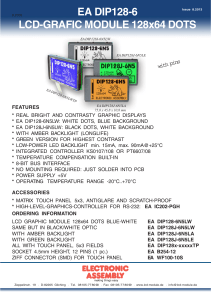
EA DIP128-6 LCD-GRAFIC MODULE 128x64 DOTS
... The blue-white display EA DIP128-6N5LW is best for indoor use with and without ambient light. Reading the display requires a minimum of backlight with about 15mA. Black and white version EA DIP128J-6N5LW and green version are especially designed for outdoor applications. These displays do provide be ...
... The blue-white display EA DIP128-6N5LW is best for indoor use with and without ambient light. Reading the display requires a minimum of backlight with about 15mA. Black and white version EA DIP128J-6N5LW and green version are especially designed for outdoor applications. These displays do provide be ...
TCP Details - CSE - University of South Carolina
... field that tells the sender how many bytes it can send before the receiver will have to toss it away (due to fixed buffer size). ...
... field that tells the sender how many bytes it can send before the receiver will have to toss it away (due to fixed buffer size). ...
CS315-L03-NetworkProtocols
... between client and server (TCP and UDP). Network layer is responsible for routing datagrams from one host to another (IP). Link layer moves frames from node to node (Ethernet, PPP). Physical layer moves individual bits of within a frame from node to node. ...
... between client and server (TCP and UDP). Network layer is responsible for routing datagrams from one host to another (IP). Link layer moves frames from node to node (Ethernet, PPP). Physical layer moves individual bits of within a frame from node to node. ...
Chapter_5_Sec4 - Department of Computer Science
... segment, uses CSMA/CD to access segment transparent hosts are unaware of presence of switches plug-and-play, self-learning switches do not need to be configured ...
... segment, uses CSMA/CD to access segment transparent hosts are unaware of presence of switches plug-and-play, self-learning switches do not need to be configured ...