7 - Hal
... competing firms. The process of competition between firms may lead to different positions. Competition may arrive at perfect coordination and the adjustment process exhibits a convergence to an equilibrium. Competition may also imply a more problematic position of imperfect coordination and the emer ...
... competing firms. The process of competition between firms may lead to different positions. Competition may arrive at perfect coordination and the adjustment process exhibits a convergence to an equilibrium. Competition may also imply a more problematic position of imperfect coordination and the emer ...
SOCIAL STUDIES SS57—Economics
... 11-12.WHST.6. Use technology, including the Internet, to produce, publish, and update individual or shared writing products in response to ongoing feedback, including new arguments or information. ...
... 11-12.WHST.6. Use technology, including the Internet, to produce, publish, and update individual or shared writing products in response to ongoing feedback, including new arguments or information. ...
Unit 3 Assignment 2
... Why DO Research • To find out what customer want, good bad points. • To decide what to buy To Sell more products= customers happy. • Promote the company. • Marketing- how to market when and where. • Price Product Place People. ...
... Why DO Research • To find out what customer want, good bad points. • To decide what to buy To Sell more products= customers happy. • Promote the company. • Marketing- how to market when and where. • Price Product Place People. ...
Revised draft decision
... • Compliance will be assessed on a pricing year basis – For all suppliers but Maui Development this results in a 15 month initial assessment period from 1 July 2013 to 30 September 2014 – For Maui Development 3 month assessment period at the end of the regulatory period (1 Jul 2017 to 30 September 2 ...
... • Compliance will be assessed on a pricing year basis – For all suppliers but Maui Development this results in a 15 month initial assessment period from 1 July 2013 to 30 September 2014 – For Maui Development 3 month assessment period at the end of the regulatory period (1 Jul 2017 to 30 September 2 ...
pdf-fulltext - International Review of Information Ethics
... An interactional approach to privacy, based on Simmel’s theory of secrecy, enables us to understand paradoxical situations. On the one hand, measures meant to protect an individual’s privacy are the very mechanisms which produce a feeling of invasion. On the other hand, such reactions do not occur i ...
... An interactional approach to privacy, based on Simmel’s theory of secrecy, enables us to understand paradoxical situations. On the one hand, measures meant to protect an individual’s privacy are the very mechanisms which produce a feeling of invasion. On the other hand, such reactions do not occur i ...
CHAPTER OVERVIEW
... 6. What consumers decide to purchase depends on their personal preferences and priorities. No two people will make exactly the same decisions. Test this hypothesis by handing out monopoly money in different amounts and asking students to write down the purchases they would make with the sum given. T ...
... 6. What consumers decide to purchase depends on their personal preferences and priorities. No two people will make exactly the same decisions. Test this hypothesis by handing out monopoly money in different amounts and asking students to write down the purchases they would make with the sum given. T ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES TECHNOLOGICAL LINKAGES, MARKET SThUCTURE, AND OPTIMUM PRODUCTION POLICIES
... of commodities imported. Gros [1987] emphasizes terms-of-trade effects and argues that even a small country is a unique supplier of its differentiated export good and thus can influence its external price. Ham and Helpman [19871 investigate a variety of industrial policies, including an output subs ...
... of commodities imported. Gros [1987] emphasizes terms-of-trade effects and argues that even a small country is a unique supplier of its differentiated export good and thus can influence its external price. Ham and Helpman [19871 investigate a variety of industrial policies, including an output subs ...
reappraisal of rational choice theory - Interdisciplinary Description of
... microscopic level is reversible, and can be described with optimization principles, while the aggregated macroscopic level is irreversible, and governed by the entropy production principle. However, this aggregation is not the same as in physics, where the aggregation is done for the large number of ...
... microscopic level is reversible, and can be described with optimization principles, while the aggregated macroscopic level is irreversible, and governed by the entropy production principle. However, this aggregation is not the same as in physics, where the aggregation is done for the large number of ...
Customer Information Sharing with E‑Vendors
... firms, and calls for a radically new e‑marketing approach within the broader field of a multidisciplinary service science [6]. Buyers can no longer meet with a salesperson, ask questions, observe body language, or actually see the physical product or experience the serviceproviding setting. The enti ...
... firms, and calls for a radically new e‑marketing approach within the broader field of a multidisciplinary service science [6]. Buyers can no longer meet with a salesperson, ask questions, observe body language, or actually see the physical product or experience the serviceproviding setting. The enti ...
unit 1. companies……………………………………………………7
... study to see if they will make money by selling in the new market (i,e. to see if the product is viable). One way to assess the market potential is to take a stand at a Trade Fair where companies can exhibit samples of their products and see what response they get from prospective customers. The Tra ...
... study to see if they will make money by selling in the new market (i,e. to see if the product is viable). One way to assess the market potential is to take a stand at a Trade Fair where companies can exhibit samples of their products and see what response they get from prospective customers. The Tra ...
Chapter 5 - Elon University Blogs
... equilibrium which is not a typical feature of educated common sense. Ideas like this may be thought troublesome not only because their integrative nature makes them difficult to learn, but also because they make the world appear a more troublesome place in the sense that it is more complex and diffi ...
... equilibrium which is not a typical feature of educated common sense. Ideas like this may be thought troublesome not only because their integrative nature makes them difficult to learn, but also because they make the world appear a more troublesome place in the sense that it is more complex and diffi ...
Circular flow and quantitative elements
... Scarcity exists because we have limited resources with which to satisfy unlimited needs and wants. Economic efficiency occurs when we make the best use of our resources to produce goods and services. Microeconomics studies the individual parts of the economy. Macroeconomics studies the functioning o ...
... Scarcity exists because we have limited resources with which to satisfy unlimited needs and wants. Economic efficiency occurs when we make the best use of our resources to produce goods and services. Microeconomics studies the individual parts of the economy. Macroeconomics studies the functioning o ...
BusinessExpenses-English
... expenditures that are called costs. A. Fixed costs are those costs that are constant regardless of level of production. 1. Examples of fixed costs include land, buildings, equipment, and tools. 2. No matter how much product is produced, these items cost the same. a. For example, two farmers raise cu ...
... expenditures that are called costs. A. Fixed costs are those costs that are constant regardless of level of production. 1. Examples of fixed costs include land, buildings, equipment, and tools. 2. No matter how much product is produced, these items cost the same. a. For example, two farmers raise cu ...
English
... expenditures that are called costs. A. Fixed costs are those costs that are constant regardless of level of production. 1. Examples of fixed costs include land, buildings, equipment, and tools. 2. No matter how much product is produced, these items cost the same. a. For example, two farmers raise cu ...
... expenditures that are called costs. A. Fixed costs are those costs that are constant regardless of level of production. 1. Examples of fixed costs include land, buildings, equipment, and tools. 2. No matter how much product is produced, these items cost the same. a. For example, two farmers raise cu ...
Sequentially complete markets remain incomplete Economics Letters
... A B S T R A C T We show by means of an example that the result of Arrow [Arrow, K.J. (1953), Le rôle des valeurs boursières pour la répartition la meilleure des risques, Econométrie, 41–47, CNRS, Paris; translated as The role of securities in the optimal allocation of risk bearing, Review of Economi ...
... A B S T R A C T We show by means of an example that the result of Arrow [Arrow, K.J. (1953), Le rôle des valeurs boursières pour la répartition la meilleure des risques, Econométrie, 41–47, CNRS, Paris; translated as The role of securities in the optimal allocation of risk bearing, Review of Economi ...
Lecture 3 Non-renewable resource exploitation: externalities, exploration, scarcity and rents
... scarcity. Remember that the shadow price depends upon prices and costs throughout the lifetime of the resource (including the backstop price), whereas price and marginal cost are current values. A trend in the shadow price, rather than a point value, is the best indicator of resource scarcity. If th ...
... scarcity. Remember that the shadow price depends upon prices and costs throughout the lifetime of the resource (including the backstop price), whereas price and marginal cost are current values. A trend in the shadow price, rather than a point value, is the best indicator of resource scarcity. If th ...
Theory of production Production Function
... output, K is the amount of capital, and L is the amount of labor used in production. This production function says that a firm can produce one unit of output for every unit of capital or labor it employs. From this production function we can see that this industry has constant returns to scale that ...
... output, K is the amount of capital, and L is the amount of labor used in production. This production function says that a firm can produce one unit of output for every unit of capital or labor it employs. From this production function we can see that this industry has constant returns to scale that ...
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from... Bureau of Economic Research Volume Title: Business Concentration and Price Policy
... verified theory of market structures and behavior.4 The limiting cases of markets characterized by perfect competition and perfect ...
... verified theory of market structures and behavior.4 The limiting cases of markets characterized by perfect competition and perfect ...
Download File
... produce estimates that underlie the costs presented in Exhibit USPS-l 1A. You also list four cost systems (IOCS, TRACS, CCS and RCS) that are described by three other Postal witnesses (Ramage (USPS-T-2), Xie (USPS-T-l) and Harahush (USPS-T-3)). With respect to each of these four cost systems: (a) Pl ...
... produce estimates that underlie the costs presented in Exhibit USPS-l 1A. You also list four cost systems (IOCS, TRACS, CCS and RCS) that are described by three other Postal witnesses (Ramage (USPS-T-2), Xie (USPS-T-l) and Harahush (USPS-T-3)). With respect to each of these four cost systems: (a) Pl ...
Attack of the Cyborgs: Economic Imperialism and
... made up of egoistic individuals, each exchanging imperfect knowledge. Through price signaling, market participants exchange information about the relative value of scarce commodities, including information itself, in an organic process of knowledge exchange that ultimately produces the most efficien ...
... made up of egoistic individuals, each exchanging imperfect knowledge. Through price signaling, market participants exchange information about the relative value of scarce commodities, including information itself, in an organic process of knowledge exchange that ultimately produces the most efficien ...
Production and Cost Analysis: Part II
... • In many businesses, the effect of learning by doing and technological change on prices is built into the firm's pricing structure. – Firms may price low in the expectation of lower costs due to learning by doing and technological change. ...
... • In many businesses, the effect of learning by doing and technological change on prices is built into the firm's pricing structure. – Firms may price low in the expectation of lower costs due to learning by doing and technological change. ...
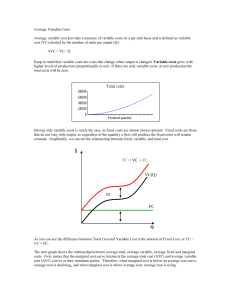
Average Variable Costs
... Average Variable Costs Average variable cost provides a measure of variable costs on a per-unit basis and is defined as variable cost (VC) divided by the number of units per output (Q): AVC = VC / Q Keep in mind that variable costs are costs that change when output is changed. Variable costs grow wi ...
... Average Variable Costs Average variable cost provides a measure of variable costs on a per-unit basis and is defined as variable cost (VC) divided by the number of units per output (Q): AVC = VC / Q Keep in mind that variable costs are costs that change when output is changed. Variable costs grow wi ...