INTERACTION BETWEEN LAVA LAKES AND PYROCLASTIC
... country rocks (Lorenz 1986). The lava lake at Badacsony exhibits irregular lower contact to the pyroclastic units, commonly showing tumuli structures (Fig. 3). The tumulis enclose highly vesicular scoriaceous lava spatter clasts, with vesicles filled by clay, calcite or quartzofeldspatic fragments, ...
... country rocks (Lorenz 1986). The lava lake at Badacsony exhibits irregular lower contact to the pyroclastic units, commonly showing tumuli structures (Fig. 3). The tumulis enclose highly vesicular scoriaceous lava spatter clasts, with vesicles filled by clay, calcite or quartzofeldspatic fragments, ...
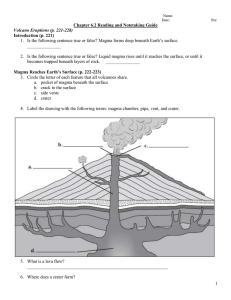
Volcanic Landforms (pages 217*223)
... 2. Explain how the magma that hardens beneath the earth’s surface creates landforms. 3. Identify other distinct features that occur in volcanic areas. ...
... 2. Explain how the magma that hardens beneath the earth’s surface creates landforms. 3. Identify other distinct features that occur in volcanic areas. ...
Slide 1
... • Magma that has a high silica content also tends to cause explosive eruptions • Has a stiff consistency • Flows slowly and tends to harden in a volcano’s vents (plugs vents) • The more the magma pushes up from below the more pressure increases and an explosive ...
... • Magma that has a high silica content also tends to cause explosive eruptions • Has a stiff consistency • Flows slowly and tends to harden in a volcano’s vents (plugs vents) • The more the magma pushes up from below the more pressure increases and an explosive ...
Minerals and Origin of the Moon - Lunar and Planetary Laboratory
... especially if the melt is pyroxene and olivine rich • Low density means that it most likely doesn’t have an iron core • Same density as ordinary rock ...
... especially if the melt is pyroxene and olivine rich • Low density means that it most likely doesn’t have an iron core • Same density as ordinary rock ...
6.2
... 9. Circle the letter of the sentence that describes the best model of a volcano a. Carbon dioxide dissolved in soda pop rushes out where the pop is opened. b. A car goes faster when the accelerator is pushed c. Water in a pot gets hotter when the pot is heated on a stove d. Clay hardens when it is b ...
... 9. Circle the letter of the sentence that describes the best model of a volcano a. Carbon dioxide dissolved in soda pop rushes out where the pop is opened. b. A car goes faster when the accelerator is pushed c. Water in a pot gets hotter when the pot is heated on a stove d. Clay hardens when it is b ...
Section 9.2
... Lahar: is a type of mudflow or debris dense, destructive mass flow composed of a slurry of pyroclastic material, rocky debris, and of very hot ash, lava water. The material flows down from a fragments, and gases ejected explosively volcano, typically along a river valley. (Volcano peaks often have i ...
... Lahar: is a type of mudflow or debris dense, destructive mass flow composed of a slurry of pyroclastic material, rocky debris, and of very hot ash, lava water. The material flows down from a fragments, and gases ejected explosively volcano, typically along a river valley. (Volcano peaks often have i ...
notable events and disasters of 2014. highlights of volcanic eruptions
... WHAT HAPPENED? • After a week of seismic activity rattled the uninhabited area 200 miles (320 kilometers) east of the capital of Reykjavik with thousands of earthquakes, Iceland's Bardarbunga volcano began erupting Saturday (Aug. 23rd) under the country's largest glacier. ...
... WHAT HAPPENED? • After a week of seismic activity rattled the uninhabited area 200 miles (320 kilometers) east of the capital of Reykjavik with thousands of earthquakes, Iceland's Bardarbunga volcano began erupting Saturday (Aug. 23rd) under the country's largest glacier. ...
Landforms at plate margins – Volcanoes and supervolcanoes
... A volcano is a cone-shaped mountain formed by surface eruptions from a magma chamber inside the Earth. The magma that reaches the surface in an eruption is called lava, and is one of the many different products that can be thrown out, including ash, cinders, pumice, dust, gases and steam. The world ...
... A volcano is a cone-shaped mountain formed by surface eruptions from a magma chamber inside the Earth. The magma that reaches the surface in an eruption is called lava, and is one of the many different products that can be thrown out, including ash, cinders, pumice, dust, gases and steam. The world ...
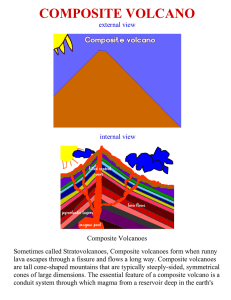
composite volcano
... form a mountain or add height to one that earlier volcanic eruptions had built. During other eruptions, lava flows cement these rocks together. Most composite volcanoes have a crater at the summit which contains a central vent or a clustered group of vents. Lava either flow through breaks in the cra ...
... form a mountain or add height to one that earlier volcanic eruptions had built. During other eruptions, lava flows cement these rocks together. Most composite volcanoes have a crater at the summit which contains a central vent or a clustered group of vents. Lava either flow through breaks in the cra ...
geothermal activity - Madison County Schools
... • Sometimes lava forms a plateau instead of a mountain. A lava plateau is a high, level area. If forms when thin lava flows out of many long cracks. ...
... • Sometimes lava forms a plateau instead of a mountain. A lava plateau is a high, level area. If forms when thin lava flows out of many long cracks. ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... – Lower silica content = lower viscosity or more fluid-like behavior (e.g., mafic lava such as basalt) Dissolved ...
... – Lower silica content = lower viscosity or more fluid-like behavior (e.g., mafic lava such as basalt) Dissolved ...
plosky tolbachik volcano in kamchatka erupts after 40 years
... are awesome manifestations of heat flowing at hot spots (e.g., Hawaii and Iceland) and in subduction zones (e.g., along almost the entire Pacific Rim). ...
... are awesome manifestations of heat flowing at hot spots (e.g., Hawaii and Iceland) and in subduction zones (e.g., along almost the entire Pacific Rim). ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... – Lower silica content = lower viscosity or more fluid-like behavior (e.g., mafic lava such as basalt) Dissolved ...
... – Lower silica content = lower viscosity or more fluid-like behavior (e.g., mafic lava such as basalt) Dissolved ...
volcanism lava tube pahoehoe aa columnar jointing pillow lava
... The process whereby magma and its associated gases rise through the crust and are extruded onto the surface or into the atmosphere. ...
... The process whereby magma and its associated gases rise through the crust and are extruded onto the surface or into the atmosphere. ...
THIS Volcano powerpoint
... the largest percent (60) of the Earth’s volcanoes. They are typically steep sided and are built from alternating layers of lava and cinders. These volcanoes can also be very explosive. Some of the world’s most majestic and beautiful mountains are this type of volcano. Mount Fuji in Japan and Mount S ...
... the largest percent (60) of the Earth’s volcanoes. They are typically steep sided and are built from alternating layers of lava and cinders. These volcanoes can also be very explosive. Some of the world’s most majestic and beautiful mountains are this type of volcano. Mount Fuji in Japan and Mount S ...
Volcano Lecture ppt
... • Hot volcanic activity can melt snow and ice • Melt water picks up rock and debris • Forms fast flowing, high energy torrents • Destroys all in its path ...
... • Hot volcanic activity can melt snow and ice • Melt water picks up rock and debris • Forms fast flowing, high energy torrents • Destroys all in its path ...
Haystack Rock - City of Cannon Beach
... Height: 71.62 meters or 235 feet - comprised of about 1 million tons of rock Comprised of basalt, feldspar, silica, olivine and pyroxene “How did the Rock get here?” Around 15 million years ago molten lava flowed from the “Yellowstone Hotspot”. Of the 300 flows that happened, Haystack Rock arrived v ...
... Height: 71.62 meters or 235 feet - comprised of about 1 million tons of rock Comprised of basalt, feldspar, silica, olivine and pyroxene “How did the Rock get here?” Around 15 million years ago molten lava flowed from the “Yellowstone Hotspot”. Of the 300 flows that happened, Haystack Rock arrived v ...
MINERAL LAB
... Three directional cleavage not at right angles Rhombohedral cleavage Hardness of three Reaction with HCL acid ...
... Three directional cleavage not at right angles Rhombohedral cleavage Hardness of three Reaction with HCL acid ...
Introducing Igneous Rocks
... If lava cools very quickly there is not enough time for the crystals to form. Instead volcanic glass is created, this is called obsidian. Lava can be erupted under water – there are many volcanoes at the bottom of the ocean, following the ocean ridges. When the lava comes into contact with the water ...
... If lava cools very quickly there is not enough time for the crystals to form. Instead volcanic glass is created, this is called obsidian. Lava can be erupted under water – there are many volcanoes at the bottom of the ocean, following the ocean ridges. When the lava comes into contact with the water ...
Igneous Processes
... If lava cools very quickly there is not enough time for the crystals to form. Instead volcanic glass is created, this is called obsidian. Lava can be erupted under water – there are many volcanoes at the bottom of the ocean, following the ocean ridges. When the lava comes into contact with the wate ...
... If lava cools very quickly there is not enough time for the crystals to form. Instead volcanic glass is created, this is called obsidian. Lava can be erupted under water – there are many volcanoes at the bottom of the ocean, following the ocean ridges. When the lava comes into contact with the wate ...
Ring of Fire – Around Pacific area, lots of volcanoes
... Magma generated by: Dropping pressure (rocks coming up quickly)/Added water Geothermal gradient – The gradual increase in heat as you go deeper into the earth Mantle is made of silly-putty-consistency slow-flowing rocks Mafic (Max): Basalt – Higher melting temperature, less viscous, most common lava ...
... Magma generated by: Dropping pressure (rocks coming up quickly)/Added water Geothermal gradient – The gradual increase in heat as you go deeper into the earth Mantle is made of silly-putty-consistency slow-flowing rocks Mafic (Max): Basalt – Higher melting temperature, less viscous, most common lava ...
Explosive Pyroclastic A volcano is a mountain formed beneath the
... Explosive Pyroclastic A volcano is a mountain formed beneath the ground when the Earth’s crust meets the mantle and magma collects there until it rises to the surface because magma is less dense than the surrounding rock is. Then the magma becomes liquid. Shield, cinder cone, and composite volcanoes ...
... Explosive Pyroclastic A volcano is a mountain formed beneath the ground when the Earth’s crust meets the mantle and magma collects there until it rises to the surface because magma is less dense than the surrounding rock is. Then the magma becomes liquid. Shield, cinder cone, and composite volcanoes ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth - Chapter 4 - sir
... Composition—silica (SiO2) content – Higher silica content = higher viscosity (e.g., felsic lava such as rhyolite). ...
... Composition—silica (SiO2) content – Higher silica content = higher viscosity (e.g., felsic lava such as rhyolite). ...
Types of Volcanoes
... • Formed from alternating quiet and explosive eruptions, depending on the amount of trapped gases and silica content at the time of eruption. • Result is alternating layers of tephra and lava. • Examples: – Convergent boundaries – Mount St. Helen’s, Mount ...
... • Formed from alternating quiet and explosive eruptions, depending on the amount of trapped gases and silica content at the time of eruption. • Result is alternating layers of tephra and lava. • Examples: – Convergent boundaries – Mount St. Helen’s, Mount ...
3A8 Week 01 Lecture 02-Rocks and minerals 01
... • Volcanic: – Lavas erupt from volcanoes either as molten fluids, or are blown out as volcanic ash by violent explosions – Black volcanoes (effusive, mostly basaltic) – Red volcanoes (explosive, mostly felsic) This classification is based on composition. Formation of phenocrysts on cooling increases ...
... • Volcanic: – Lavas erupt from volcanoes either as molten fluids, or are blown out as volcanic ash by violent explosions – Black volcanoes (effusive, mostly basaltic) – Red volcanoes (explosive, mostly felsic) This classification is based on composition. Formation of phenocrysts on cooling increases ...
Lava

Lava is the molten rock expelled by a volcano during an eruption and the resulting rock after solidification and cooling. This molten rock is formed in the interior of some planets, including Earth, and some of their satellites. The source of the heat that liquefies the rock within the earth is geothermal energy. When first erupted from a volcanic vent, lava is a liquid at temperatures from 700 to 1,200 °C (1,292 to 2,192 °F). Up to 100,000 times as viscous as water, lava can flow great distances before cooling and solidifying because of its thixotropic and shear thinning properties.A lava flow is a moving outpouring of lava, which is created during a non-explosive effusive eruption. When it has stopped moving, lava solidifies to form igneous rock. The term lava flow is commonly shortened to lava. Explosive eruptions produce a mixture of volcanic ash and other fragments called tephra, rather than lava flows. The word ""lava"" comes from Italian, and is probably derived from the Latin word labes which means a fall or slide. The first use in connection with extruded magma (molten rock below the Earth's surface) was apparently in a short account written by Francesco Serao on the eruption of Vesuvius between May 14 and June 4, 1737. Serao described ""a flow of fiery lava"" as an analogy to the flow of water and mud down the flanks of the volcano following heavy rain.