Volcanoes
... What is a volcano? • An opening in the Earth that erupts gases, ash, and lava. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xExdEXOaA9A ...
... What is a volcano? • An opening in the Earth that erupts gases, ash, and lava. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xExdEXOaA9A ...
TURNING 2011`S DISASTERS INTO EDUCATIONAL SURGES
... Iceland lies on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, the highly volatile, divergent boundary between the Eurasian and North American tectonic plates that is marked by volcanic eruptions and the associated volcano hazards. ...
... Iceland lies on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, the highly volatile, divergent boundary between the Eurasian and North American tectonic plates that is marked by volcanic eruptions and the associated volcano hazards. ...
FORMS OF ERUPTIONS
... The composition of the magma plays a big part in determining the manner in which energy is released during a volcanic eruption. Other factors that determine the force of an eruption: Amount of water vapor and other gases Its temperature Silica content ...
... The composition of the magma plays a big part in determining the manner in which energy is released during a volcanic eruption. Other factors that determine the force of an eruption: Amount of water vapor and other gases Its temperature Silica content ...
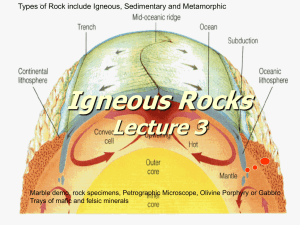
Igneous rocks
... Igneous Rocks: Terminology • Igneous rocks are formed as a result of cooling and crystallization from a magma. • Magma is molten rock (fluid), rich in silica (SiO2), which contains dissolved volatiles (e.g. CO2 and H2O). • Lava is magma extruded on or very near the Earth’s surface. Most lavas have ...
... Igneous Rocks: Terminology • Igneous rocks are formed as a result of cooling and crystallization from a magma. • Magma is molten rock (fluid), rich in silica (SiO2), which contains dissolved volatiles (e.g. CO2 and H2O). • Lava is magma extruded on or very near the Earth’s surface. Most lavas have ...
Document
... the islands, and some of the debris has traveled hundreds of kilometers offshore. Most of the Hawaiian Islands have irregular shapes, not like the round volcanoes. This is because their sides tend to collapse in gigantic landslides, leaving chunks the size of cities scattered around the deep sea flo ...
... the islands, and some of the debris has traveled hundreds of kilometers offshore. Most of the Hawaiian Islands have irregular shapes, not like the round volcanoes. This is because their sides tend to collapse in gigantic landslides, leaving chunks the size of cities scattered around the deep sea flo ...
Volcanoes
... eruptions, over time Many layers of different kinds of lava flows This equals a composite of layers such as lava, volcanic ash, pumice, and tephra ...
... eruptions, over time Many layers of different kinds of lava flows This equals a composite of layers such as lava, volcanic ash, pumice, and tephra ...
Volcanology - Departments
... Types of Lava • Lava resulting from the process of subduction is described as ANDESITIC and occurs as/at: • Island arcs • Destructive plate boundaries where oceanic crust is being destroyed and gases are being added ...
... Types of Lava • Lava resulting from the process of subduction is described as ANDESITIC and occurs as/at: • Island arcs • Destructive plate boundaries where oceanic crust is being destroyed and gases are being added ...
Quiz Three (2:00 to 2:05 PM) - University of South Alabama
... hotspots has made it to the surface of the Earth quickly and is still hot (up to 1800 °C) and fluid (low viscosity). Lava erupted at convergent plate boundaries and continental hotspots has made it to the surface of the Earth very slowly. It is cooler (as low as 800 °C) and very contaminated by coun ...
... hotspots has made it to the surface of the Earth quickly and is still hot (up to 1800 °C) and fluid (low viscosity). Lava erupted at convergent plate boundaries and continental hotspots has made it to the surface of the Earth very slowly. It is cooler (as low as 800 °C) and very contaminated by coun ...
File
... or stop erupting. This, in turn, has led to conflicts between the tourism and geothermal energy production in New Zealand and Iceland. Minerals Volcanic rocks have a wide variety of economic uses, for example pumice is used as an abrasive and cinder for road construction. In Arequipa, Peru, the volc ...
... or stop erupting. This, in turn, has led to conflicts between the tourism and geothermal energy production in New Zealand and Iceland. Minerals Volcanic rocks have a wide variety of economic uses, for example pumice is used as an abrasive and cinder for road construction. In Arequipa, Peru, the volc ...
Volcano
... Roads, highways, and airport runways can be made treacherous or impassable because ash is slippery and may reduce visibility to near zero. Cars driving faster than 5 miles per hour on ashcovered roads stir up thick clouds of ash, reducing visibility and causing accidents. Ash also clogs filters used ...
... Roads, highways, and airport runways can be made treacherous or impassable because ash is slippery and may reduce visibility to near zero. Cars driving faster than 5 miles per hour on ashcovered roads stir up thick clouds of ash, reducing visibility and causing accidents. Ash also clogs filters used ...
2 Effects of Volcanic Eruptions
... 4. Small earthquakes occur much more often than large earthquakes. 5. Possible answers: The car is on fire; the car is in a dangerous location (e.g., railroad tracks). ...
... 4. Small earthquakes occur much more often than large earthquakes. 5. Possible answers: The car is on fire; the car is in a dangerous location (e.g., railroad tracks). ...
mountain building - Catawba County Schools
... fracture. This is called brittle deformation or brittle fracture • At depth, where temperatures and pressure is high, rocks show ductile behavior. Ductile deformation produces a change in the rock size or shape without fracture ...
... fracture. This is called brittle deformation or brittle fracture • At depth, where temperatures and pressure is high, rocks show ductile behavior. Ductile deformation produces a change in the rock size or shape without fracture ...
volcanic activity guided notes
... the magma chamber to Earth’s surface. __________ - an opening in the volcano where gases and molten rock leave. __________ ________ – The area covered by lava as it pours out of a vent. Crater – A _________-__________ area that may form at the top of a volcano around the volcano’s central ____ ...
... the magma chamber to Earth’s surface. __________ - an opening in the volcano where gases and molten rock leave. __________ ________ – The area covered by lava as it pours out of a vent. Crater – A _________-__________ area that may form at the top of a volcano around the volcano’s central ____ ...
Unit 3 - Rocks and Minerals - Igenous Rock Vocabualry
... rock body, that is overlain by sedimentary rocks. It represents a period of erosion of the igneous or metamorphic body prior to the deposition of the sedimentary rocks or the volcanic “sediments”. Rock types are totally different above and below the break in sequence they are (Not alike). Disconform ...
... rock body, that is overlain by sedimentary rocks. It represents a period of erosion of the igneous or metamorphic body prior to the deposition of the sedimentary rocks or the volcanic “sediments”. Rock types are totally different above and below the break in sequence they are (Not alike). Disconform ...
PDF 115KB
... in april 2010, global attention shifted towards iceland, a remote northern island resting on the mid-atlantic ridge. eyjafjallajökull had erupted for the first time since 1823, spewing a massive ash cloud and causing the largest shutdown of european airspace since world war ii (oxford economics, 201 ...
... in april 2010, global attention shifted towards iceland, a remote northern island resting on the mid-atlantic ridge. eyjafjallajökull had erupted for the first time since 1823, spewing a massive ash cloud and causing the largest shutdown of european airspace since world war ii (oxford economics, 201 ...
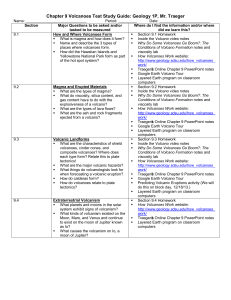
Chapter 9 Volcanoes Test Study Guide: Geology 1P, Mr. Traeger
... § Section 9.1 Homework § Inside the Volcano video notes § What is magma and how does it form? § Why Do Some Volcanoes Go Boom?: The § Name and describe the 3 types of Conditions of Volcano Formation notes and places where volcanoes form. § How did the Hawaiian Islands and viscosity lab § How Volcano ...
... § Section 9.1 Homework § Inside the Volcano video notes § What is magma and how does it form? § Why Do Some Volcanoes Go Boom?: The § Name and describe the 3 types of Conditions of Volcano Formation notes and places where volcanoes form. § How did the Hawaiian Islands and viscosity lab § How Volcano ...
Unit 5.2 Notes
... surround it, a ___________________forms. • When magma forces its way through rock layers by following existing fractures or by creating new fractures, a _______________ forms. Dikes cut across layers rather than lying parallel to the rock layers. • Sills and __________________vary in thickness from ...
... surround it, a ___________________forms. • When magma forces its way through rock layers by following existing fractures or by creating new fractures, a _______________ forms. Dikes cut across layers rather than lying parallel to the rock layers. • Sills and __________________vary in thickness from ...
Color Luster Streak
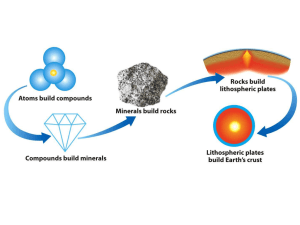
... Sediment – rock material that forms where rocks are broken down into smaller pieces or dissolved in water as rocks erode rock cycle – the series of processes that change one type of rock into another type of rock Section 8.2 igneous rock – rock formed from magma or lava that has been cooled and hard ...
... Sediment – rock material that forms where rocks are broken down into smaller pieces or dissolved in water as rocks erode rock cycle – the series of processes that change one type of rock into another type of rock Section 8.2 igneous rock – rock formed from magma or lava that has been cooled and hard ...
Constructive and Destructive Forces - Matthew H.
... and steep slopes. Alternating layers of lava and ash create steep slopes. This type of volcano is a constructive volcano. Ashflow Caldera volcanoes are also known as supervolcanoes because they are the most violent and powerful volcanoes. They usually have wide open vents surrounded by hills of ash. ...
... and steep slopes. Alternating layers of lava and ash create steep slopes. This type of volcano is a constructive volcano. Ashflow Caldera volcanoes are also known as supervolcanoes because they are the most violent and powerful volcanoes. They usually have wide open vents surrounded by hills of ash. ...
Petrogenesis and correlation of the mid
... biotite, with plagioclase being slightly more abundant. Quartz in notably absent among the phenocryst phases. The texture is vitrophyric and most of the phenocrysts are less than 2 mm. The UBT is distinct from the lower Bonanza tuff, which is dacitic in composition and more crystal rich. The lower t ...
... biotite, with plagioclase being slightly more abundant. Quartz in notably absent among the phenocryst phases. The texture is vitrophyric and most of the phenocrysts are less than 2 mm. The UBT is distinct from the lower Bonanza tuff, which is dacitic in composition and more crystal rich. The lower t ...
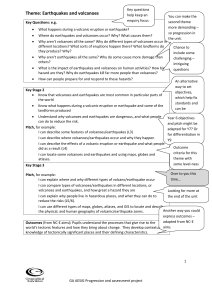
Theme: Earthquakes and volcanoes
... Why aren’t volcanoes all the same? Why do different types of volcanoes occur in different locations? What sorts of eruptions happen there? What landforms do they produce? Why? ...
... Why aren’t volcanoes all the same? Why do different types of volcanoes occur in different locations? What sorts of eruptions happen there? What landforms do they produce? Why? ...
Identifying volcanic rocks
... There are many different types of volcanoes around New Zealand, from volcanic fields in the north, to cone volcanoes and calderas in the south. Each type of volcano is associated with a different type of lava, which cools to form rocks. By examining the chemical composition of rocks that they find, ...
... There are many different types of volcanoes around New Zealand, from volcanic fields in the north, to cone volcanoes and calderas in the south. Each type of volcano is associated with a different type of lava, which cools to form rocks. By examining the chemical composition of rocks that they find, ...
Tuff

Tuff (from the Italian tufo) is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is compacted into a solid rock in a process called consolidation. Tuff is sometimes called tufa, particularly when used as construction material, although tufa also refers to a quite different rock. Rock that contains greater than 50% tuff is considered tuffaceous. Tuff is a relatively soft rock, so it has been used for construction since ancient times. Since it is common in Italy the Romans used it often for construction. The Rapa Nui people used it to make most of the moai statues in Easter Island.Tuff can be classified as either sedimentary or igneous rocks. They are usually studied in the context of igneous petrology, although they are sometimes described using sedimentological terms.