No Slide Title
... Clouds of hot ash and chunks of molten rock, shooting out of a vent at high speed. ...
... Clouds of hot ash and chunks of molten rock, shooting out of a vent at high speed. ...
Volcanoes
... • A vent that lets out heat from inside the Earth , spewing out lava and eventually forming a mountain. • 3 classifications of volcanic activity: extinct (does not erupt), dormant (sleeping), and active (currently erupting). • The most active volcano on the Earth is Kilauea on the big island of Hawa ...
... • A vent that lets out heat from inside the Earth , spewing out lava and eventually forming a mountain. • 3 classifications of volcanic activity: extinct (does not erupt), dormant (sleeping), and active (currently erupting). • The most active volcano on the Earth is Kilauea on the big island of Hawa ...
Objective: Identify and describe the three kinds of volcanic cones
... Both active and inactive volcanoes can be found in many places around the world. They are also found in space. Jupiter’s moon Io is the first moon or body other than Earth on which scientists have seen active volcanoes. The volcanoes on Io are so powerful that they shoot out many metric tons of mate ...
... Both active and inactive volcanoes can be found in many places around the world. They are also found in space. Jupiter’s moon Io is the first moon or body other than Earth on which scientists have seen active volcanoes. The volcanoes on Io are so powerful that they shoot out many metric tons of mate ...
Volcanoes: The Fire Within
... • A vent that lets out heat from inside the Earth , spewing out lava (molten rock on the surface) and eventually forming a mountain. • 3 classifications of volcanic activity: extinct (does not erupt), dormant (sleeping), and active (currently erupting). • The most active volcano on the Earth is Kila ...
... • A vent that lets out heat from inside the Earth , spewing out lava (molten rock on the surface) and eventually forming a mountain. • 3 classifications of volcanic activity: extinct (does not erupt), dormant (sleeping), and active (currently erupting). • The most active volcano on the Earth is Kila ...
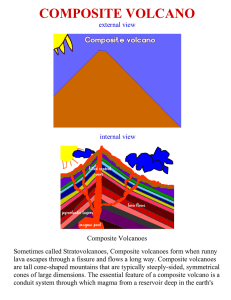
composite volcano
... crust rises to the surface. The volcano is built up by the accumulation of material erupted through the conduit and increases in size as lava, cinders, ash etc. are added to its slopes. Composite volcanoes erupt in different ways at different times. These volcanoes are built in layers by multiple e ...
... crust rises to the surface. The volcano is built up by the accumulation of material erupted through the conduit and increases in size as lava, cinders, ash etc. are added to its slopes. Composite volcanoes erupt in different ways at different times. These volcanoes are built in layers by multiple e ...
Volcanoes SHOW
... Combination of explosive activity (pyroclastic) and lava flows Responsible for most deaths of any type of volcano ex. Mount Saint Helens Mt. Pinatubo Mt. Fuji Mt. Vesuvius ...
... Combination of explosive activity (pyroclastic) and lava flows Responsible for most deaths of any type of volcano ex. Mount Saint Helens Mt. Pinatubo Mt. Fuji Mt. Vesuvius ...
VOLCANOES STUDY GUIDE Test 1/14/15 Key Words • Volcano
... Dormant volcano-has not erupted in a long time Extinct volcano-has stopped erupting Shield Volcano-built by thinner, fluid lava that spreads over a large area Cinder-Cone Volcanoes-built by thick lava, cone shape mountain, steep sides Composite Volcanoes-built by layers of ash and cinders sandwich ...
... Dormant volcano-has not erupted in a long time Extinct volcano-has stopped erupting Shield Volcano-built by thinner, fluid lava that spreads over a large area Cinder-Cone Volcanoes-built by thick lava, cone shape mountain, steep sides Composite Volcanoes-built by layers of ash and cinders sandwich ...
Inside Earth 3-2 Worksheets 2013
... Monitoring volcanoes – easier for geologists than earthquakes – because there are usually signs/warnings that a volcano will erupt -pimples What are some changes or clues that geologists look for when they are monitoring volcanoes? _________________________________________________________________ _ ...
... Monitoring volcanoes – easier for geologists than earthquakes – because there are usually signs/warnings that a volcano will erupt -pimples What are some changes or clues that geologists look for when they are monitoring volcanoes? _________________________________________________________________ _ ...
Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... cinders and other rock particles that have been blown into the air. Narrow bases with steep sides due to loosely arranged cinder type eruptions. ...
... cinders and other rock particles that have been blown into the air. Narrow bases with steep sides due to loosely arranged cinder type eruptions. ...
Chapter 5: Volcanoes
... from the magma chamber to the pipe until it flows or explodes out of the vent. ...
... from the magma chamber to the pipe until it flows or explodes out of the vent. ...
Additional notes on management of volcanic hazards
... Ozone depletion following release of huge amounts of sulphur dioxide ...
... Ozone depletion following release of huge amounts of sulphur dioxide ...
Cornell Notes Template
... o Example- Mount St. Helens Violent eruptions usually eject pyroclastic material (rock fragments) from the vent. The pyroclastic material can range in size from ash to volcanic blocks the size of houses ...
... o Example- Mount St. Helens Violent eruptions usually eject pyroclastic material (rock fragments) from the vent. The pyroclastic material can range in size from ash to volcanic blocks the size of houses ...
Science 1 Notes: Volcanoes
... Lava flowing from fissures (long cracks in the ground) are more common than volcanoes. Magma is molten rock. Magma, which reaches the surface and flows, is called lava. Lava refers to both the molten rock itself and to the rocks that it forms. How the lava behaves depends on the amount of silicate ( ...
... Lava flowing from fissures (long cracks in the ground) are more common than volcanoes. Magma is molten rock. Magma, which reaches the surface and flows, is called lava. Lava refers to both the molten rock itself and to the rocks that it forms. How the lava behaves depends on the amount of silicate ( ...
Ch. 4 Volcanism and Extrusive Ignous Rocks
... – Large amounts of ash and volcanic gases in atmosphere can trigger rapid climate changes and contribute to mass extinctions ...
... – Large amounts of ash and volcanic gases in atmosphere can trigger rapid climate changes and contribute to mass extinctions ...
Ch. 9 Study Guide Answers
... • Volcanic Ash high in the atmosphere could block sunlight, causing (regions of earths) temperatures to drop. ...
... • Volcanic Ash high in the atmosphere could block sunlight, causing (regions of earths) temperatures to drop. ...
Answers to the 13-2 two column notes
... Caldera (Define and example)It is when a magma chamber empties and the volcanic cone collapses to leave a large , basin shaped depression called a caldera. Mount Mazama in Oregon erupted and formed a caldera that later filled with water and is now called Crater Lake. ...
... Caldera (Define and example)It is when a magma chamber empties and the volcanic cone collapses to leave a large , basin shaped depression called a caldera. Mount Mazama in Oregon erupted and formed a caldera that later filled with water and is now called Crater Lake. ...
Put your text here… - Social Circle City Schools
... earth’s surface was formed f. describe the effects of volcanic eruption on earth’s geological features ...
... earth’s surface was formed f. describe the effects of volcanic eruption on earth’s geological features ...
Impact of Volcanoes
... If a volcano erupts under the ocean, it can cause a tsunami—not only from its blast, but from the earthquake it creates. Lava and ____________________ flows can set fire to homes, cars, or anything else that is combustible. A ___________ can spit out debris that blocks a river channel or causes a cr ...
... If a volcano erupts under the ocean, it can cause a tsunami—not only from its blast, but from the earthquake it creates. Lava and ____________________ flows can set fire to homes, cars, or anything else that is combustible. A ___________ can spit out debris that blocks a river channel or causes a cr ...
Formation of volcanic features| sample answer
... Volcanic features found on the earths surface (external features) are caused by lava emerging from the mantle through the crust and cools when it reaches the surface. These features include; lava plateau, craters and calderas, volcanic plugs and the main feature; volcanic cones. Volcanic cones are e ...
... Volcanic features found on the earths surface (external features) are caused by lava emerging from the mantle through the crust and cools when it reaches the surface. These features include; lava plateau, craters and calderas, volcanic plugs and the main feature; volcanic cones. Volcanic cones are e ...
_____ 1. What happens to the atmosphere after large
... the left. Write the letter in the space provided. You may use the volcanoes listed on the right more than once. ...
... the left. Write the letter in the space provided. You may use the volcanoes listed on the right more than once. ...
Topic 8 Volcanoes
... Earth's surface. It is also a bowl-shaped depression at the top of the volcano where volcanic materials like, ash, lava, and other pyroclastic materials are released. ...
... Earth's surface. It is also a bowl-shaped depression at the top of the volcano where volcanic materials like, ash, lava, and other pyroclastic materials are released. ...
Force of Volcanoes
... Types of Eruptions and Volcanoes (video) ______________ volcanoes form from long, gradual lava flows, pouring out in all directions. The ___________ ______________ are short and built from these ejected materials, mainly ash and rocks that fall near the summit or crate of the volcano. ______________ ...
... Types of Eruptions and Volcanoes (video) ______________ volcanoes form from long, gradual lava flows, pouring out in all directions. The ___________ ______________ are short and built from these ejected materials, mainly ash and rocks that fall near the summit or crate of the volcano. ______________ ...
Three basic types of volcanoes
... Volcanoes that erupt only lava and gas The most common type of eruption ...
... Volcanoes that erupt only lava and gas The most common type of eruption ...
Volcanoes I - Faculty Washington
... Volcanoes Lesson Objectives As a result of this lesson and the reading, you should be able to: Define the following terms or phrases: Shield Volcano, Stratovolcano, Flood Basalts, Lahar, Pyroclastics, Lava. Distinguish between the volcanism found over hot spots, subduction zones, and spreading c ...
... Volcanoes Lesson Objectives As a result of this lesson and the reading, you should be able to: Define the following terms or phrases: Shield Volcano, Stratovolcano, Flood Basalts, Lahar, Pyroclastics, Lava. Distinguish between the volcanism found over hot spots, subduction zones, and spreading c ...
Mount Edziza volcanic complex

The Mount Edziza volcanic complex is a large and potentially active north-south trending complex volcano in Stikine Country, northwestern British Columbia, Canada, located 38 kilometres (24 mi) southeast of the small community of Telegraph Creek. It occupies the southeastern portion of the Tahltan Highland, an upland area of plateau and lower mountain ranges, lying east of the Boundary Ranges and south of the Inklin River, which is the east fork of the Taku River. As a volcanic complex, it consists of many types of volcanoes, including shield volcanoes, calderas, lava domes, stratovolcanoes, and cinder cones.Most of the Mount Edziza volcanic complex is encompassed within a large provincial park called Mount Edziza Provincial Park. Named after Mount Edziza, this 2,660.95 km2 (1,027.40 sq mi) park was established in 1972 to preserve the volcanic and cultural treasures unique to the northern British Columbia area. The Mount Edziza volcanic complex is remote, and, without roads, accessible only along trails. The easiest access is from Highway 37 and a spur road from Dease Lake to Telegraph Creek. From Kinaskan Lake, on Highway 37, a poorly maintained trail extends west for 30 kilometres (19 mi) into the heart of the complex. From Telegraph Creek another trail extends east for 25 kilometres (16 mi) to the north slope of Mount Edziza.