7B27 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... circuit indication. Amplitude modulation is used to implement transformer isolation (100 V rms, continuous). Isolated frontend circuitry power is supplied by a DC/DC converter. The output section contains a demodulator, a two-pole low pass filter (-3 dB @ 3 Hz), a buffer amplifier and a power oscill ...
... circuit indication. Amplitude modulation is used to implement transformer isolation (100 V rms, continuous). Isolated frontend circuitry power is supplied by a DC/DC converter. The output section contains a demodulator, a two-pole low pass filter (-3 dB @ 3 Hz), a buffer amplifier and a power oscill ...
VLSI_final powerPoint
... sometimes get when I touch a doorknob after walking across the carpet at work). Sometimes this problem is called electrical overstress (EOS) since most ESD-related failures are caused not by gate-oxide breakdown, but by the thermal stress (melting) that occurs when the n -channel transistor in an ou ...
... sometimes get when I touch a doorknob after walking across the carpet at work). Sometimes this problem is called electrical overstress (EOS) since most ESD-related failures are caused not by gate-oxide breakdown, but by the thermal stress (melting) that occurs when the n -channel transistor in an ou ...
TD-1436
... [2] The accuracy will not be affected by power interruptions up to 1 millisecond, spaced at least 10 milliseconds apart. Transient and power loss specifications are based on a maximum duty cycle of 1/50. [3] EMI test limits will not be exceeded during the timing interval or when continuously energiz ...
... [2] The accuracy will not be affected by power interruptions up to 1 millisecond, spaced at least 10 milliseconds apart. Transient and power loss specifications are based on a maximum duty cycle of 1/50. [3] EMI test limits will not be exceeded during the timing interval or when continuously energiz ...
Two Page Summary
... ii) Net torques about any point =-zero Do problem with diagram showing direction of torques about a specific point OR c) Further electronics Transformer Describe its role. Do a turns ratio problem with proper labeling of primary and secondary AC voltages Draw a sine curve on a grid and label ...
... ii) Net torques about any point =-zero Do problem with diagram showing direction of torques about a specific point OR c) Further electronics Transformer Describe its role. Do a turns ratio problem with proper labeling of primary and secondary AC voltages Draw a sine curve on a grid and label ...
Measuring Voltage and Current
... 2. Connect the voltmeter across the power supply and measure the supply voltage. 3. Then connect the voltmeter across the resistance (R) and measure this voltage. ...
... 2. Connect the voltmeter across the power supply and measure the supply voltage. 3. Then connect the voltmeter across the resistance (R) and measure this voltage. ...
c_notebook_3_unit_11_electricity_magnetism_20131021
... P= 0,1144 KW 6.- Calculate the intensity drawn by an electric motor whose power is 1,2 Kw connected to a tension of 220V. If the motor would be connected to a tension of 380V, calculate the intensity of the current drawn in this case. I (220V) = 5,45A / I (380V)= 3,16A 7.- a) Draw a circuit with a p ...
... P= 0,1144 KW 6.- Calculate the intensity drawn by an electric motor whose power is 1,2 Kw connected to a tension of 220V. If the motor would be connected to a tension of 380V, calculate the intensity of the current drawn in this case. I (220V) = 5,45A / I (380V)= 3,16A 7.- a) Draw a circuit with a p ...
800 kVA - 1153 Amps per phase
... is incorporated into the Stamford Permanent Magnet Generator (PMG) system and is fitted as standard to generators of this type. The PMG provides power via the AVR to the main exciter, giving a source of constant excitation power independent of generator output. The main exciter output is then fed to ...
... is incorporated into the Stamford Permanent Magnet Generator (PMG) system and is fitted as standard to generators of this type. The PMG provides power via the AVR to the main exciter, giving a source of constant excitation power independent of generator output. The main exciter output is then fed to ...
An Ultra Low-Power Non-Volatile Memory Design Enabled
... long pulses (see Table I). This makes power-hungry circuits (e.g., charge pumps) unavoidable and the use of some powersaving design techniques more difficult [3]. In contrast, RRAM cells operate by physical mechanisms which are inherently low-voltage, high-speed, and low-energy [4-6]. The emergence ...
... long pulses (see Table I). This makes power-hungry circuits (e.g., charge pumps) unavoidable and the use of some powersaving design techniques more difficult [3]. In contrast, RRAM cells operate by physical mechanisms which are inherently low-voltage, high-speed, and low-energy [4-6]. The emergence ...
Project Proposal on DCDC converters for the 42V Automotive
... In order to handle high current at low voltages, SR is needed Low Rdson MOSFET greatly reduces losses at the output rectifier ...
... In order to handle high current at low voltages, SR is needed Low Rdson MOSFET greatly reduces losses at the output rectifier ...
Specification Sheet
... The AC input shall be a two-wire, universal voltage capable 120 thru 277 VAC, 50/60 Hz and be UL Classified to Category Control Number (CCN) FTBR, Emergency Lighting and Power Equipment, and FTBV, Emergency Light-Emitting-Diode Drivers for field installation. Maximum input power of the emergency dri ...
... The AC input shall be a two-wire, universal voltage capable 120 thru 277 VAC, 50/60 Hz and be UL Classified to Category Control Number (CCN) FTBR, Emergency Lighting and Power Equipment, and FTBV, Emergency Light-Emitting-Diode Drivers for field installation. Maximum input power of the emergency dri ...
7. Application Circuits / Converter Array Design Considerations
... Logic Disable. (Figure 7–1) The GATE IN pin of the module may be used to turn the module on or off. When GATE IN is pulled low (<0.65 V @ 6 mA, referenced to –Vin), the module is turned off. When GATE IN is floating (open collector), the module is turned on. The open circuit voltage of the GATE IN p ...
... Logic Disable. (Figure 7–1) The GATE IN pin of the module may be used to turn the module on or off. When GATE IN is pulled low (<0.65 V @ 6 mA, referenced to –Vin), the module is turned off. When GATE IN is floating (open collector), the module is turned on. The open circuit voltage of the GATE IN p ...
ECE3050 — Assignment 17 1. The figures show inverting amplifier
... 14. The figure shows a three op amp instrumentation amplifier. (a) Design the circuit such that vO1 − vO2 = 10 (vI1 − vI2 ) and vO = 10 (vO1 − vO2 ). Answers: 1 + 2RF 1 /R1 = 10, choose R1 = 2 kΩ and RF 1 = 9 kΩ, RF 2 /R2 = 10, choose RF 2 = 10 kΩ, and R2 = 1 kΩ. (b) For vI1 = 0.03 V and vI2 = 0.01 ...
... 14. The figure shows a three op amp instrumentation amplifier. (a) Design the circuit such that vO1 − vO2 = 10 (vI1 − vI2 ) and vO = 10 (vO1 − vO2 ). Answers: 1 + 2RF 1 /R1 = 10, choose R1 = 2 kΩ and RF 1 = 9 kΩ, RF 2 /R2 = 10, choose RF 2 = 10 kΩ, and R2 = 1 kΩ. (b) For vI1 = 0.03 V and vI2 = 0.01 ...
TeamCommonGroundPhas2 - Department of Applied
... The 3.3 volt regulator input pin needs to be connected to the output pin of the 5 volt regulator. This is an MCP1702 regulator that will take the 5 volts down to 3.3 volts with a maximum current output of 250mA. This will power the XBee which is the serial communications receiver, but the regulator ...
... The 3.3 volt regulator input pin needs to be connected to the output pin of the 5 volt regulator. This is an MCP1702 regulator that will take the 5 volts down to 3.3 volts with a maximum current output of 250mA. This will power the XBee which is the serial communications receiver, but the regulator ...
Multi-functional Packaged Antennas for Next
... Example: A t room temperature a certain transistor has β = 150. Calculate gm and rπ if ICQ = 10 mA. ...
... Example: A t room temperature a certain transistor has β = 150. Calculate gm and rπ if ICQ = 10 mA. ...
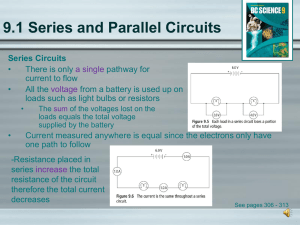
PP-Series and Parrellel circuts
... Current measured anywhere is equal since the electrons only have one path to follow -Resistance placed in series increase the total resistance of the circuit therefore the total current decreases ...
... Current measured anywhere is equal since the electrons only have one path to follow -Resistance placed in series increase the total resistance of the circuit therefore the total current decreases ...
Induction
... A simple ac alternator is used to generate a peak output voltage of 24.0 V. The square armature (rotating loops) consists of windings that are 5.0 cm on a side and rotates in a magnetic field of 0.500 T at a rate of 60 rev/s. How many loops, N, of wire must be wound on the square armature? 24.0 V ...
... A simple ac alternator is used to generate a peak output voltage of 24.0 V. The square armature (rotating loops) consists of windings that are 5.0 cm on a side and rotates in a magnetic field of 0.500 T at a rate of 60 rev/s. How many loops, N, of wire must be wound on the square armature? 24.0 V ...
multiple choice II
... 6. ConcepTest 19.3b Short Circuit II Two lightbulbs A and B are connected in series to a constant voltage source. When a wire is connected across B, bulb A will: ...
... 6. ConcepTest 19.3b Short Circuit II Two lightbulbs A and B are connected in series to a constant voltage source. When a wire is connected across B, bulb A will: ...
Switched-mode power supply

A switched-mode power supply (switching-mode power supply, switch-mode power supply, SMPS, or switcher) is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator to convert electrical power efficiently. Like other power supplies, an SMPS transfers power from a source, like mains power, to a load, such as a personal computer, while converting voltage and current characteristics. Unlike a linear power supply, the pass transistor of a switching-mode supply continually switches between low-dissipation, full-on and full-off states, and spends very little time in the high dissipation transitions, which minimizes wasted energy. Ideally, a switched-mode power supply dissipates no power. Voltage regulation is achieved by varying the ratio of on-to-off time. In contrast, a linear power supply regulates the output voltage by continually dissipating power in the pass transistor. This higher power conversion efficiency is an important advantage of a switched-mode power supply. Switched-mode power supplies may also be substantially smaller and lighter than a linear supply due to the smaller transformer size and weight.Switching regulators are used as replacements for linear regulators when higher efficiency, smaller size or lighter weight are required. They are, however, more complicated; their switching currents can cause electrical noise problems if not carefully suppressed, and simple designs may have a poor power factor.