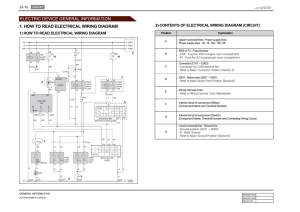
OM2324102416
... the renewable and green energy sources such as the solar arrays and the fuel cells. Moreover, the power systems based on battery sources and super capacitors have been increased. Unfortunately, the output voltages of these sources are relatively low. Therefore, the step-up power conversion is requir ...
... the renewable and green energy sources such as the solar arrays and the fuel cells. Moreover, the power systems based on battery sources and super capacitors have been increased. Unfortunately, the output voltages of these sources are relatively low. Therefore, the step-up power conversion is requir ...
a Wideband, High Output Current, Fast Settling Op Amp AD842*
... in a gain-of-2 follower configuration. The AD842 maintains a typical slew rate of 375 V/µs, which means it can drive a ± 10 V, 6.0 MHz signal or a ± 3 V, 19.9 MHz signal. The termination resistor, RT, (when equal to the characteristic impedance of the cable) minimizes reflections from the far end of ...
... in a gain-of-2 follower configuration. The AD842 maintains a typical slew rate of 375 V/µs, which means it can drive a ± 10 V, 6.0 MHz signal or a ± 3 V, 19.9 MHz signal. The termination resistor, RT, (when equal to the characteristic impedance of the cable) minimizes reflections from the far end of ...
Superposition Analysis LectureNotes
... Notice that although we could expect currents I2 and I3 to flow in opposite directions just from looking at the circuit, we have them flowing in the same direction as when we used KVL on the voltage source circuit. This is to maintain consistency across equations and avoid problems with signs later ...
... Notice that although we could expect currents I2 and I3 to flow in opposite directions just from looking at the circuit, we have them flowing in the same direction as when we used KVL on the voltage source circuit. This is to maintain consistency across equations and avoid problems with signs later ...
Unit 3 Study Design 2009 Motion in one and two dimensions • apply
... • interpret information from the display of an oscilloscope in terms of voltage as a function of time; • analyse circuits, including fault diagnosis, following selection and use of appropriate measuring devices, including analogue meters, multimeters, oscilloscope; • evaluate the operation of a circ ...
... • interpret information from the display of an oscilloscope in terms of voltage as a function of time; • analyse circuits, including fault diagnosis, following selection and use of appropriate measuring devices, including analogue meters, multimeters, oscilloscope; • evaluate the operation of a circ ...
Introduction - facstaff.bucknell.edu
... Sometimes a nonsymmetrical square wave, also called a rectangular wave, is required. There are many ways to generate square waves, but if a high-quality signal source is not required, one of the easiest and least expensive approaches is to use an op-amp. In this lab experiment you will build a type ...
... Sometimes a nonsymmetrical square wave, also called a rectangular wave, is required. There are many ways to generate square waves, but if a high-quality signal source is not required, one of the easiest and least expensive approaches is to use an op-amp. In this lab experiment you will build a type ...
DRN4-Multiple DDC Signal Input to Proportional Resistance Output
... Be sure to follow all local and electrical codes. Refer to wiring diagram for connection information. Be sure to make all connections with the power off. 1. If required by BAS or controller specification, the 24 volt AC neutral can be earth grounded at the transformer. Analog input, digital input, a ...
... Be sure to follow all local and electrical codes. Refer to wiring diagram for connection information. Be sure to make all connections with the power off. 1. If required by BAS or controller specification, the 24 volt AC neutral can be earth grounded at the transformer. Analog input, digital input, a ...
Section J6: FET Amplifiers & Amplifier Analysis
... detail. Similar to the BJT amplifier analysis, we will derive equations for the voltage gain, current gain, input resistance and output resistance. For the 90-gajillionth time, ¾ Always keep in mind that the total voltage and current are composed of a dc component and an ac component. For the small- ...
... detail. Similar to the BJT amplifier analysis, we will derive equations for the voltage gain, current gain, input resistance and output resistance. For the 90-gajillionth time, ¾ Always keep in mind that the total voltage and current are composed of a dc component and an ac component. For the small- ...
FJP13009 High Voltage Fast-Switching NPN Power Transistor FJP13009 High V
... 2. A critical component in any component of a life support, device, or system whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life support device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness. ...
... 2. A critical component in any component of a life support, device, or system whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life support device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness. ...
NC7NZ17 TinyLogic UHS Triple Buffer with Schmitt Trigger Inputs
... The NC7NZ17 is a triple buffer with Schmitt trigger inputs from Fairchild’s Ultra High Speed Series of TinyLogic in the US8 package. The device is fabricated with advanced CMOS technology to achieve ultra high speed with high output drive while maintaining low static power dissipation over a very b ...
... The NC7NZ17 is a triple buffer with Schmitt trigger inputs from Fairchild’s Ultra High Speed Series of TinyLogic in the US8 package. The device is fabricated with advanced CMOS technology to achieve ultra high speed with high output drive while maintaining low static power dissipation over a very b ...
Experiment 10: Inverting Amplifier
... – Take a screen shot of the input and output voltage as a function of time, displaying at least 3 cycles. – Remove Rf from the circuit. Measure and record the resistance between pins 1 and 2. – Measure the output voltage at the following input voltages: • 0V, +/-1V, +/-2V, +/-3V, +/- 4V, and +/-5V. ...
... – Take a screen shot of the input and output voltage as a function of time, displaying at least 3 cycles. – Remove Rf from the circuit. Measure and record the resistance between pins 1 and 2. – Measure the output voltage at the following input voltages: • 0V, +/-1V, +/-2V, +/-3V, +/- 4V, and +/-5V. ...
DN040 -- Reduced Battery Current Using CC112x, CC1175_and
... Figure 3.1 TPS62730 Typical Application Circuit and Layout The TPS62730 requires only two additional components to the design and its recommended ...
... Figure 3.1 TPS62730 Typical Application Circuit and Layout The TPS62730 requires only two additional components to the design and its recommended ...
AD580 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... bandgap concept to produce a stable, low temperature coefficient voltage reference suitable for high accuracy data acquisition components and systems. The device makes use of the underlying physical nature of a silicon transistor base-emitter voltage in the forward-biased operating region. All such ...
... bandgap concept to produce a stable, low temperature coefficient voltage reference suitable for high accuracy data acquisition components and systems. The device makes use of the underlying physical nature of a silicon transistor base-emitter voltage in the forward-biased operating region. All such ...
High-Speed Electronic Circuits for 100 Gb/s Transport Networks M. Möller
... swing (Vmax), gain (G), transimpedance (ZTI), for 50-Ω input: ZTI =voltage gain + 34 dB, max./min. voltage gain (Gmax/Gmin), 1) 75Ω driver, 2) TIA and AGC, 3) additional 1.6 W are consumed by a full-wave recifier. ...
... swing (Vmax), gain (G), transimpedance (ZTI), for 50-Ω input: ZTI =voltage gain + 34 dB, max./min. voltage gain (Gmax/Gmin), 1) 75Ω driver, 2) TIA and AGC, 3) additional 1.6 W are consumed by a full-wave recifier. ...
27 3.2 0 0 0 0 0 30.2 Measured Required Result Measured
... Can the battery[ies] in this notebook computer be easily replaced by users themselves ...
... Can the battery[ies] in this notebook computer be easily replaced by users themselves ...
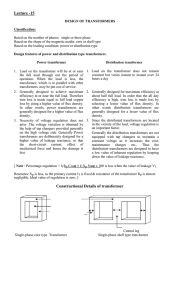
Constructional Details of transformer
... 1. Load on the transformer will be at or near 1. Load on the transformer does not remain constant but varies instant to instant over 24 the full load through out the period of hours a day operation. When the load is less, the transformer, which is in parallel with other transformers, may be put out ...
... 1. Load on the transformer will be at or near 1. Load on the transformer does not remain constant but varies instant to instant over 24 the full load through out the period of hours a day operation. When the load is less, the transformer, which is in parallel with other transformers, may be put out ...
RESISTORS FOR ENERGY METERING
... by contributing to series inductance, but also by reducing the Q factor of the input network, thereby minimising the effect of any resonances. Critically, it serves to limit the peak MOV current during a lightning strike transient, reducing the stress on the MOV by dissipating a share of the pulse e ...
... by contributing to series inductance, but also by reducing the Q factor of the input network, thereby minimising the effect of any resonances. Critically, it serves to limit the peak MOV current during a lightning strike transient, reducing the stress on the MOV by dissipating a share of the pulse e ...
Switched-mode power supply

A switched-mode power supply (switching-mode power supply, switch-mode power supply, SMPS, or switcher) is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator to convert electrical power efficiently. Like other power supplies, an SMPS transfers power from a source, like mains power, to a load, such as a personal computer, while converting voltage and current characteristics. Unlike a linear power supply, the pass transistor of a switching-mode supply continually switches between low-dissipation, full-on and full-off states, and spends very little time in the high dissipation transitions, which minimizes wasted energy. Ideally, a switched-mode power supply dissipates no power. Voltage regulation is achieved by varying the ratio of on-to-off time. In contrast, a linear power supply regulates the output voltage by continually dissipating power in the pass transistor. This higher power conversion efficiency is an important advantage of a switched-mode power supply. Switched-mode power supplies may also be substantially smaller and lighter than a linear supply due to the smaller transformer size and weight.Switching regulators are used as replacements for linear regulators when higher efficiency, smaller size or lighter weight are required. They are, however, more complicated; their switching currents can cause electrical noise problems if not carefully suppressed, and simple designs may have a poor power factor.