Chapter 2: Diode Applications
... Because the diode is only forward biased for one-half of the AC cycle, it is also reverse biased for one-half cycle. It is important that the reverse breakdown voltage rating of the diode be high enough to withstand the peak, reverse-biasing AC voltage. ...
... Because the diode is only forward biased for one-half of the AC cycle, it is also reverse biased for one-half cycle. It is important that the reverse breakdown voltage rating of the diode be high enough to withstand the peak, reverse-biasing AC voltage. ...
BasisBlock MC1 - IPU Industrial Power
... The switching panel is of a bolted construction using high-quality galvanised sheet steel with a thickness of 2 mm. An extraordinarily torsionally rigid, self-supporting sheet steel structure is achieved by the appropriate folding of the edges. The front uses pressure resistant doors whic ...
... The switching panel is of a bolted construction using high-quality galvanised sheet steel with a thickness of 2 mm. An extraordinarily torsionally rigid, self-supporting sheet steel structure is achieved by the appropriate folding of the edges. The front uses pressure resistant doors whic ...
Single Channel Operational Amplifier
... Figure 17. High Level Output Voltage Swing vs. Output Current at 32 V Supply ...
... Figure 17. High Level Output Voltage Swing vs. Output Current at 32 V Supply ...
ssr series voltage regulators
... APPLICATION: The SSR Series Voltage Regulators provide reliable, high performance voltage regulation for 50/60 and 400 Hz brushless generators requiring 12A of excitation at either 32, 63 or 125 Vdc. The SSR Voltage Regulator receives its power for precise voltage regulation from a PMG (Permanent Ma ...
... APPLICATION: The SSR Series Voltage Regulators provide reliable, high performance voltage regulation for 50/60 and 400 Hz brushless generators requiring 12A of excitation at either 32, 63 or 125 Vdc. The SSR Voltage Regulator receives its power for precise voltage regulation from a PMG (Permanent Ma ...
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-ISSN: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331,
... necessary to operate the PV at its maximum power point. Short-circuit current is directly proportional to the insolation. The solar cell operates in two regions, that is, constant voltage and constant current region. So it is essential to operate PV module at MPP always. MPPT is a two-step procedure ...
... necessary to operate the PV at its maximum power point. Short-circuit current is directly proportional to the insolation. The solar cell operates in two regions, that is, constant voltage and constant current region. So it is essential to operate PV module at MPP always. MPPT is a two-step procedure ...
Part 2
... A circuit consisting of an inductor and a resistor will begin with most of the voltage drop across the inductor, as the current is changing rapidly. With time, the current will increase less and less, until all the voltage is across the resistor. ...
... A circuit consisting of an inductor and a resistor will begin with most of the voltage drop across the inductor, as the current is changing rapidly. With time, the current will increase less and less, until all the voltage is across the resistor. ...
EP4301856861
... The switches in the voltage source inverter (See Fig. 6) can be turned on and off as required. In the simplest approach, the top switch is turned on and off only once in each cycle, a square waveform results. However, if turned on several times in a cycle an improved harmonic profile may be achieved ...
... The switches in the voltage source inverter (See Fig. 6) can be turned on and off as required. In the simplest approach, the top switch is turned on and off only once in each cycle, a square waveform results. However, if turned on several times in a cycle an improved harmonic profile may be achieved ...
LTC1152 - Rail-to-Rail Input Rail-to-Rail Output Zero-Drift Op Amp
... rail-to-rail output swing and rail-to-rail input commonmode range (CMR); the input CMR actually extends beyond either rail by about 0.3V. This allows unity-gain buffer circuits to operate with any input signal within the power supply rails; input signal swing is limited only by the output stage swin ...
... rail-to-rail output swing and rail-to-rail input commonmode range (CMR); the input CMR actually extends beyond either rail by about 0.3V. This allows unity-gain buffer circuits to operate with any input signal within the power supply rails; input signal swing is limited only by the output stage swin ...
Worksheet: Chapter 34 Test Review
... 3. What are the units for the following: a. voltageb. currentc. charged. powere. resistancef. potential difference4. In solid conductors, electric current is the flow of _____________________. 5. What is the frequency of AC current in North America? 6. Any path along which electrons can flow is call ...
... 3. What are the units for the following: a. voltageb. currentc. charged. powere. resistancef. potential difference4. In solid conductors, electric current is the flow of _____________________. 5. What is the frequency of AC current in North America? 6. Any path along which electrons can flow is call ...
Electricity and Circuits
... This is how much work our circuit does Corresponds to how much grain is milled, etc. Measured in Watts (W) High Power = lots of work which can mean heat. 100 W light bulb is hotter and brighter than 60W. ...
... This is how much work our circuit does Corresponds to how much grain is milled, etc. Measured in Watts (W) High Power = lots of work which can mean heat. 100 W light bulb is hotter and brighter than 60W. ...
The Two-Stage Op-Amp Input Common
... Figure shows the basic two stage op-amp made using an NMOS diff-amp and a PMOS commonsource amplifier (M7). As seen in Fig. M7 is biased to have the same current as M3 and M4. Note also the addition of the compensating network consisting of a compensation capacitor, Cc, (Miller compensation) and a z ...
... Figure shows the basic two stage op-amp made using an NMOS diff-amp and a PMOS commonsource amplifier (M7). As seen in Fig. M7 is biased to have the same current as M3 and M4. Note also the addition of the compensating network consisting of a compensation capacitor, Cc, (Miller compensation) and a z ...
16890_chapter-14-resistive-ac-circuits
... total current, and individual branch currents in a parallel AC circuit. ...
... total current, and individual branch currents in a parallel AC circuit. ...
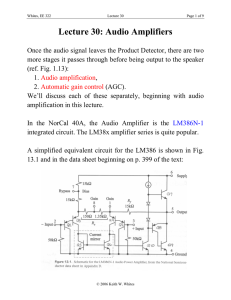
Lecture 30: Audio Amplifiers
... We’ll describe the operation of this circuit beginning near the input. (Note that Sedra and Smith, 5th edition, Sec. 14.8 has a nice description of a closely related circuit: the LM380 IC.) There are three stages of amplification in the LM386: 1. pnp common-emitter amplifiers (Q1 and Q2), 2. pnp dif ...
... We’ll describe the operation of this circuit beginning near the input. (Note that Sedra and Smith, 5th edition, Sec. 14.8 has a nice description of a closely related circuit: the LM380 IC.) There are three stages of amplification in the LM386: 1. pnp common-emitter amplifiers (Q1 and Q2), 2. pnp dif ...
fast pulser for high-altitude ignition research
... where μ0 is the permeability of free space, l is the average circumference of the core, and C0 is the capacitance per stage. In this equation, we assume that the load is a capacitor with a capacitance equal to the upstream capacitance; this gives an effective capacitance that is half that of a singl ...
... where μ0 is the permeability of free space, l is the average circumference of the core, and C0 is the capacitance per stage. In this equation, we assume that the load is a capacitor with a capacitance equal to the upstream capacitance; this gives an effective capacitance that is half that of a singl ...
Procedure and Questions
... 1. Measure the component values first, then build the common emitter amplifier shown above. With the input voltage disconnected, measure the DC voltages VCC, VC, VE, and VB characterizing the quiescent operating point. VC, VE, and VB refer to the voltages at the collector, emitter, and base terminal ...
... 1. Measure the component values first, then build the common emitter amplifier shown above. With the input voltage disconnected, measure the DC voltages VCC, VC, VE, and VB characterizing the quiescent operating point. VC, VE, and VB refer to the voltages at the collector, emitter, and base terminal ...
WARNING: These products may present a possible shock or fire
... cap, LED-END-350, into any open ports to complete the series wiring. When powering fixtures such as these in series, every port of each power connector must be connected to an end cap, another power connector or a fixture. The whole set will not light if any port remains empty. 2. To connect to LED- ...
... cap, LED-END-350, into any open ports to complete the series wiring. When powering fixtures such as these in series, every port of each power connector must be connected to an end cap, another power connector or a fixture. The whole set will not light if any port remains empty. 2. To connect to LED- ...
SERIES AND PARALLEL CIRCUITS
... or the ratio of the currents through resistors connected in parallel. (3) Calculate the equivalent resistance of a network of resistors that can be broken down into series and parallel combinations. ...
... or the ratio of the currents through resistors connected in parallel. (3) Calculate the equivalent resistance of a network of resistors that can be broken down into series and parallel combinations. ...
Full Text PDF - AE International Journal of Science and Technology
... and input current references, but the closed-loop configuration automatically rejects any steady-state error. The closed-loop controller can be implemented with several types of controllers ranging from the simple PI controller in rotating coordinates up to more sophisticated controllers such as LQR ...
... and input current references, but the closed-loop configuration automatically rejects any steady-state error. The closed-loop controller can be implemented with several types of controllers ranging from the simple PI controller in rotating coordinates up to more sophisticated controllers such as LQR ...
L6376
... To avoid the forwarding of misleading — i.e. short diagnostic pulses in coincidence with the intervention of the current limiting circuits when operating on capacitive loads — the activation of the diagnostic can be delayed with respect to the intervention of one of the current limiting circuits. Th ...
... To avoid the forwarding of misleading — i.e. short diagnostic pulses in coincidence with the intervention of the current limiting circuits when operating on capacitive loads — the activation of the diagnostic can be delayed with respect to the intervention of one of the current limiting circuits. Th ...
Switched-mode power supply

A switched-mode power supply (switching-mode power supply, switch-mode power supply, SMPS, or switcher) is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator to convert electrical power efficiently. Like other power supplies, an SMPS transfers power from a source, like mains power, to a load, such as a personal computer, while converting voltage and current characteristics. Unlike a linear power supply, the pass transistor of a switching-mode supply continually switches between low-dissipation, full-on and full-off states, and spends very little time in the high dissipation transitions, which minimizes wasted energy. Ideally, a switched-mode power supply dissipates no power. Voltage regulation is achieved by varying the ratio of on-to-off time. In contrast, a linear power supply regulates the output voltage by continually dissipating power in the pass transistor. This higher power conversion efficiency is an important advantage of a switched-mode power supply. Switched-mode power supplies may also be substantially smaller and lighter than a linear supply due to the smaller transformer size and weight.Switching regulators are used as replacements for linear regulators when higher efficiency, smaller size or lighter weight are required. They are, however, more complicated; their switching currents can cause electrical noise problems if not carefully suppressed, and simple designs may have a poor power factor.