Lecture no 16 & 17
... using complementary transistors (a pair of one npn and one pnp transistors, with matched characteristics). A npn transistor that provides the positive half of the AC cycle. An pnp transistor that provides the negative half of the AC cycle. No required input and output Transformers. This conf ...
... using complementary transistors (a pair of one npn and one pnp transistors, with matched characteristics). A npn transistor that provides the positive half of the AC cycle. An pnp transistor that provides the negative half of the AC cycle. No required input and output Transformers. This conf ...
ppt
... 3) When a switch is pressed on your circuit, send your theme song wirelessly to other xbee chips. 4) When a song is received from another group, play their theme song on your piezo. ...
... 3) When a switch is pressed on your circuit, send your theme song wirelessly to other xbee chips. 4) When a song is received from another group, play their theme song on your piezo. ...
LM386 Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier (Rev. A)
... For 6 dB effective bass boost: R . 15 kΩ, the lowest value for good stable operation is R = 10 kΩ if pin 8 is open. If pins 1 and 8 are bypassed then R as low as 2 kΩ can be used. This restriction is because the amplifier is only compensated for closed-loop gains greater than 9. ...
... For 6 dB effective bass boost: R . 15 kΩ, the lowest value for good stable operation is R = 10 kΩ if pin 8 is open. If pins 1 and 8 are bypassed then R as low as 2 kΩ can be used. This restriction is because the amplifier is only compensated for closed-loop gains greater than 9. ...
Series and Parallel Circuits
... 2) Find any parallel loads. Calculate their equivalent resistance with 1 1 1 1 RT R1 R2 R3 Draw a new schematic with one resistor with the new value. 3) Find any resistor in series. Calculate their equivalent resistance by adding. Draw a new schematic with a new resistor with that valu ...
... 2) Find any parallel loads. Calculate their equivalent resistance with 1 1 1 1 RT R1 R2 R3 Draw a new schematic with one resistor with the new value. 3) Find any resistor in series. Calculate their equivalent resistance by adding. Draw a new schematic with a new resistor with that valu ...
www.BDTIC.com/ON/ Test Procedure for the NCP1562 Evaluation Board
... 1. Configure Multimeter 1 (MM1) for measuring current. Connect Power Supply (+) terminal to MM1 current measurement terminal. 2. Connect MM1 ground terminal to demo board (Vin+) terminal. 3. Connect Power Supply (-) terminal to demo board (Vin-) terminal. 4. Configure Multimeter 2 (MM2) for measurin ...
... 1. Configure Multimeter 1 (MM1) for measuring current. Connect Power Supply (+) terminal to MM1 current measurement terminal. 2. Connect MM1 ground terminal to demo board (Vin+) terminal. 3. Connect Power Supply (-) terminal to demo board (Vin-) terminal. 4. Configure Multimeter 2 (MM2) for measurin ...
The anti-sleep driving alarm for people doing all night drives as well
... The most common function of a diode is to allow an electric current to pass in one direction (called the diode's forward bias direction) while blocking current in the opposite direction (the reverse direction). Thus, the diode can be thought of as an electronic version of a check valve. This unidire ...
... The most common function of a diode is to allow an electric current to pass in one direction (called the diode's forward bias direction) while blocking current in the opposite direction (the reverse direction). Thus, the diode can be thought of as an electronic version of a check valve. This unidire ...
FJB102 High Voltage Power Darlington Transistor F JB
... A critical component is any component of a life support device or system whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life support device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness. ...
... A critical component is any component of a life support device or system whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life support device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness. ...
FSB137HL ™) Green-Mode Fairchild Power Switch (FPS FS
... minimizes losses in the EMI filter stage by eliminating the X-cap discharge resistors while meeting IEC61010-1 safety requirements. mWSaver™ Green Mode gradually decreases switching frequency as load decreases to minimize switching losses. Proprietary asynchronous jitter decreases EMI emission and b ...
... minimizes losses in the EMI filter stage by eliminating the X-cap discharge resistors while meeting IEC61010-1 safety requirements. mWSaver™ Green Mode gradually decreases switching frequency as load decreases to minimize switching losses. Proprietary asynchronous jitter decreases EMI emission and b ...
Evaluates: MAX8515/MAX8515A MAX8515 Evaluation Kit General Description Features
... on the EV kit. The input voltage source supplies the isolated voltage-feedback circuit and the OVP circuit on the EV kit. The EV kit operates from a nominal input voltage of 8V and has a range of 6V to 10V. The input voltage is nominally set to 8V by current-limiting resistors R1 and R8 that limit t ...
... on the EV kit. The input voltage source supplies the isolated voltage-feedback circuit and the OVP circuit on the EV kit. The EV kit operates from a nominal input voltage of 8V and has a range of 6V to 10V. The input voltage is nominally set to 8V by current-limiting resistors R1 and R8 that limit t ...
HI-303/883 Datasheet
... All Intersil U.S. products are manufactured, assembled and tested utilizing ISO9000 quality systems. Intersil Corporation’s quality certifications can be viewed at www.intersil.com/design/quality Intersil products are sold by description only. Intersil Corporation reserves the right to make changes ...
... All Intersil U.S. products are manufactured, assembled and tested utilizing ISO9000 quality systems. Intersil Corporation’s quality certifications can be viewed at www.intersil.com/design/quality Intersil products are sold by description only. Intersil Corporation reserves the right to make changes ...
Piezo-electromagnetic Scavenger Power Supply
... one hundred kilohertz (30 –100 kHz) is most suitable for this device. Further iterations will be smaller and higher in frequency, somewhere between one to ten megahertz, which should generate even more power due to greater efficiencies. The problem with ever-higher frequencies is electromagnetic rad ...
... one hundred kilohertz (30 –100 kHz) is most suitable for this device. Further iterations will be smaller and higher in frequency, somewhere between one to ten megahertz, which should generate even more power due to greater efficiencies. The problem with ever-higher frequencies is electromagnetic rad ...
Experiment No. 1 Study of Separately
... generator must, therefore, be mechanically driven in order to produce electricity. Since the field winding is an electromagnet, current must flow through it to produce a magnetic field. This current is called the excitation current, and can be supplied to the field winding in one of two ways; it can ...
... generator must, therefore, be mechanically driven in order to produce electricity. Since the field winding is an electromagnet, current must flow through it to produce a magnetic field. This current is called the excitation current, and can be supplied to the field winding in one of two ways; it can ...
MCW100C, E Time Proportional Rotary Position
... The transducer transforms this shaft rotation into an electrical signal through the rotor/ stator interaction, shown in Figure 1. A 440 Hz square wave from the amplifier is applied to the primaries of coils A and B. The stator position with respect to the rotor determines the voltages from the coil ...
... The transducer transforms this shaft rotation into an electrical signal through the rotor/ stator interaction, shown in Figure 1. A 440 Hz square wave from the amplifier is applied to the primaries of coils A and B. The stator position with respect to the rotor determines the voltages from the coil ...
P220 Planar Magnetics For 1 kW to 3.0 kW Converters
... Transformers based on our 220 size core are designed for a wide variety of topologies such as forward, half and full bridge, full bridge ZVS, and push-pull. These parts are used in 1 kW to 3.0 kW off-line power supplies and DC-DC converters delivering up to 250 amperes for a single output or 20-50 a ...
... Transformers based on our 220 size core are designed for a wide variety of topologies such as forward, half and full bridge, full bridge ZVS, and push-pull. These parts are used in 1 kW to 3.0 kW off-line power supplies and DC-DC converters delivering up to 250 amperes for a single output or 20-50 a ...
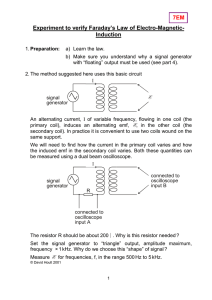
Experiment to verify Faraday’s Law of Electro-Magnetic- Induction 7EM
... maintain a constant peak voltage - why resistor R is needed - how your results verify Faraday’s law (assuming that they do !) Your report should also include a diagram showing what you saw on the oscilloscope screen. 4. The experiment will be done using a coil like the one shown below. In this case ...
... maintain a constant peak voltage - why resistor R is needed - how your results verify Faraday’s law (assuming that they do !) Your report should also include a diagram showing what you saw on the oscilloscope screen. 4. The experiment will be done using a coil like the one shown below. In this case ...
Switched-mode power supply

A switched-mode power supply (switching-mode power supply, switch-mode power supply, SMPS, or switcher) is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator to convert electrical power efficiently. Like other power supplies, an SMPS transfers power from a source, like mains power, to a load, such as a personal computer, while converting voltage and current characteristics. Unlike a linear power supply, the pass transistor of a switching-mode supply continually switches between low-dissipation, full-on and full-off states, and spends very little time in the high dissipation transitions, which minimizes wasted energy. Ideally, a switched-mode power supply dissipates no power. Voltage regulation is achieved by varying the ratio of on-to-off time. In contrast, a linear power supply regulates the output voltage by continually dissipating power in the pass transistor. This higher power conversion efficiency is an important advantage of a switched-mode power supply. Switched-mode power supplies may also be substantially smaller and lighter than a linear supply due to the smaller transformer size and weight.Switching regulators are used as replacements for linear regulators when higher efficiency, smaller size or lighter weight are required. They are, however, more complicated; their switching currents can cause electrical noise problems if not carefully suppressed, and simple designs may have a poor power factor.







![[PDF]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008779546_1-e58bb7eeacffbdd4ead5276b5caa02c6-300x300.png)