Integrated Receiver Simplifies the Analog Side of Digital Predistortion - High Frequency Electronics July 2009
... peak to average ratio (PAR) is about 15 dBm. To set the average input power to the mixer of the receive chain at –15 dBm, the combination of the coupler and attenuator insertion ...
... peak to average ratio (PAR) is about 15 dBm. To set the average input power to the mixer of the receive chain at –15 dBm, the combination of the coupler and attenuator insertion ...
Design of a Low Noise Amplifier and Mixer in 0
... the noise created by mixers. Communication systems also require baseband information signals to be shifted to a frequency suitable for electromagnetic propagation to the desired destination. At the destination, we reverse this process, shifting the received radiofrequency signal back to baseband to ...
... the noise created by mixers. Communication systems also require baseband information signals to be shifted to a frequency suitable for electromagnetic propagation to the desired destination. At the destination, we reverse this process, shifting the received radiofrequency signal back to baseband to ...
design_review
... bridge rectifier, and the DC/DC converter. The piezoelectric material can be modeled as an AC source, capacitor, and resistor parallel to each other. The AC output of the piezoelectric material is converted into DC by the bridge rectifier, which is then stored by the capacitor. The rectified output ...
... bridge rectifier, and the DC/DC converter. The piezoelectric material can be modeled as an AC source, capacitor, and resistor parallel to each other. The AC output of the piezoelectric material is converted into DC by the bridge rectifier, which is then stored by the capacitor. The rectified output ...
Digital-to Analog Converter
... Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky ...
... Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky ...
PSPICE tutorial: MOSFETs
... The MOSFET models that we will use are the the MbreakN3 and MbreakN4 devices for NMOS and the MbreakP3 and MbreakP4 models for PMOS. These are nearly identical, with a subtle difference between the “3” and “4” versions. The “4” versions have 4 terminals (D, S, G + body) – the body connection must be ...
... The MOSFET models that we will use are the the MbreakN3 and MbreakN4 devices for NMOS and the MbreakP3 and MbreakP4 models for PMOS. These are nearly identical, with a subtle difference between the “3” and “4” versions. The “4” versions have 4 terminals (D, S, G + body) – the body connection must be ...
Day One 1) Basic Electrical Theory a) 4 principles of electricity i
... 1) Basic Electrical Theory a) 4 principles of electricity i) Electrons flow of electrons through a conductor ii) Results from a difference of potential iii) Returns to source through a complete circuit iv) Favors the path of least resistance b) Watt’s and Ohm’s Law i) Definitions (1) Watts (2) Volts ...
... 1) Basic Electrical Theory a) 4 principles of electricity i) Electrons flow of electrons through a conductor ii) Results from a difference of potential iii) Returns to source through a complete circuit iv) Favors the path of least resistance b) Watt’s and Ohm’s Law i) Definitions (1) Watts (2) Volts ...
SNP-G20
... SNP-G20x is for ITE application which requires standby mode. SNP-G20x-A is for ITE application but without burst sound and no standby mode. SNP-G20x-M is for medical application which requires standby mode. SNP-G20x-MA is for medical application but without burst sound and no standby mode. ...
... SNP-G20x is for ITE application which requires standby mode. SNP-G20x-A is for ITE application but without burst sound and no standby mode. SNP-G20x-M is for medical application which requires standby mode. SNP-G20x-MA is for medical application but without burst sound and no standby mode. ...
Strain Gauge/Bridge/Load Cell/Pressure Transducer to DC
... 0.89" W x 4.62" H x 4.81" D 22.5 mm W x 117 mm H x 122 mm D Height includes connectors Power Standard: 85-265 VAC, 50/60 Hz or 60-300 VDC D option: 9-30 VDC (either polarity) or 10-32 VAC Power: 2 to 5 Watts depending on number of load cells Description The APD 4059 accepts an input from one to ...
... 0.89" W x 4.62" H x 4.81" D 22.5 mm W x 117 mm H x 122 mm D Height includes connectors Power Standard: 85-265 VAC, 50/60 Hz or 60-300 VDC D option: 9-30 VDC (either polarity) or 10-32 VAC Power: 2 to 5 Watts depending on number of load cells Description The APD 4059 accepts an input from one to ...
Ch. 23 Electric Current
... Several Circuits will be modified by changing the number of light bulbs. Your task will be to predict and explain how adding the light bulbs will change the reading on the ammeter and the brightness of each bulb. ...
... Several Circuits will be modified by changing the number of light bulbs. Your task will be to predict and explain how adding the light bulbs will change the reading on the ammeter and the brightness of each bulb. ...
16-Channel, 1 MSPS, 12-Bit ADC with Sequencer in 28-Lead TSSOP AD7490-EP Data Sheet
... clocked into the register on the falling edge of SCLK (see the AD7490 data sheet). Data Out. Logic output. The conversion result from the AD7490-EP is provided on this output as a serial data stream. The bits are clocked out on the falling edge of the SCLK input. The data stream consists of four add ...
... clocked into the register on the falling edge of SCLK (see the AD7490 data sheet). Data Out. Logic output. The conversion result from the AD7490-EP is provided on this output as a serial data stream. The bits are clocked out on the falling edge of the SCLK input. The data stream consists of four add ...
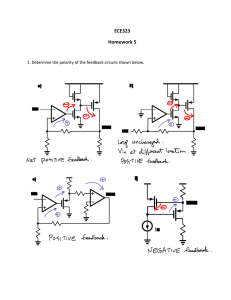
solutions
... 4. The BJT source follower has the approximate transfer characteristic as shown in figure 4(a). Consider this follower to be driven by a differential amplifier with a gain of 100 as shown in figure 4(b). Explain the transfer characteristics Vo vs. Vi of the resulting feedback amplifier. ...
... 4. The BJT source follower has the approximate transfer characteristic as shown in figure 4(a). Consider this follower to be driven by a differential amplifier with a gain of 100 as shown in figure 4(b). Explain the transfer characteristics Vo vs. Vi of the resulting feedback amplifier. ...
Paper - Benjamin Hershberg
... and embedding a voltage offset of opposite polarity into each path (i.e. Fig. 1, top left). This creates a small input-referred dead-zone for which neither output transistor will conduct, and when operating in feedback, the ringamp rapidly charges-to, stabilizes, and then locks into this dead-zone r ...
... and embedding a voltage offset of opposite polarity into each path (i.e. Fig. 1, top left). This creates a small input-referred dead-zone for which neither output transistor will conduct, and when operating in feedback, the ringamp rapidly charges-to, stabilizes, and then locks into this dead-zone r ...
Lab 1 Introduction to Laboratory Instruments
... of 0.5 sec. Use this signal as the clock input to the counter. Your digital display should show sequential increment from 0 to 9, followed by unrecognizable displays of hex numbers A through F. The display should then go back to 0 and repeat the above sequence. Demonstrate the function of your circu ...
... of 0.5 sec. Use this signal as the clock input to the counter. Your digital display should show sequential increment from 0 to 9, followed by unrecognizable displays of hex numbers A through F. The display should then go back to 0 and repeat the above sequence. Demonstrate the function of your circu ...
RC Circuits - Chabot College
... By now you should be comfortable making connections on a circuit board, and measuring current and voltage digitally using the Vernier equipment and standalone multimeters. This lab activity will challenge you to verify the equations for charging and discharging capacitors in simple DC circuit arrang ...
... By now you should be comfortable making connections on a circuit board, and measuring current and voltage digitally using the Vernier equipment and standalone multimeters. This lab activity will challenge you to verify the equations for charging and discharging capacitors in simple DC circuit arrang ...
Ohm`s Law
... thus preventing further increases in current without further increases in battery voltage. Consequently, voltage and current do not follow the simple model predicted by Ohm's Law in this circuit with a stable resistance value of 3 Ω, because an incandescent lamp's filament resistance does not remain ...
... thus preventing further increases in current without further increases in battery voltage. Consequently, voltage and current do not follow the simple model predicted by Ohm's Law in this circuit with a stable resistance value of 3 Ω, because an incandescent lamp's filament resistance does not remain ...
FPF2193 / FPF2194 / FPF2195 Full
... blanking time of 30 ms, nominally, during which the switch acts as a constant current source. At the end of the blanking time, the switch is turned off. The FPF2195 has no current limit blanking period, so it remains in a constant current state until the ON pin is deactivated or the thermal shutdown ...
... blanking time of 30 ms, nominally, during which the switch acts as a constant current source. At the end of the blanking time, the switch is turned off. The FPF2195 has no current limit blanking period, so it remains in a constant current state until the ON pin is deactivated or the thermal shutdown ...
Record: 1 AN INTRODUCTION TO REACTANCE Page 1 of 8
... (or electromotive force), can never be as great as the original current, but since it is of opposite polarity, it restricts the rate at which current in the coil can increase. When the field around each turn of wire stops expanding, there is no longer any induced counterEMF, so the final value of cu ...
... (or electromotive force), can never be as great as the original current, but since it is of opposite polarity, it restricts the rate at which current in the coil can increase. When the field around each turn of wire stops expanding, there is no longer any induced counterEMF, so the final value of cu ...
Design , Implementation and Testing of SPWM Inverter on dSPACE
... areas of concern, as it is the ac output voltage may be connected to the grid or in a standalone system may be used as power supply to various equipments. Thus the lesser the harmonic content in the voltage waveforms i.e lower the % THD improved quality of supply is ascertained [6]. As pulse width m ...
... areas of concern, as it is the ac output voltage may be connected to the grid or in a standalone system may be used as power supply to various equipments. Thus the lesser the harmonic content in the voltage waveforms i.e lower the % THD improved quality of supply is ascertained [6]. As pulse width m ...
EW lab manual - WordPress.com
... signal is fed into one connection of the active device and the amplified version taken from another connection. In a transistor, the signal can be applied to the base connection and the amplified version taken from the collector. Some of the active components are diodes, transistors, integrated circ ...
... signal is fed into one connection of the active device and the amplified version taken from another connection. In a transistor, the signal can be applied to the base connection and the amplified version taken from the collector. Some of the active components are diodes, transistors, integrated circ ...
Switched-mode power supply

A switched-mode power supply (switching-mode power supply, switch-mode power supply, SMPS, or switcher) is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator to convert electrical power efficiently. Like other power supplies, an SMPS transfers power from a source, like mains power, to a load, such as a personal computer, while converting voltage and current characteristics. Unlike a linear power supply, the pass transistor of a switching-mode supply continually switches between low-dissipation, full-on and full-off states, and spends very little time in the high dissipation transitions, which minimizes wasted energy. Ideally, a switched-mode power supply dissipates no power. Voltage regulation is achieved by varying the ratio of on-to-off time. In contrast, a linear power supply regulates the output voltage by continually dissipating power in the pass transistor. This higher power conversion efficiency is an important advantage of a switched-mode power supply. Switched-mode power supplies may also be substantially smaller and lighter than a linear supply due to the smaller transformer size and weight.Switching regulators are used as replacements for linear regulators when higher efficiency, smaller size or lighter weight are required. They are, however, more complicated; their switching currents can cause electrical noise problems if not carefully suppressed, and simple designs may have a poor power factor.